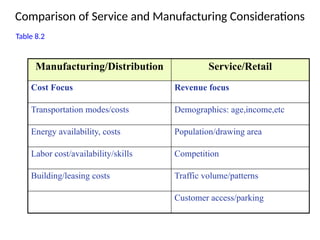
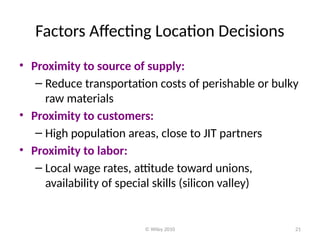
The document discusses location theory, focusing on the geographic placement of economic activities and the strategic importance of making location decisions for firms. It outlines factors affecting location choices, such as proximity to resources and markets, community considerations, and globalization impacts. Various methods for evaluating locations, including cost-volume analysis and transportation models, are also described.