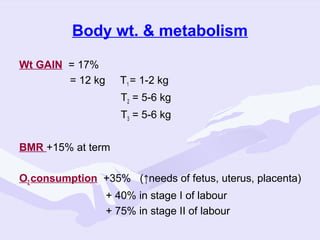
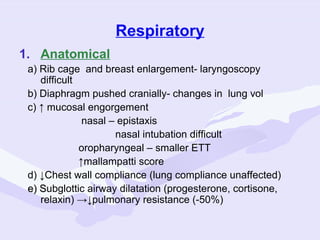
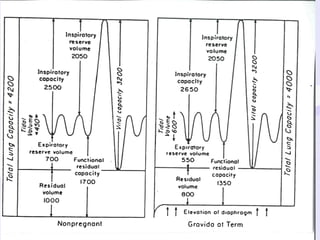
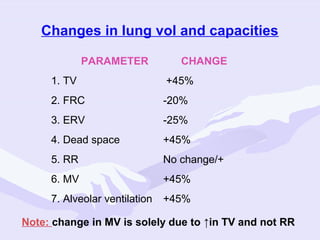
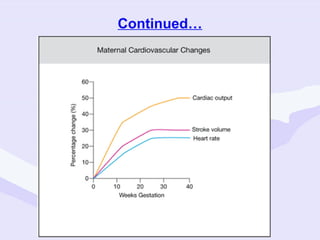
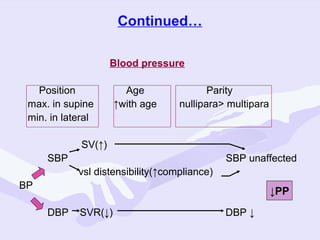
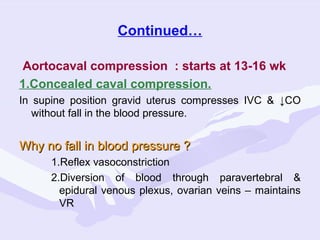
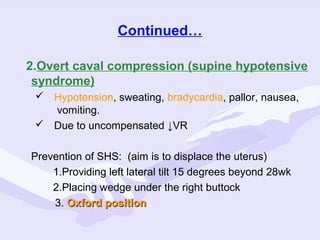
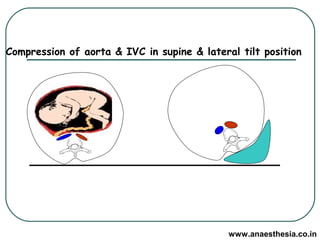
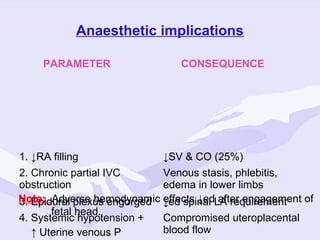
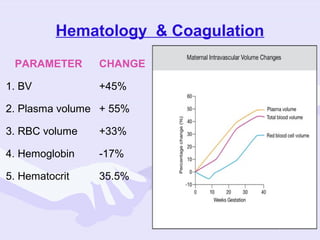
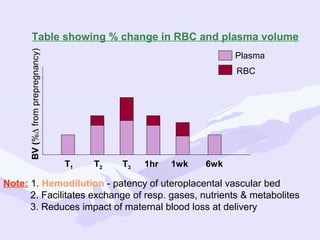
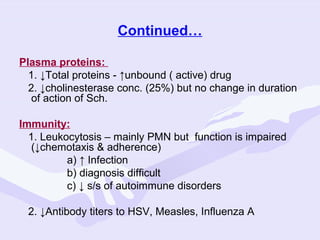
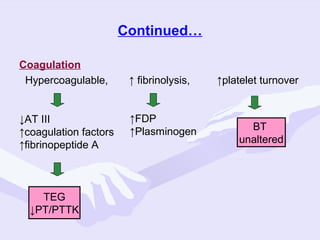
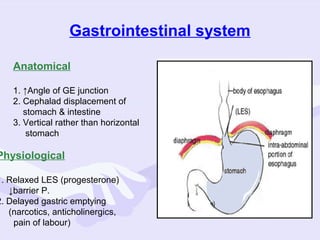
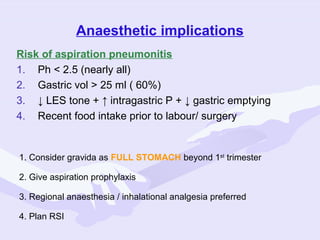
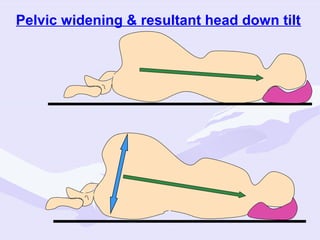
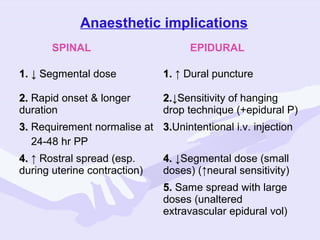
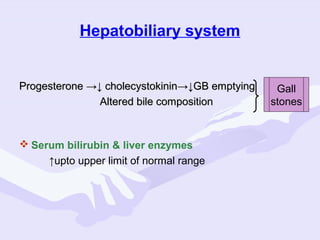
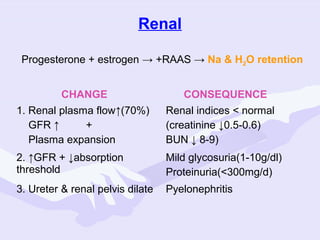
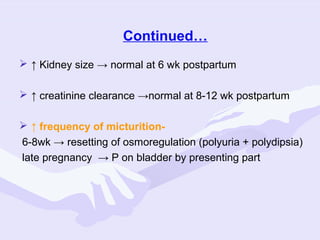
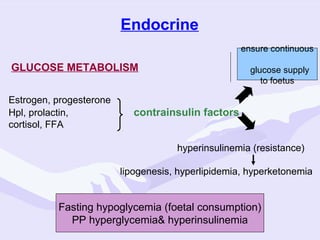
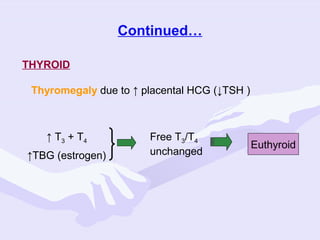
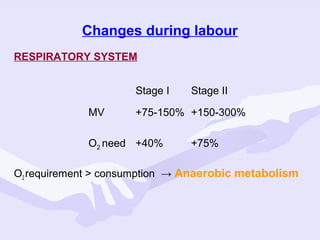
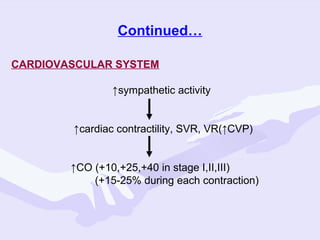
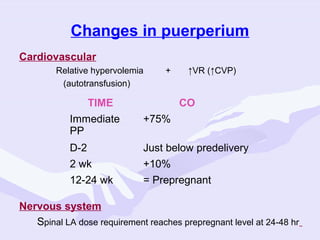
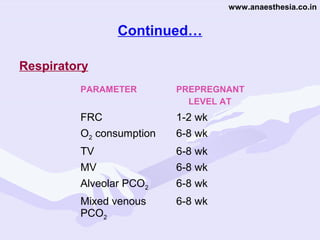
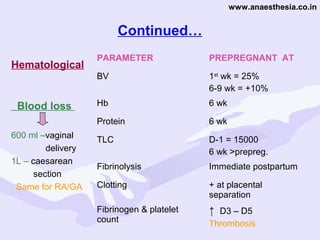
Physiological changes in pregnancy are due to hormonal changes and fetal growth. Systems affected include respiratory (increased lung volumes), cardiovascular (increased cardiac output and stroke volume), hematologic (hemodilution), gastrointestinal (delayed gastric emptying), and renal (increased glomerular filtration rate). These changes result in implications for anesthesia like rapid denitrogenation and hypoxia during apnea due to decreased functional residual capacity. Spinal and epidural requirements are lower due to neural sensitivity changes. Changes revert to pre-pregnancy levels postpartum, generally within 6-12 weeks.