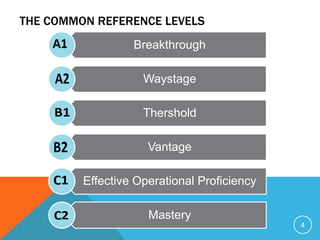
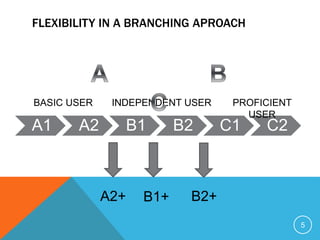
Plurilingualism refers to knowledge of multiple languages that co-exist in a society, while multilingualism describes the diversity of languages within an education system. The Common European Framework of Reference for Languages establishes common reference levels for language proficiency from Beginner to Mastery. It also describes communicative language competencies and activities like conversation, correspondence, and speech.
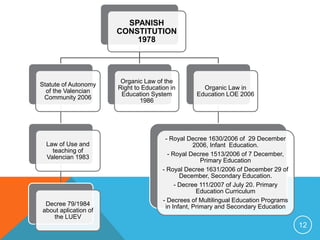
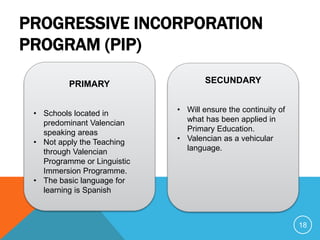
Bilingual education models in Spain include compensatory/transitional programs, maintenance programs, and enrichment programs. The Valencian educational system offers programs based on territory, basic learning language, and student's usual language. These include Teaching through Valencian, Linguistic Immersion, and Progressive Incorporation programs for Valencian-speaking areas