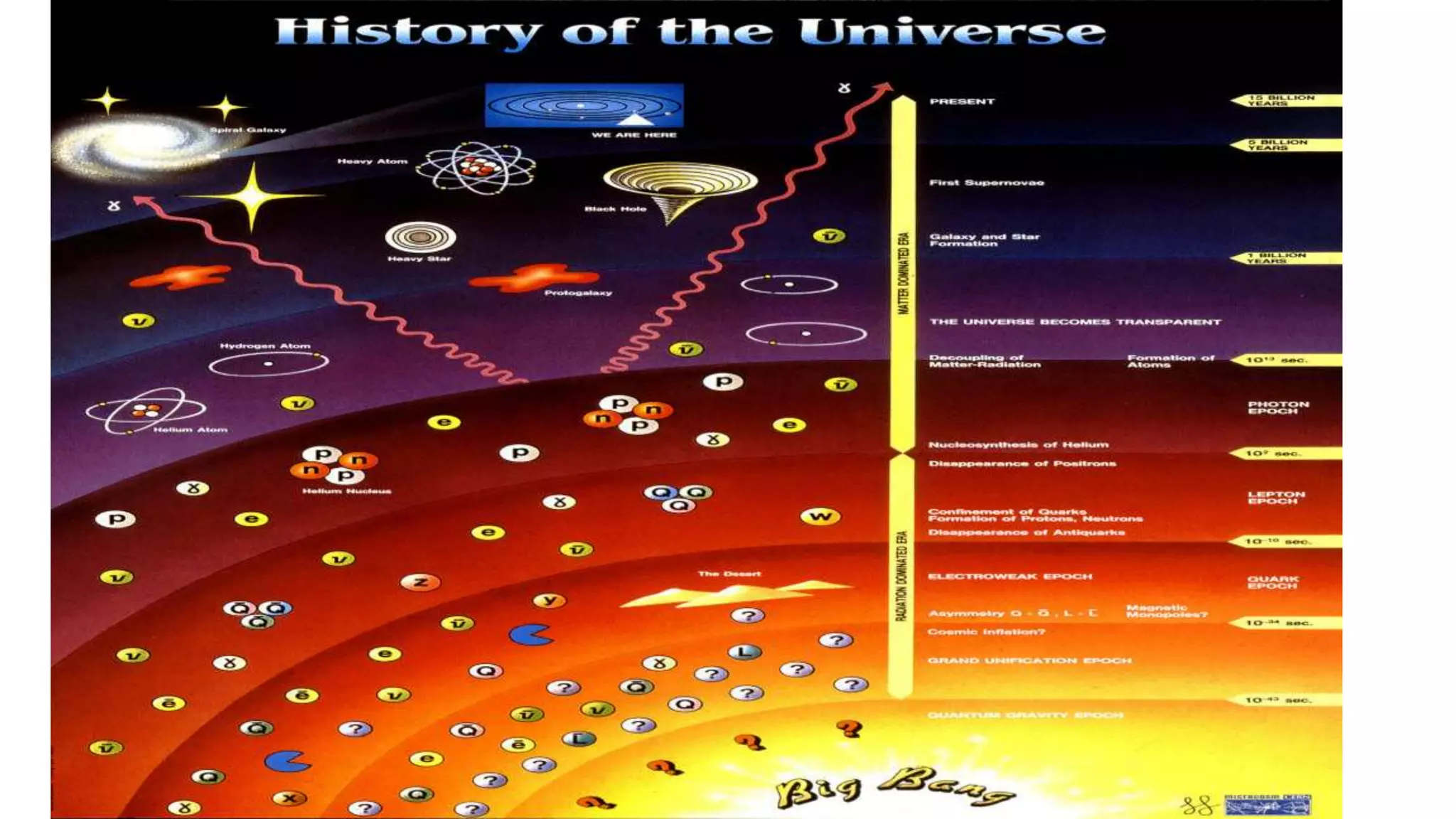
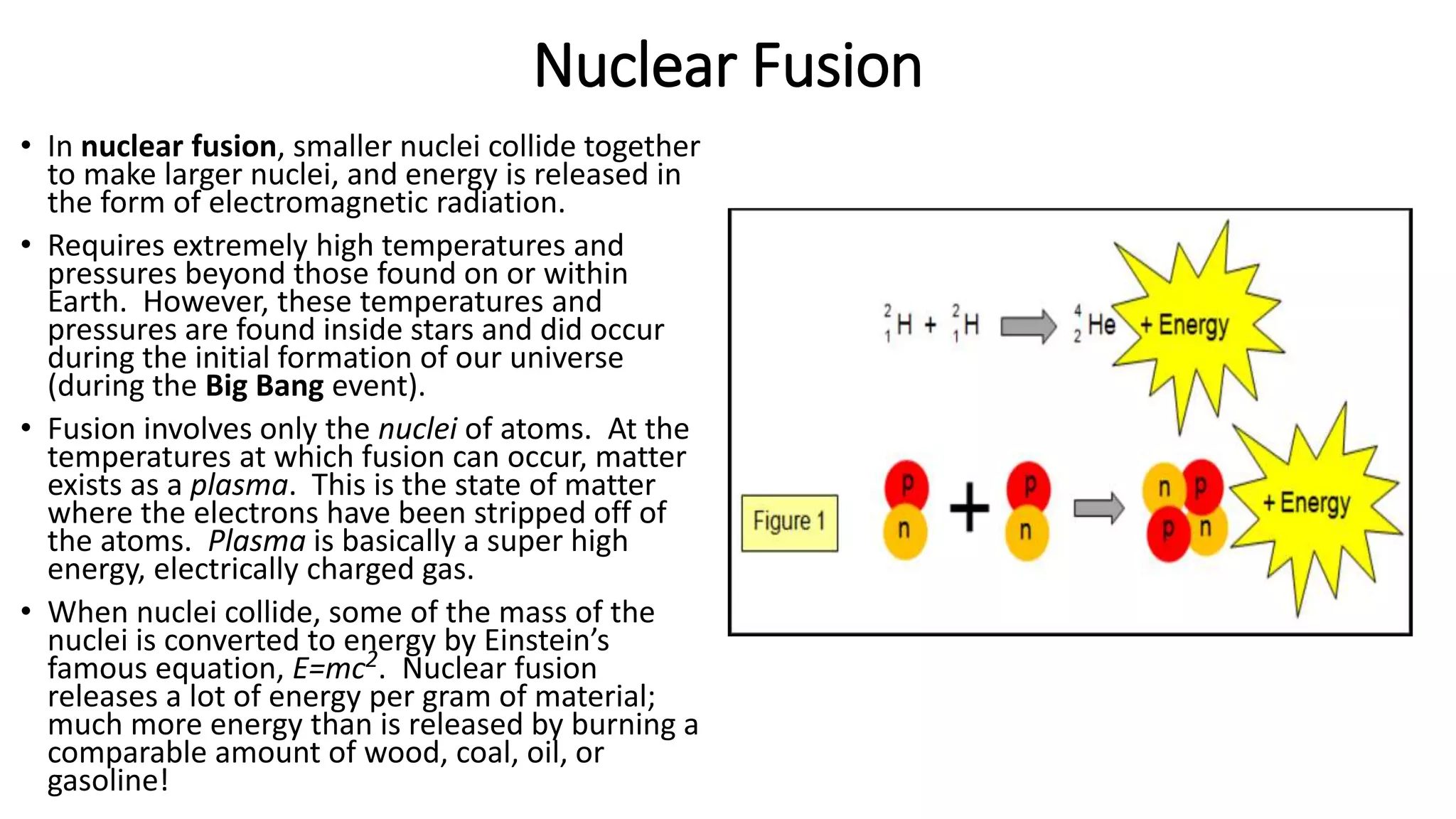
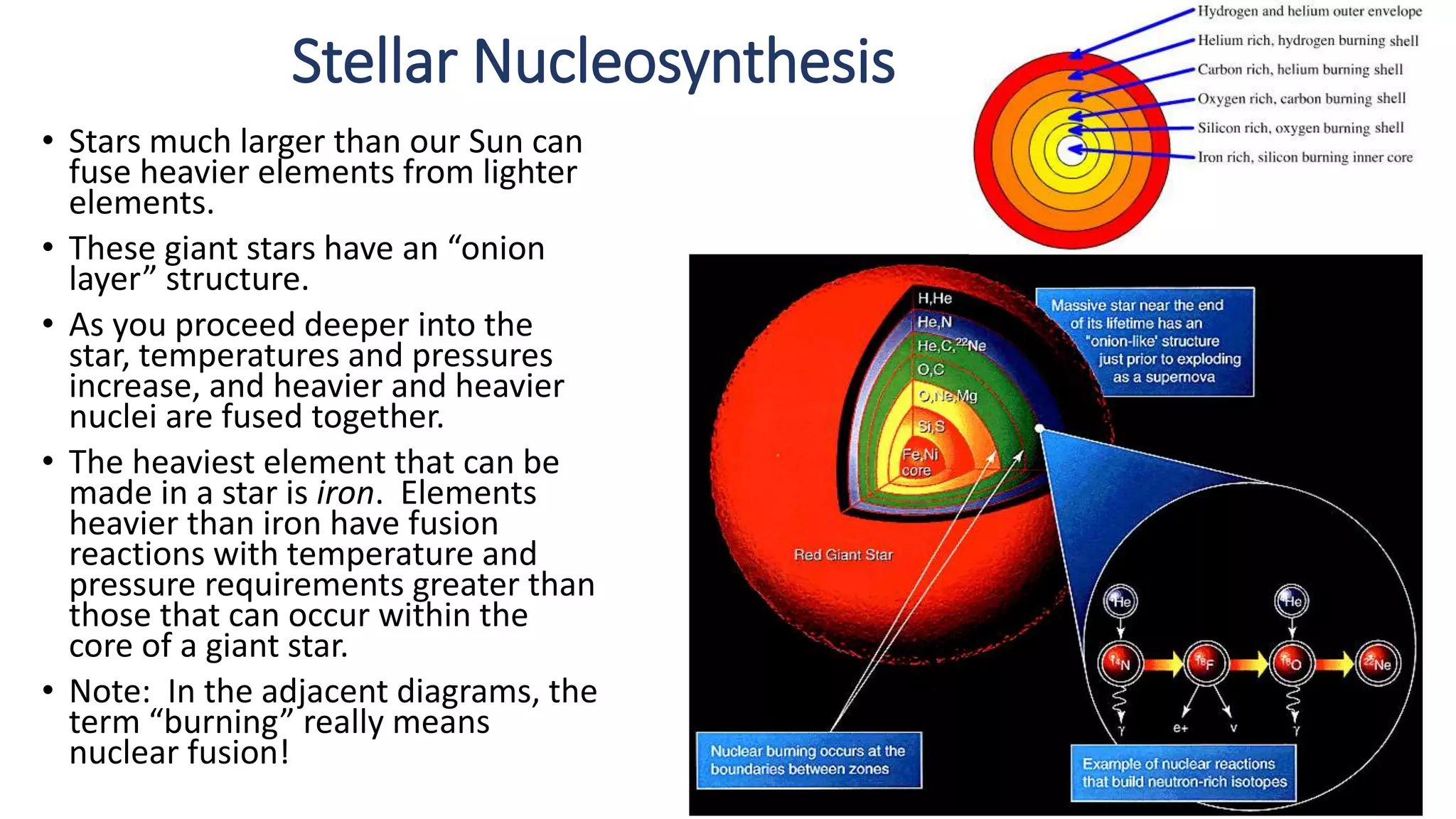
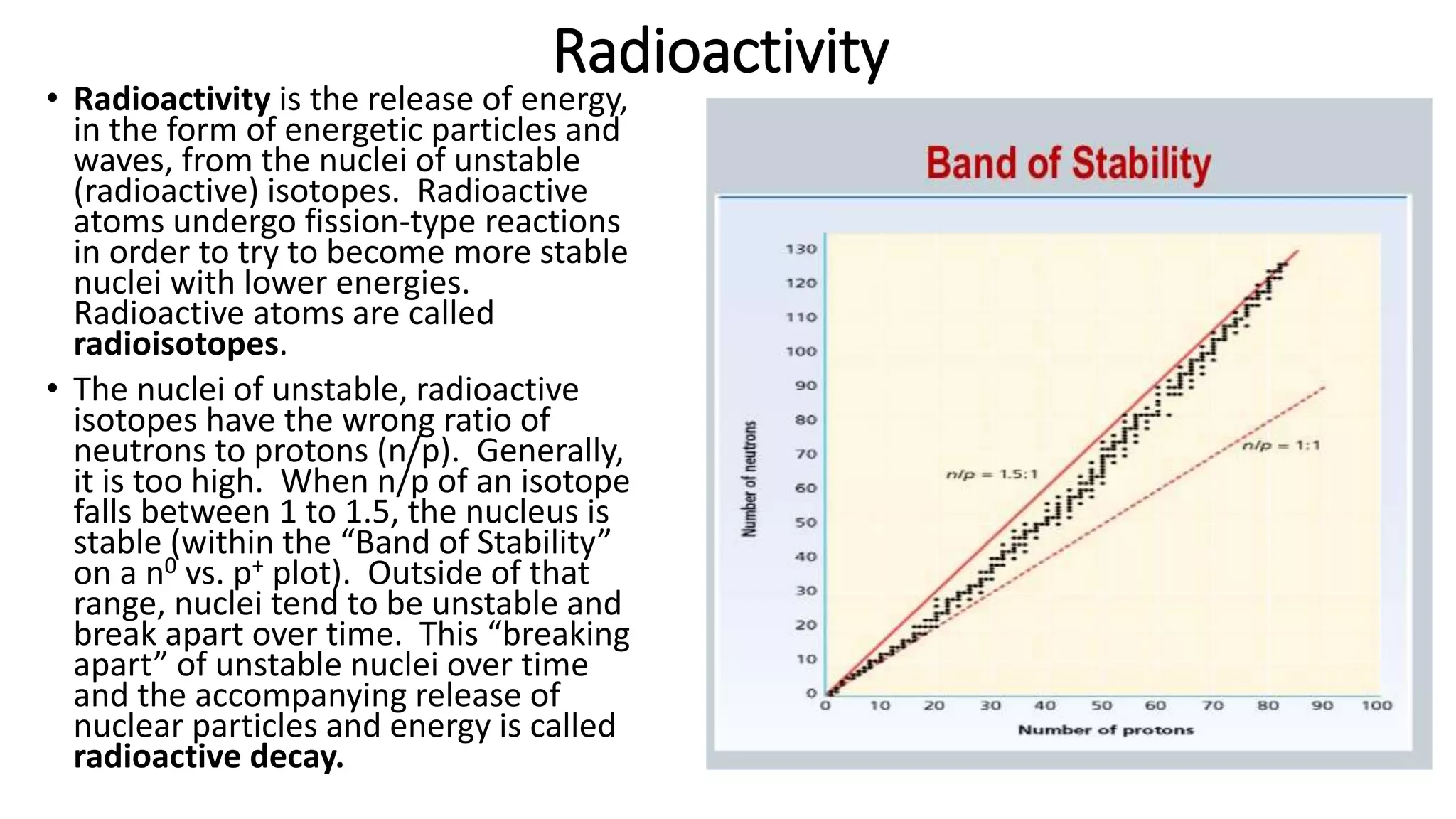
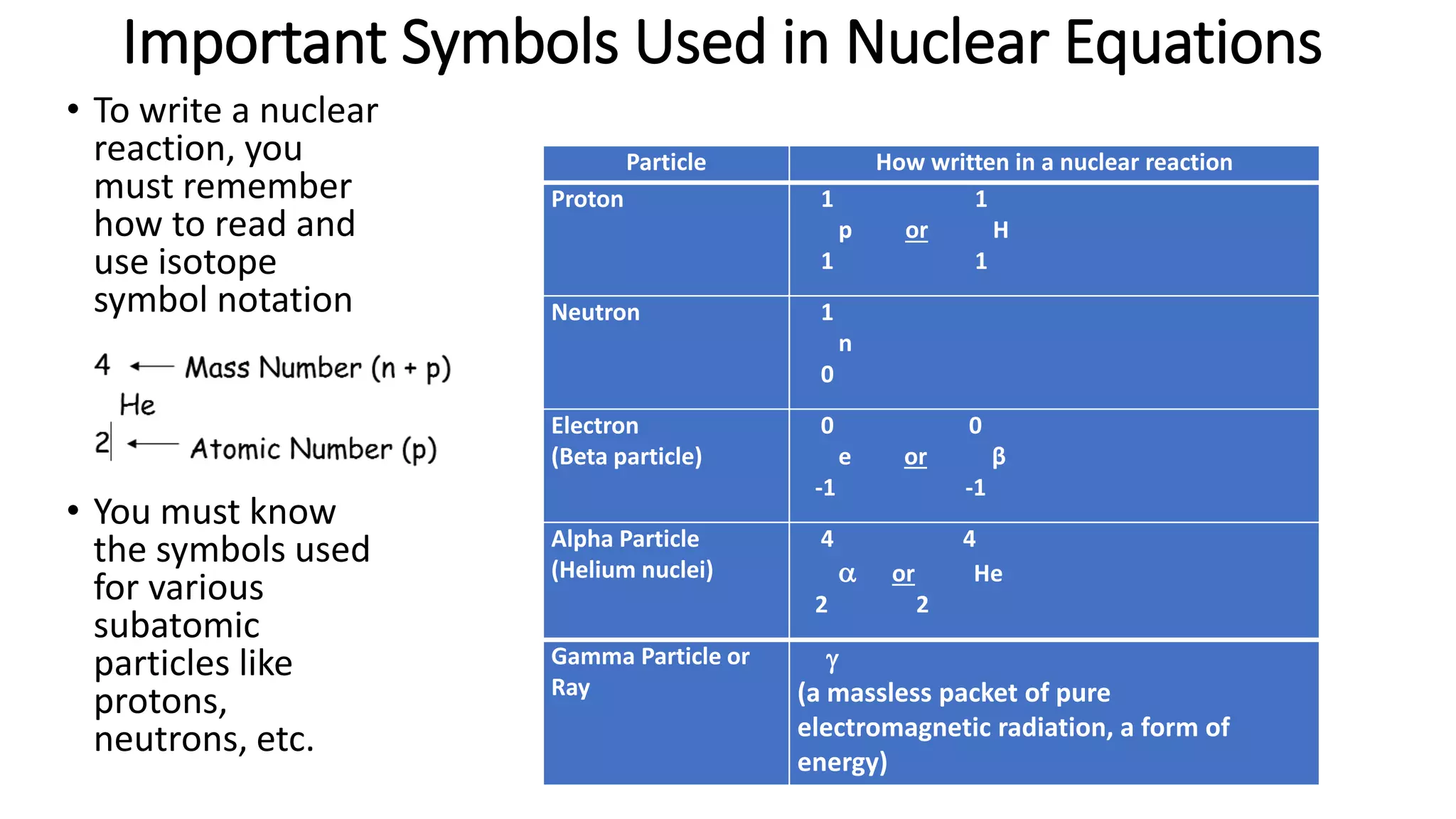
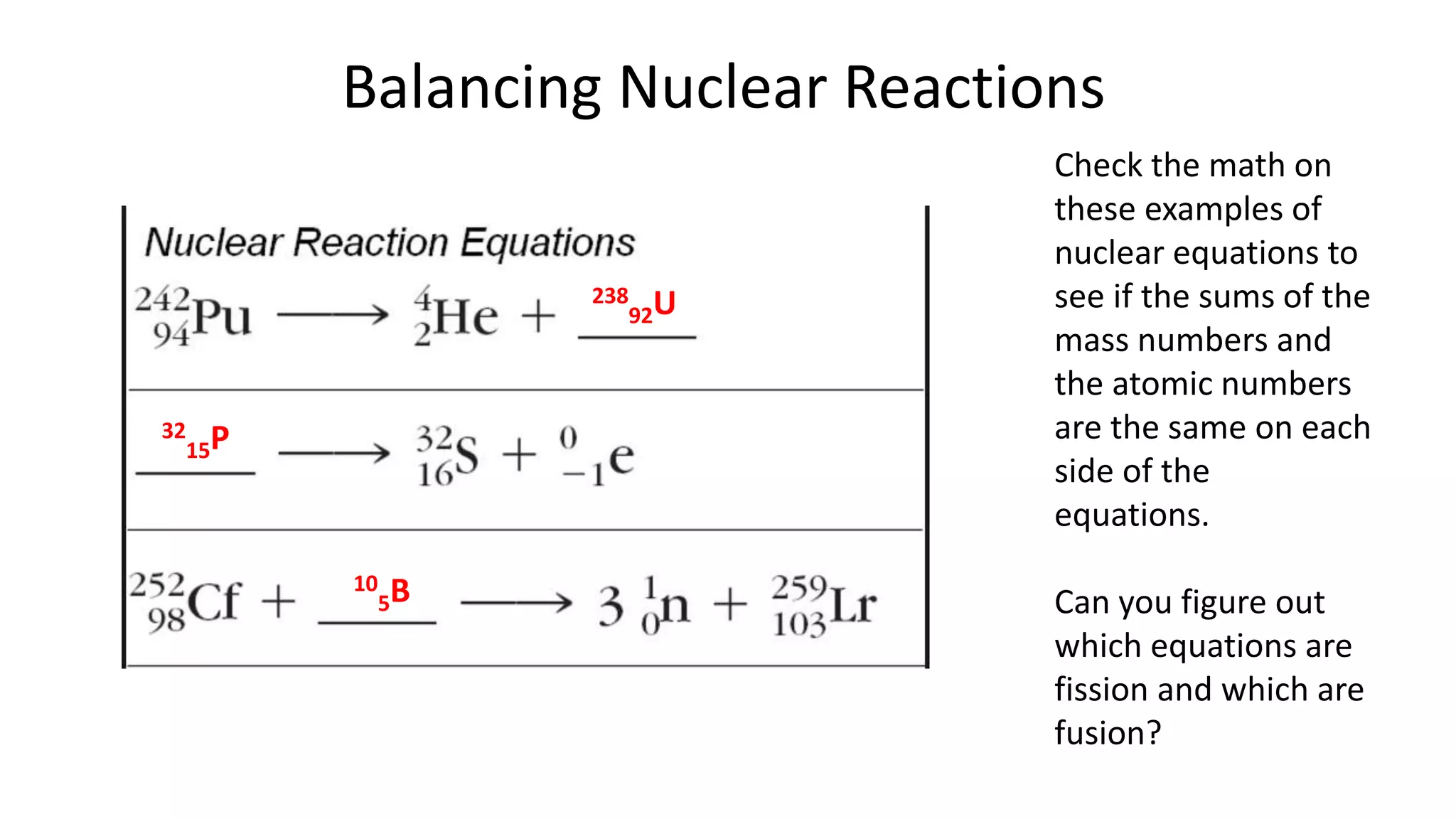
The document discusses how elements are formed in the universe through three main nuclear reactions: nucleosynthesis during the Big Bang formed light elements like hydrogen and helium, nuclear fusion in stars forms heavier elements up to iron, and neutron capture reactions during supernovae explosions produce elements heavier than iron. These nuclear reactions require extremely high temperatures and pressures to fuse atomic nuclei together or allow neutron capture, conditions only found in the early universe, inside stars and supernovae. Element formation relies on balancing the number of protons and neutrons in atomic nuclei to achieve stable configurations through fusion, fission, radioactive decay, or transmutation into other elements.