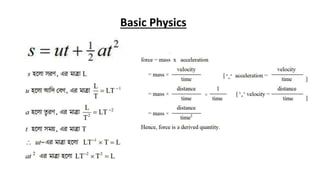
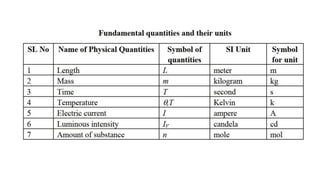
The document provides an overview of basic physics concepts, focusing on motion, types of motion (linear, rotational, periodic, vibratory), and the principles of scalar and vector quantities. It also discusses gravity and Newton's laws related to falling bodies, detailing the effects of gravitational force on motion. Key concepts include different classifications of motion and fundamental principles of dynamics related to forces and acceleration.