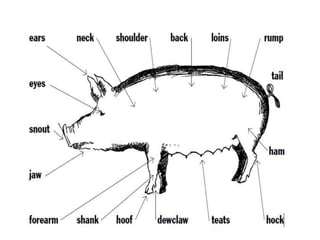
Pig production is one of the oldest domesticated animals found around the world. Pigs are a major source of meat, comprising 38% of world meat production. Pigs have advantages such as efficient conversion of feed to food, high growth rates, tolerance to various feeds and environments, and ability to improve soil fertility through manure. Proper pig raising requires adequate food, water, shelter, health care and space.