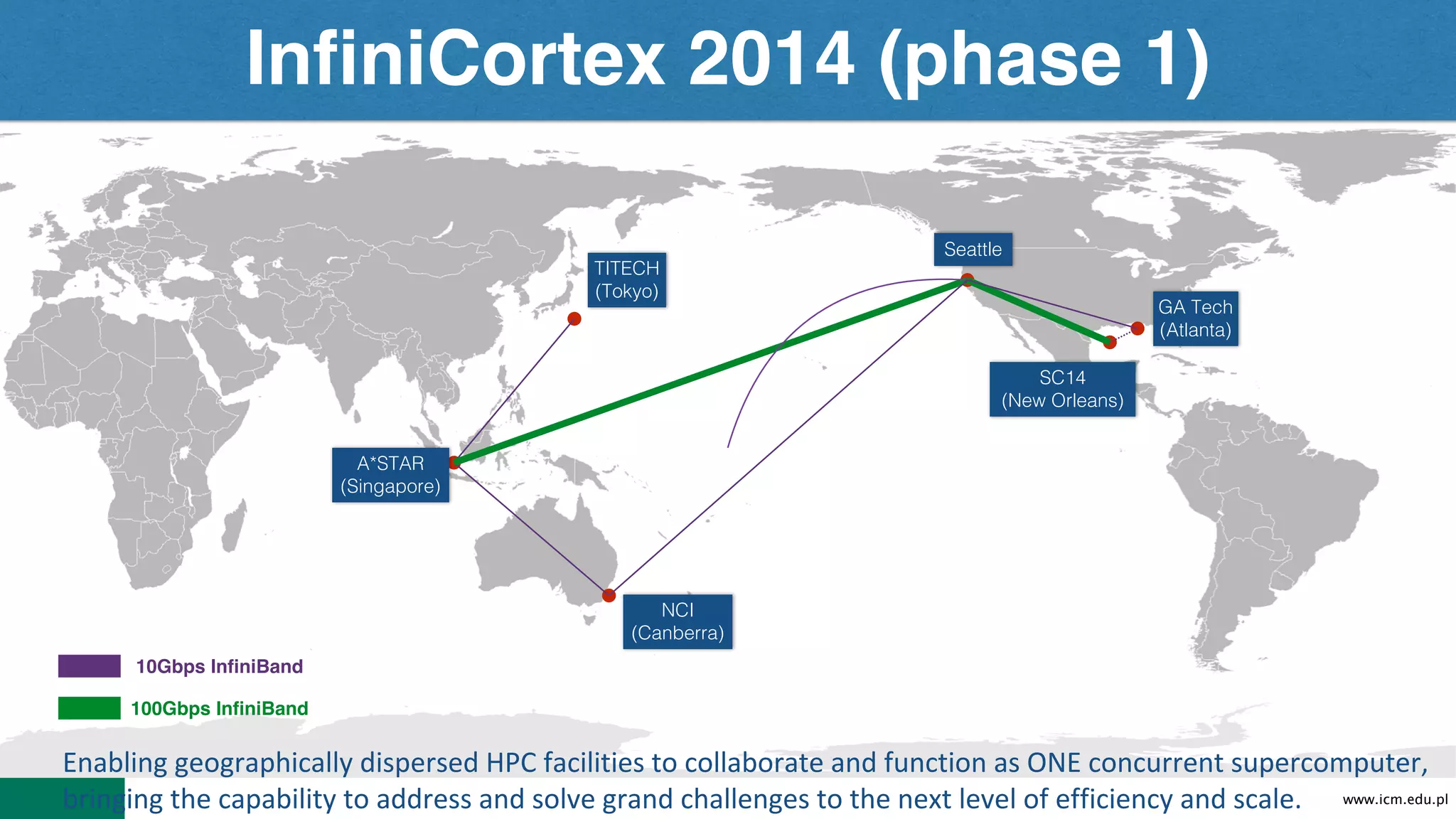
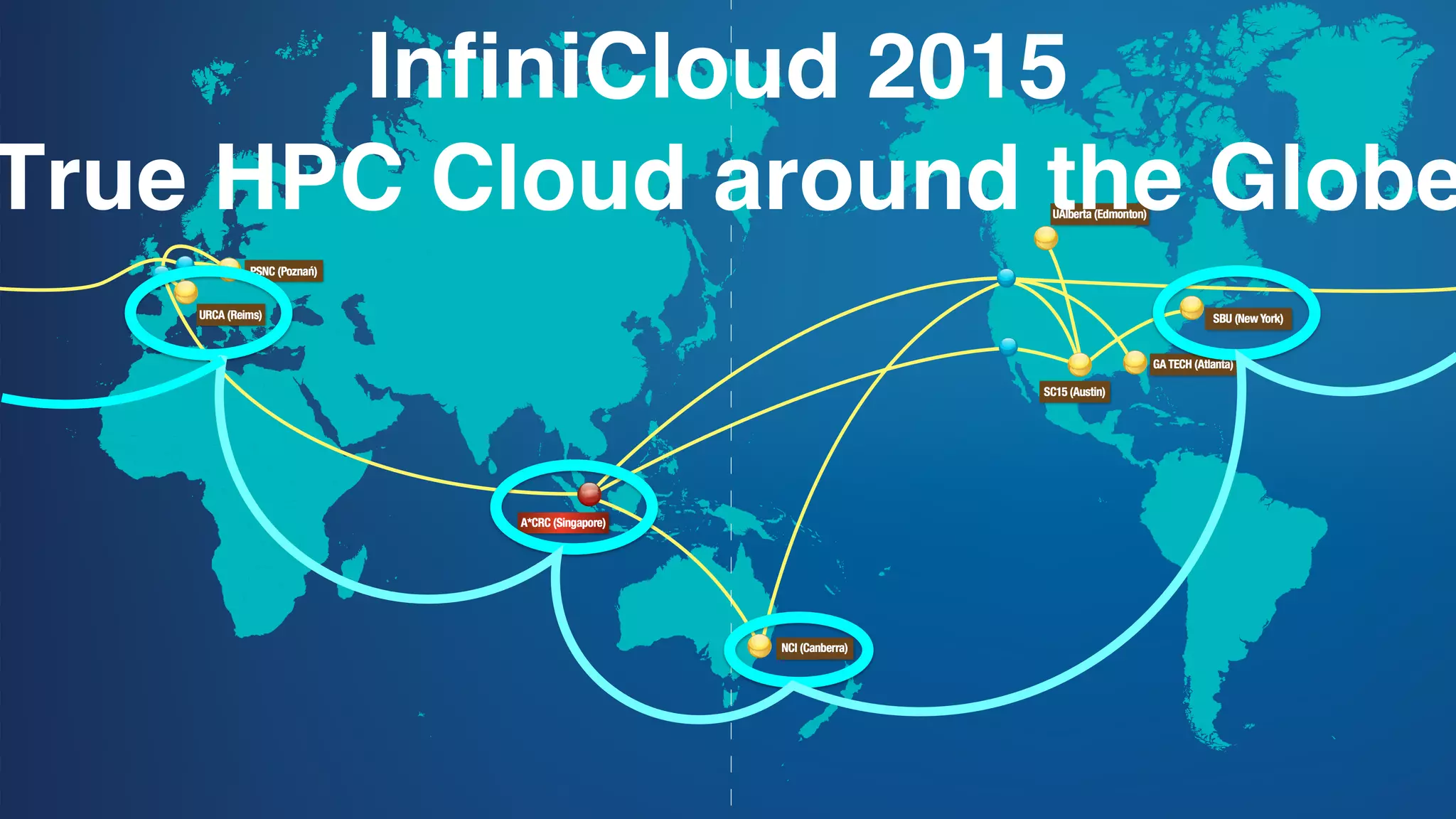
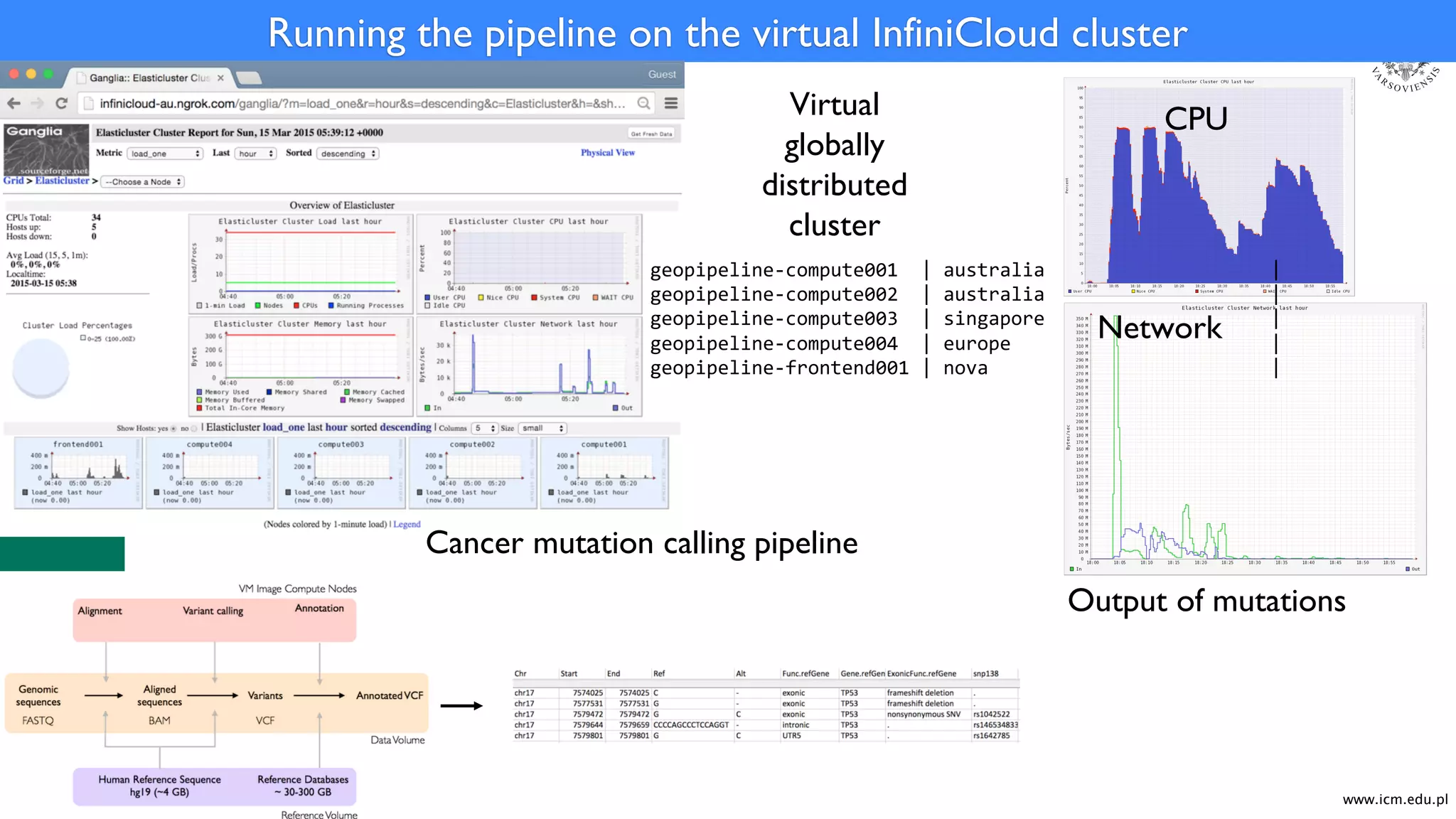
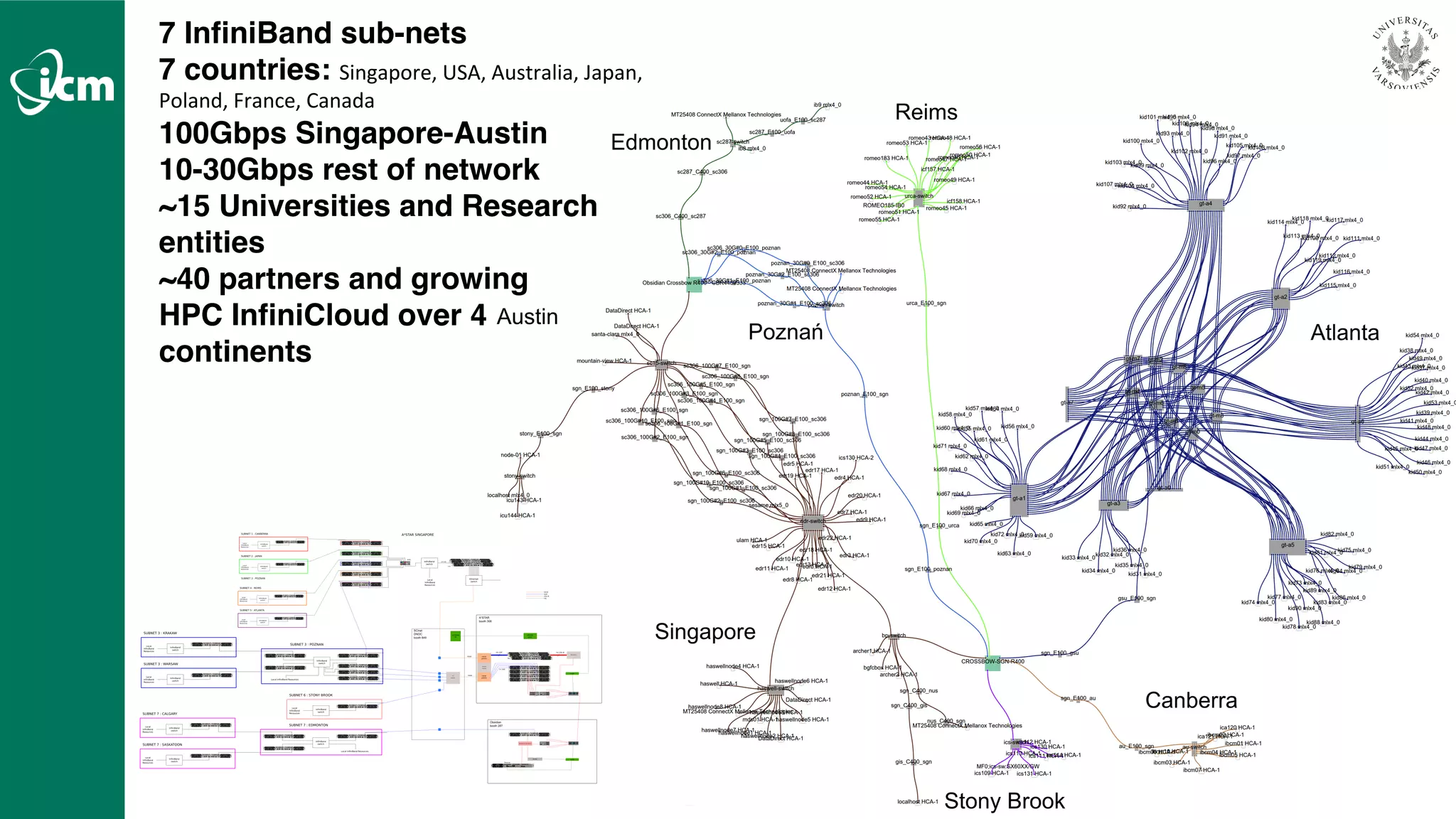
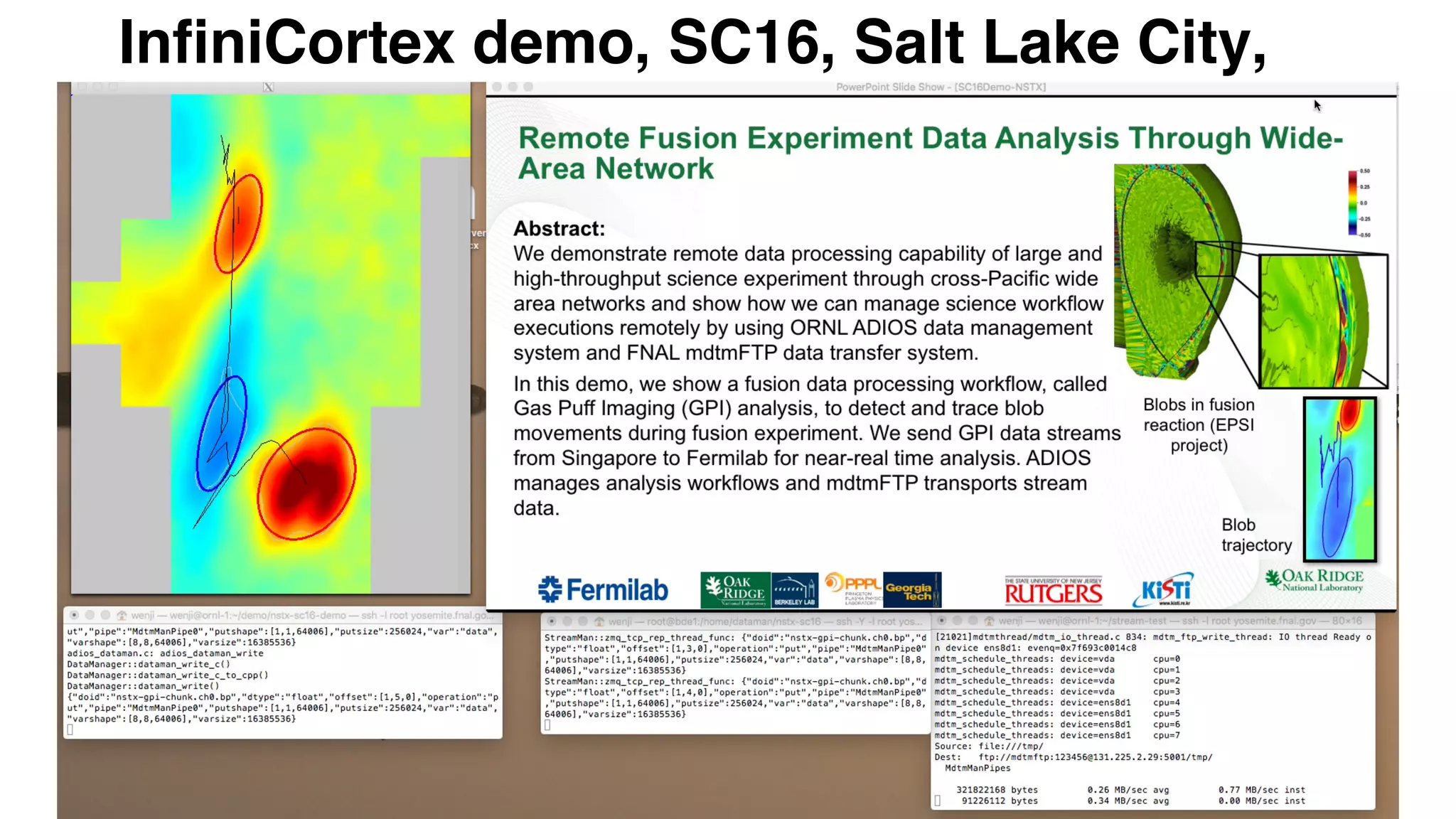
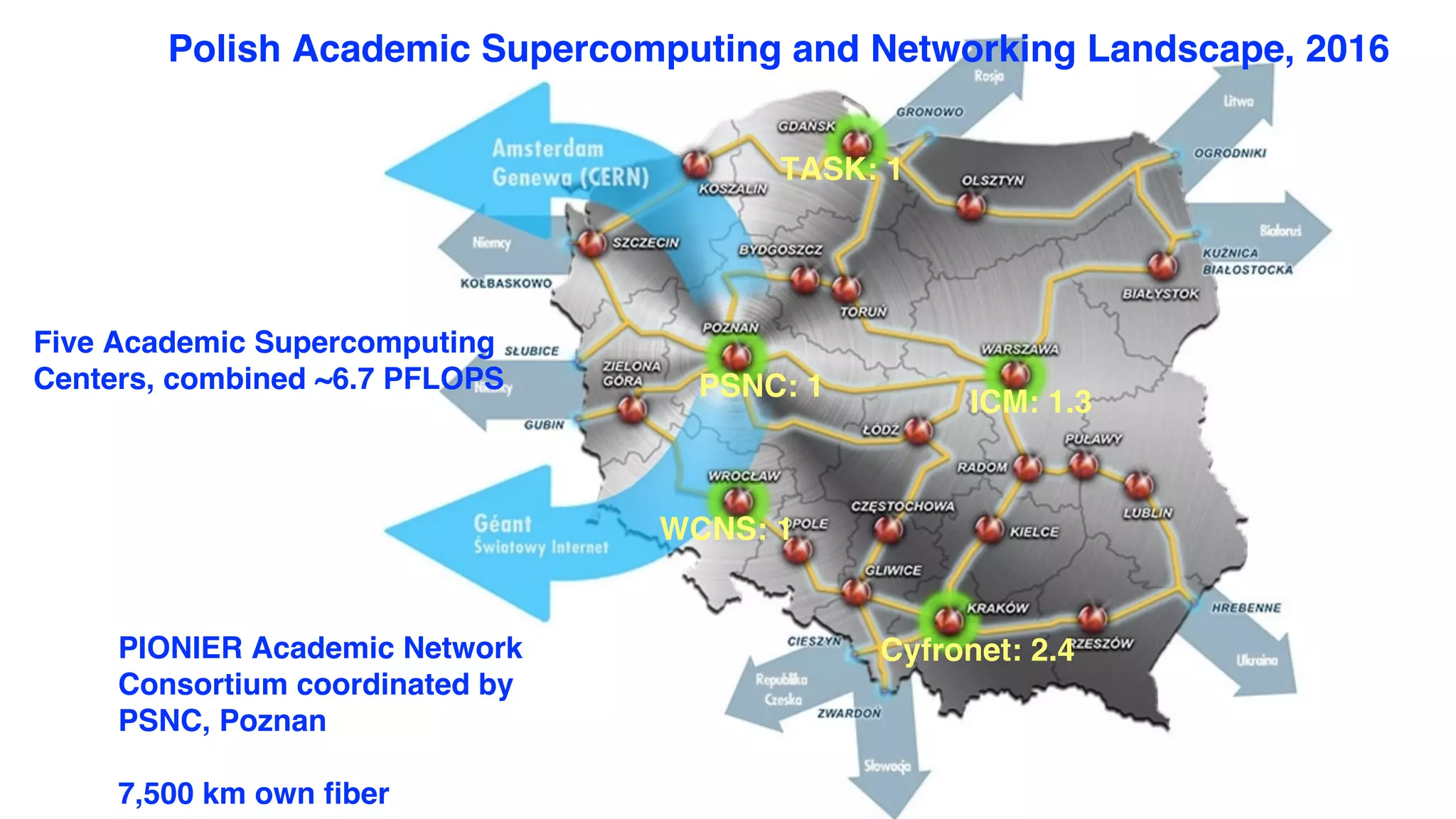
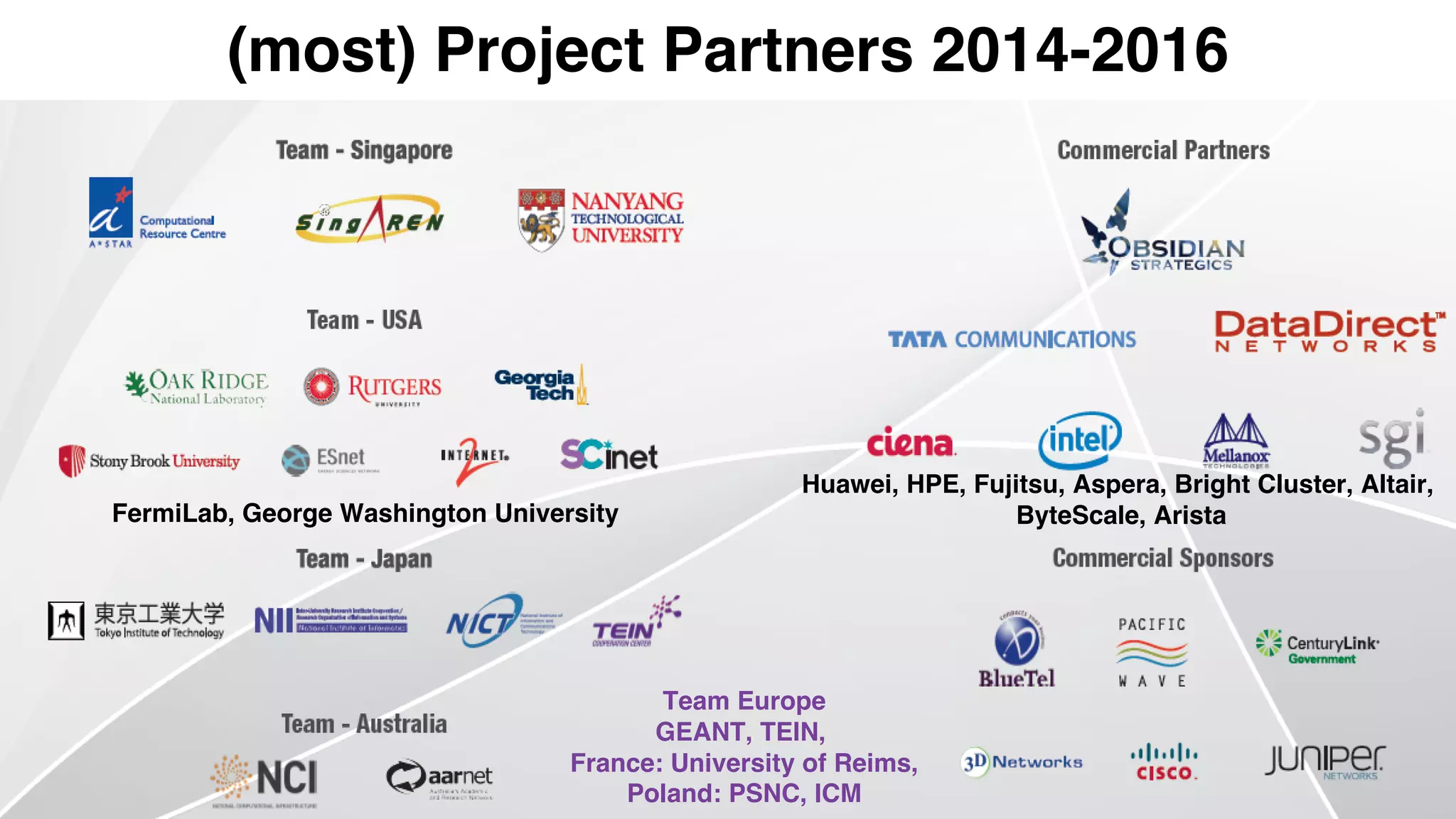
The document discusses Infinicortex, a global supercomputing network that connects multiple supercomputers across continents using advanced interconnect technologies like InfiniBand. It aims to enhance computational power and efficiency, enabling collaboration on large-scale scientific projects by facilitating high-speed data transfer and workflows. Key features include a vast network of supercomputers, partnerships with various institutions, and innovative solutions for complex data analysis and computation.







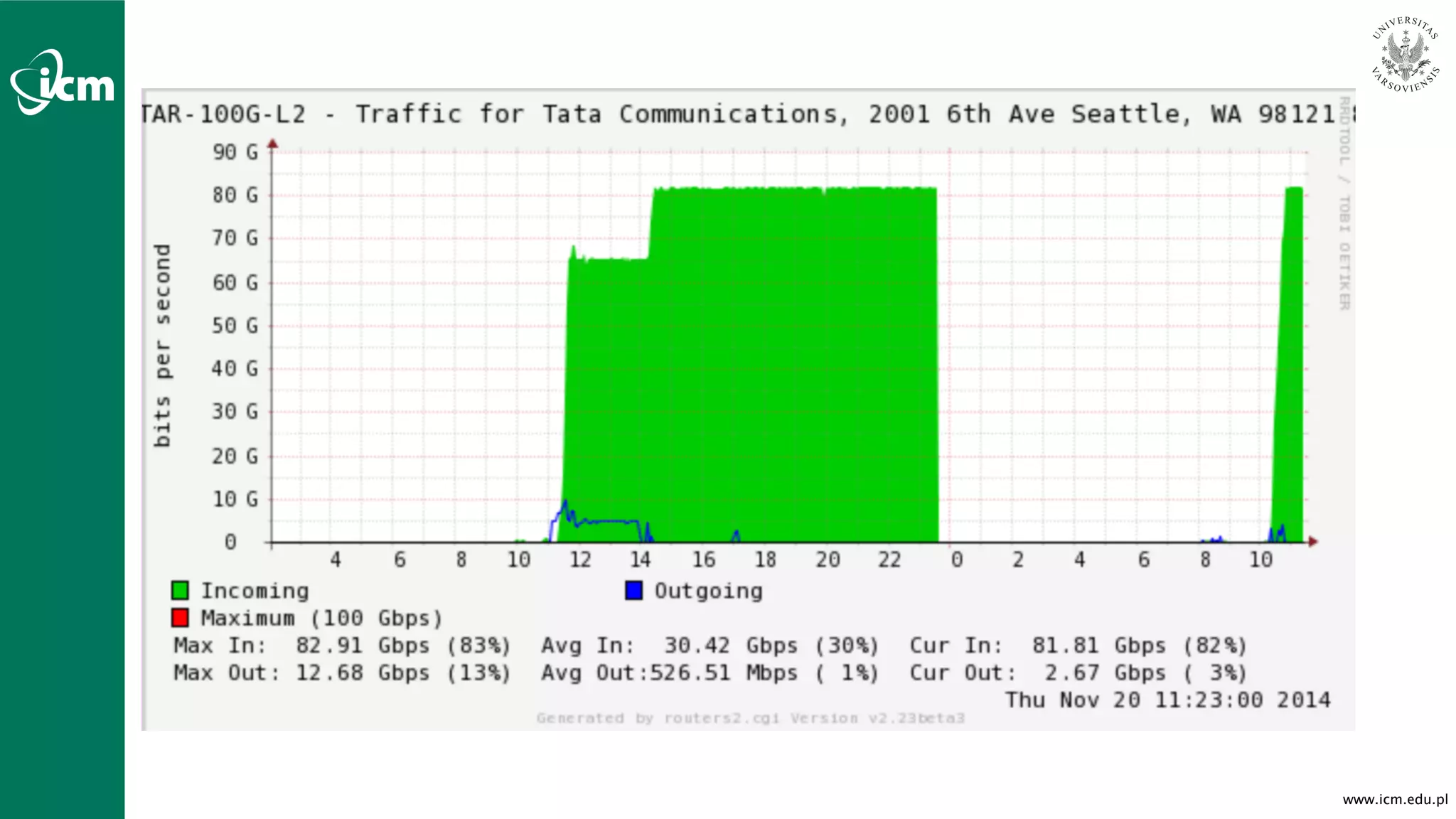
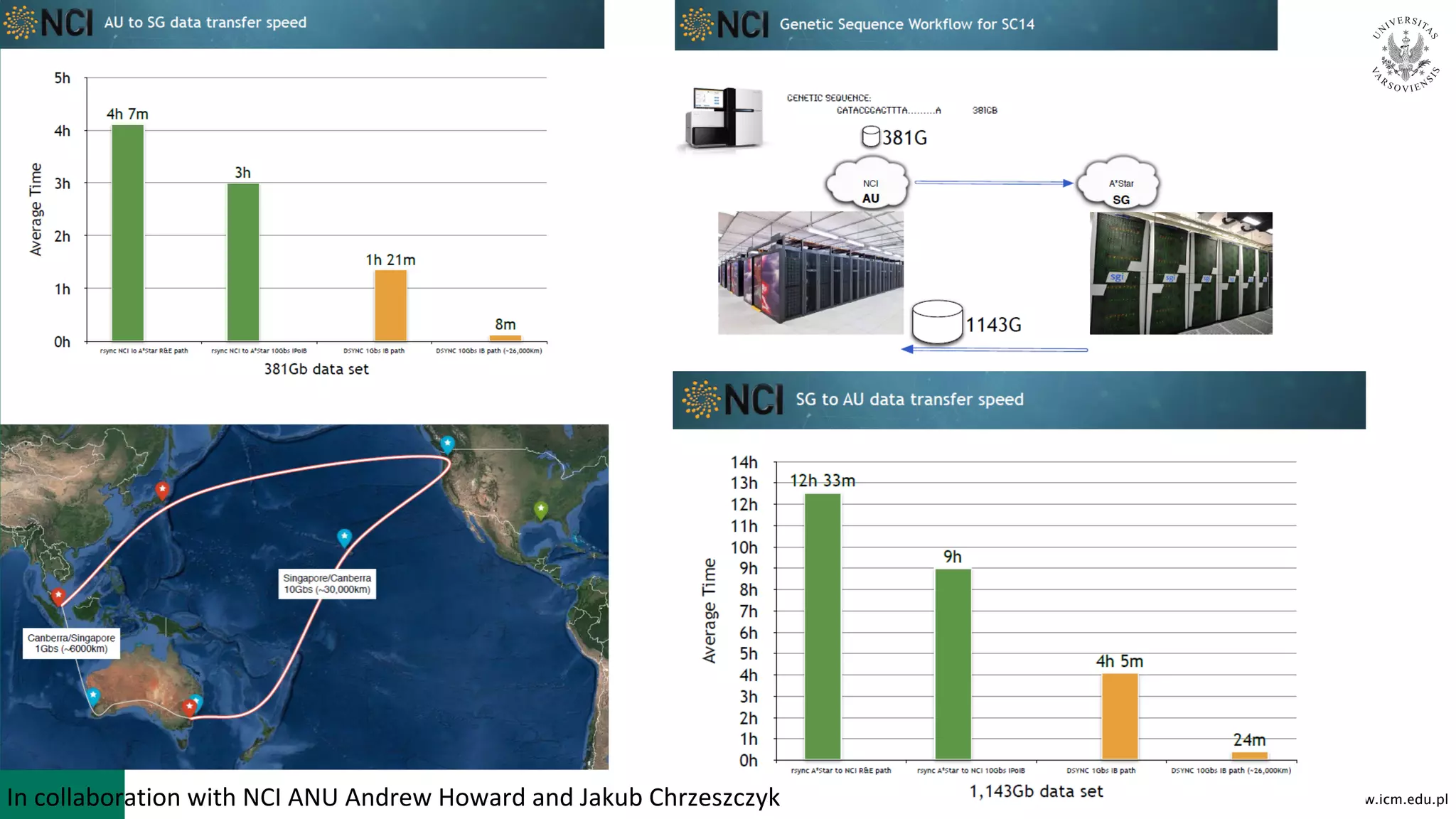
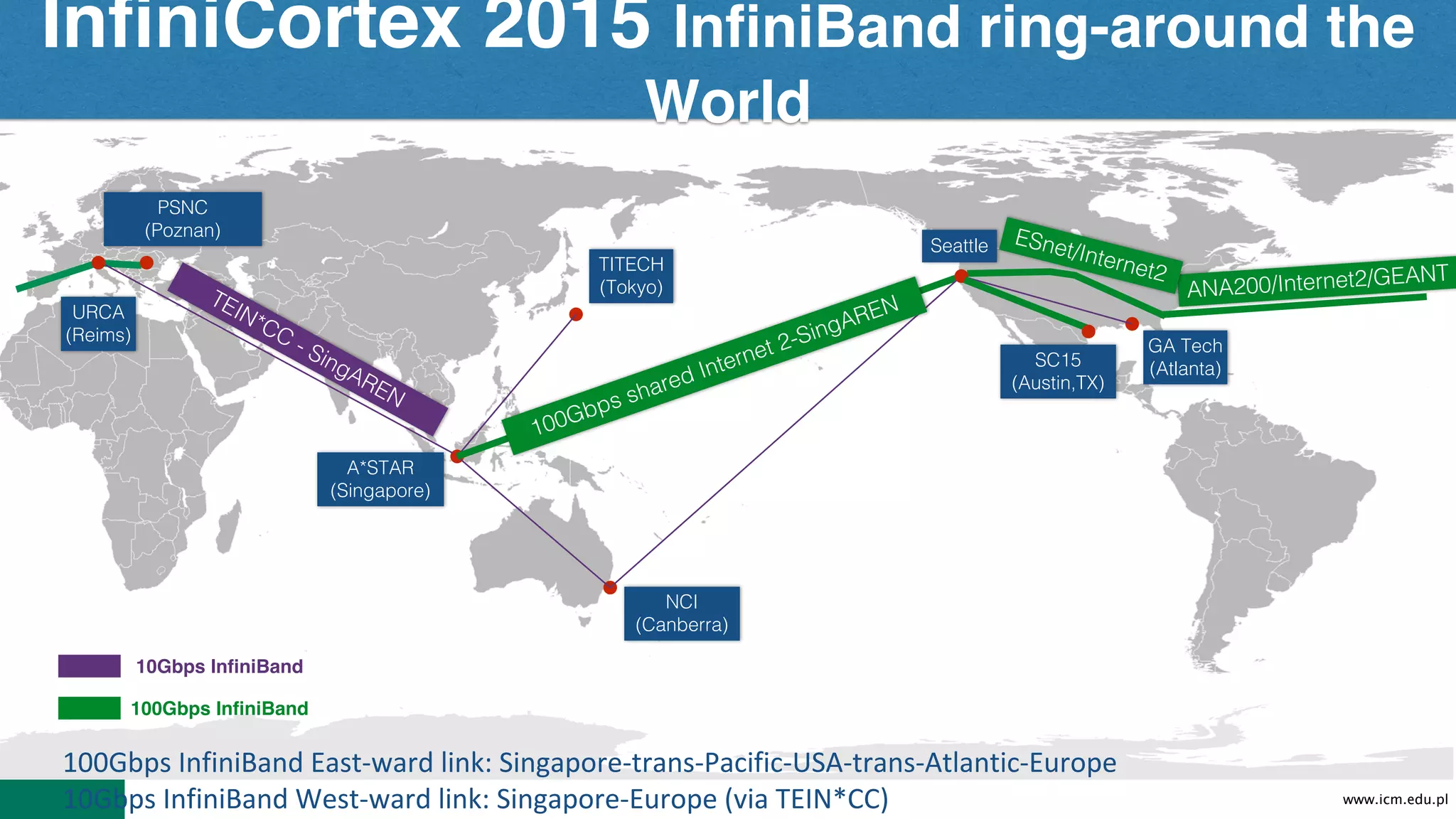
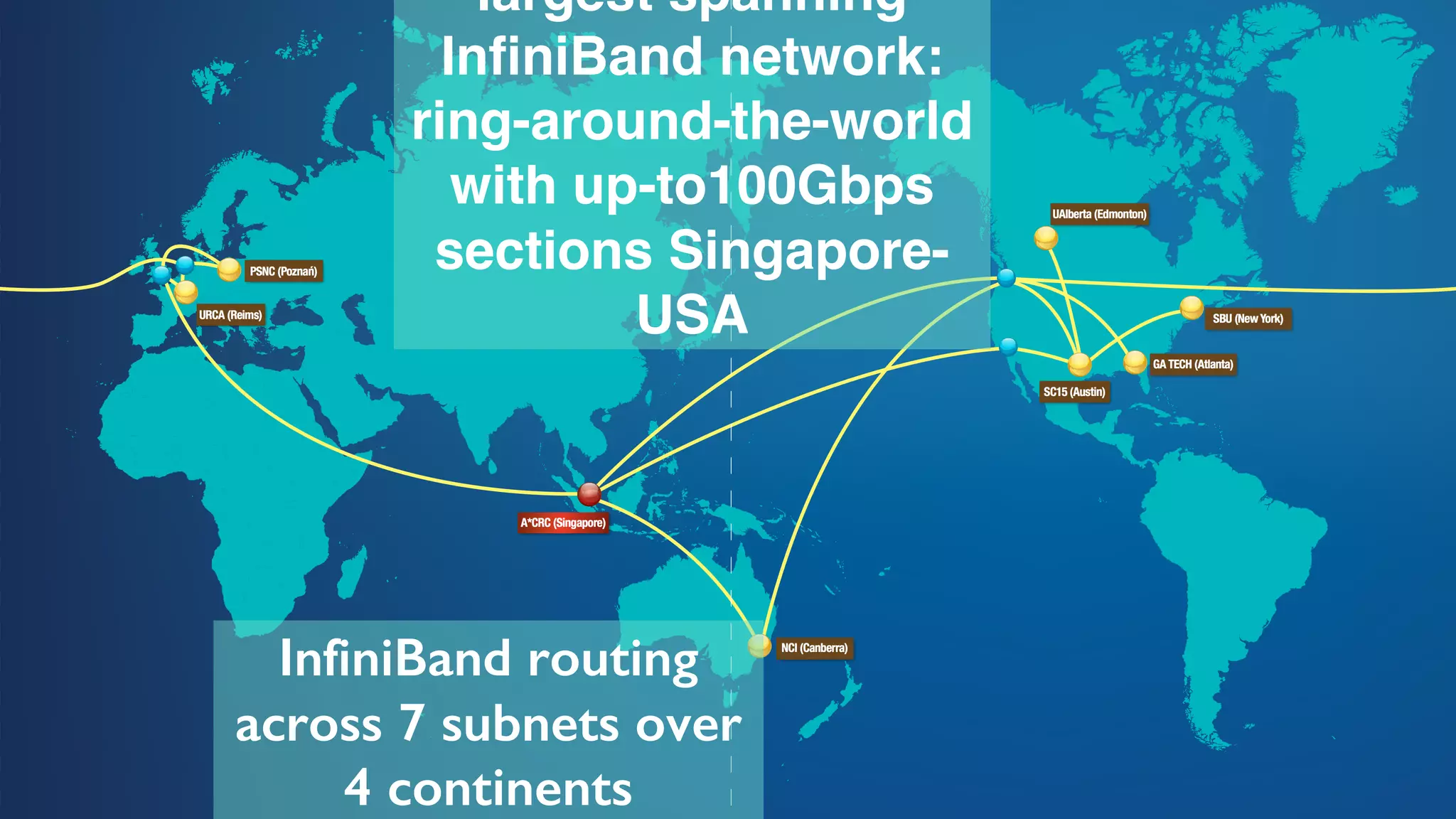







![www.icm.edu.pl
Bell's law of computer classes
Roughly every decade a new, lower priced computer class forms based on a new
programming platform, network, and interface resulting in new usage and the
establishment of a new industry.
Computer classes that conform to the law
• mainframes (1960s)
• minicomputers (1970s)[3] These are essentially replaced by clusters of PCs for a twenty-year (1965-1985)
lifespan. [4]
• personal computers and workstations evolving into a network enabled by Local Area Networking or
Ethernet (1980s)
• web browser client-server structures enabled by the Internet (1990s)
• cloud computing, e.g. Amazon Web Services,{2006} or Microsoft Azure (2012)
• hand held devices from media players and cell phones to tablets, e.g.Creative, iPods, BlackBerrys, iPhones,
Smartphones, Kindles, iPads (c. 2000-2010)
• Wireless Sensor Networks that enable sensor [5] and actuator interconnection, enabling the evolving
Internet of Things. (c. >2005)
Can we consider InfiniCortex to be a new class of computers in Bell’s
Law sense?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ddrmarekmichalewicz-infinicortexsuperkomputerwielkijakswiat2-170328143925/75/PLNOG-18-Dr-Marek-Michalewicz-InfiniCortex-Superkomputer-wielki-jak-swiat-37-2048.jpg)