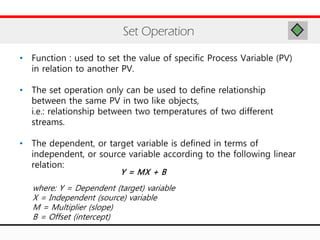
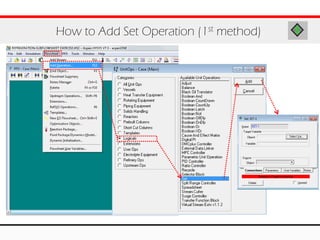
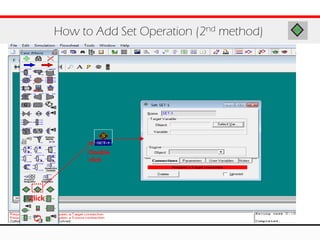
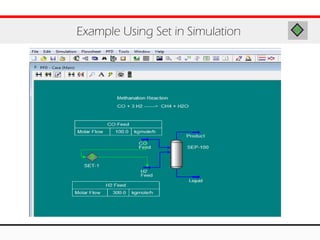
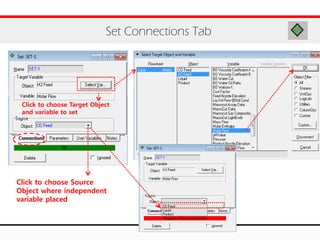
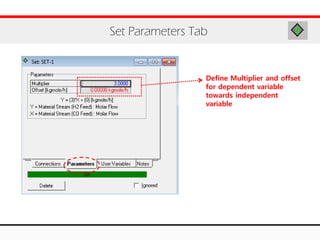
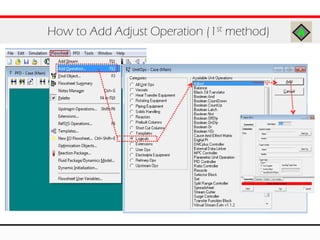
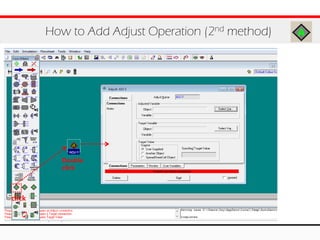
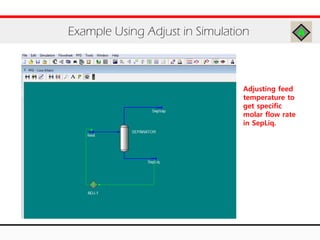
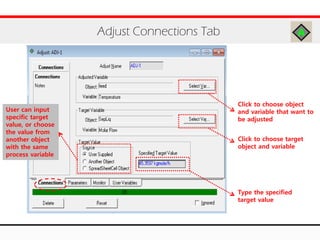
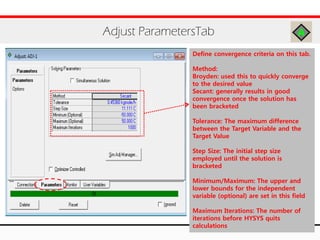
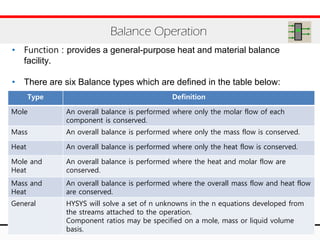
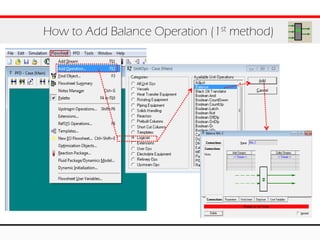
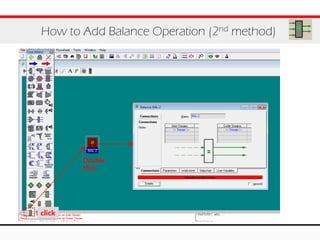
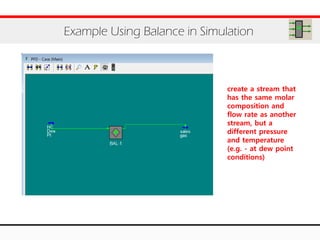
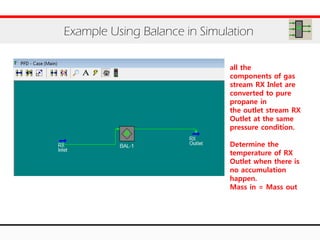
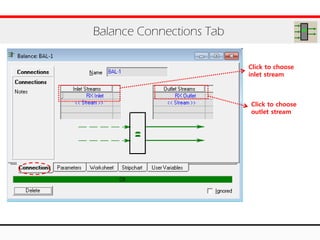
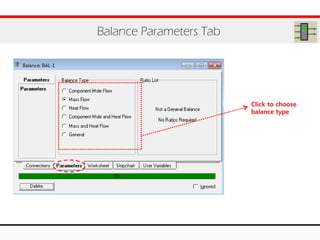
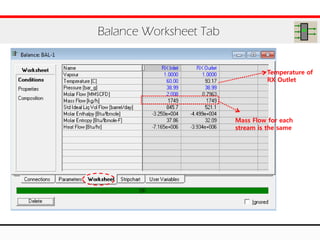
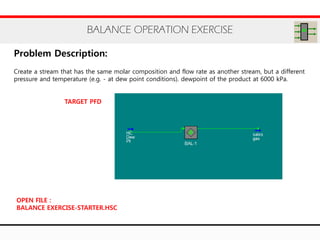
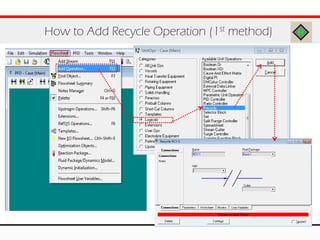
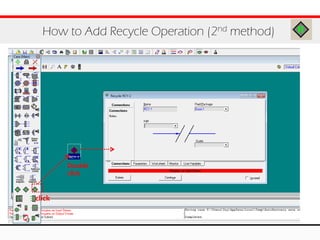
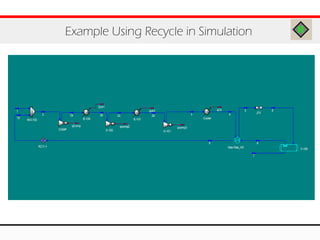
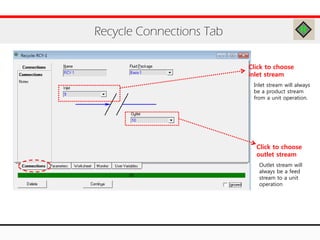
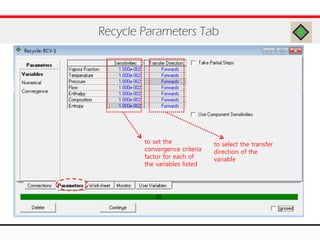
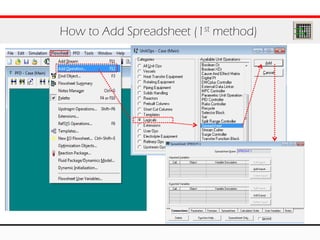
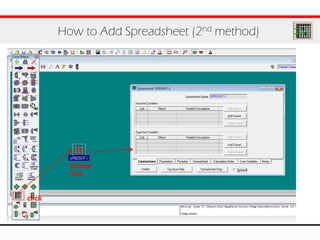
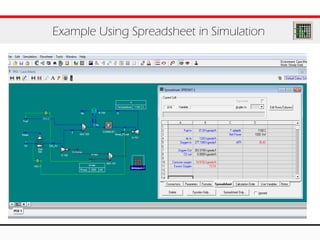
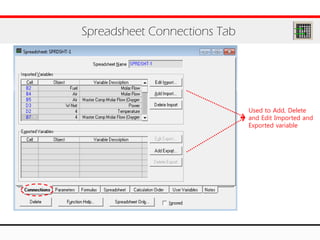
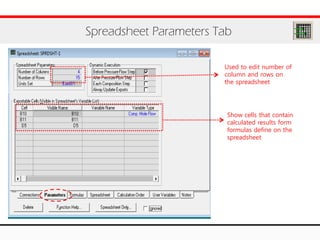
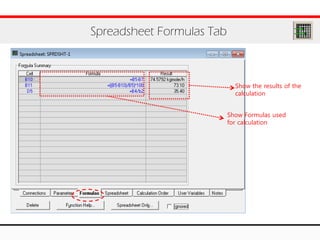
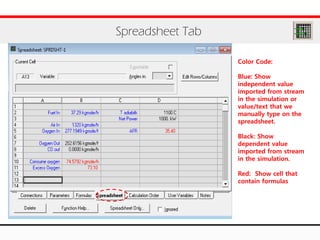
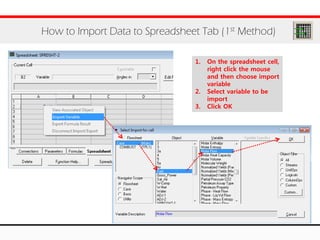
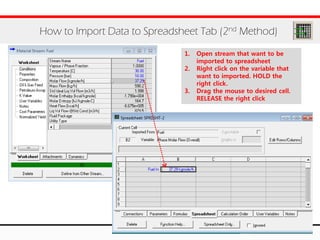
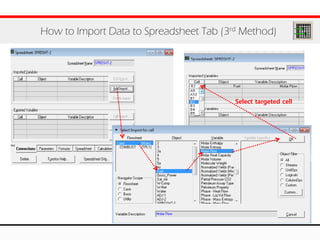
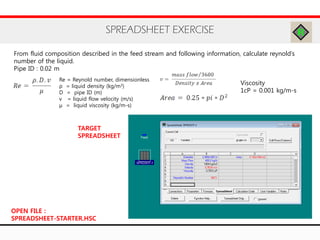
The document provides an overview of logical operations in Aspen HYSYS, including set, adjust, balance, recycle operations, and spreadsheet functionalities for process modeling. It describes how to implement each operation, their functions, and includes examples and exercises to reinforce understanding. Emphasis is placed on the relationship between process variables and the integration of these operations within simulations.