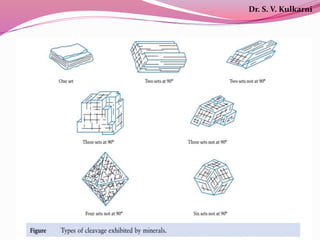
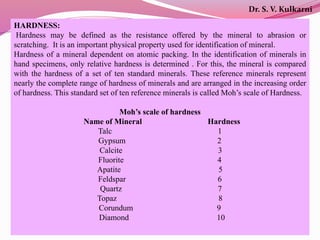
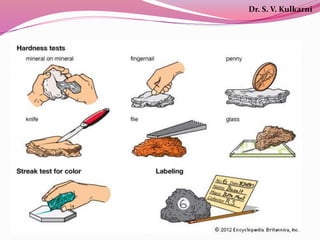
The document discusses various physical properties used to identify minerals, including luster, cleavage, fracture, hardness, specific gravity, and other diagnostic characteristics. It provides definitions and examples of different types of luster (metallic, sub-metallic, non-metallic), cleavage (perfect, imperfect, absent), fracture (even, uneven, hackly, conchoidal), Mohs scale of hardness (ranging from 1 to 10), approaches to measuring specific gravity, and other properties like color, streak, and reaction to acid that can aid identification. The document also includes examples of analyzing physical properties to identify mineral specimens.





![Specimen No. :-
A] Chemical composition :- SiO2
B ] Crystal System :- HEXAGONAL
C ] Physical properties :-
1. Form / Habit – Crystalline
2. Colour – Colourless
3. Streak – White / Absent
4. Lustre – Vitreous
5. Cleavage – Absent
6. Fracture – Conchoidal
7. Hardness – Can not be scratched by knife (7)
8. Specific gravity – Medium
D] Diagnostic character – Crystalline form, Absence of cleavage,
Conchoidal Fracture, Hardness 7
On the basis of above physical properties , the mineral may
be identified as QUARTZ
Dr. S. V. Kulkarni](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/physicalproperties-210210134818/85/Physical-properties-9-320.jpg)
![Specimen No. :-
A] Chemical composition :- CaCO3
B ] Crystal System :- HEXAGONAL
C ] Physical properties :-
1. Form / Habit – Crystalline / Rhombohedral
2. Colour – White
3. Streak – White
4. Lustre – Vitreous
5. Cleavage – Perfect
6. Fracture – Even
7. Hardness – Can be scratched by knife (3-3.5)
8. Specific gravity – Medium
D] Diagnostic character – Rhombohedral form, Perfect Cleavage
Even Fracture, Hardness 3, Gives +ve
acid test
On the basis of above physical properties , the mineral
may be identified as CALCITE.
Dr. S. V. Kulkarni](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/physicalproperties-210210134818/85/Physical-properties-10-320.jpg)
![Specimen No. :-
A] Chemical composition :- KAlSi3O8 (Potassium aluminium
silicate)
B ] Crystal System :- TRICLINIC
C ] Physical properties :-
1. Form / Habit – Crystalline/ Tabular
2. Colour – Flesh red
3. Streak – Absent
4. Lustre – Vitreous
5. Cleavage – Present
6. Fracture – Even
7. Hardness – Can be scratched by knife (6-6.5)
8. Specific gravity – Medium
D] Diagnostic character – Flesh red colour, Perfect cleavage,
Vitreous lustre, Hardness 6, Tabular form
On the basis of above physical properties , the mineral may
be identified as MICROCLINE
Dr. S. V. Kulkarni](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/physicalproperties-210210134818/85/Physical-properties-11-320.jpg)
![Specimen No. :-
A] Chemical composition :- KAlSi3O8 (Potassium aluminum
silicate)
B ] Crystal System :- TRICLINIC
C ] Physical properties :-
1. Form / Habit – Massive/ Tabular
2. Colour – White
3. Streak – White
4. Lustre – Vitreous
5. Cleavage – Present
6. Fracture – Uneven
7. Hardness – Can be scratched by knife (6-6.5)
8. Specific gravity – Medium
D] Diagnostic character – White colour, Perfect cleavage,
Vitreous lustre, Hardness 6, Massive form
On the basis of above physical properties , the mineral may
be identified as ORTHOCLASE
Dr. S. V. Kulkarni](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/physicalproperties-210210134818/85/Physical-properties-12-320.jpg)
![Specimen No. :-
A] Chemical composition :- KAl2(Al Si3O10) (OH)2 Hydrous Silicate
of K & Al
B ] Crystal System :- MONOCLINIC
C ] Physical properties :-
1. Form / Habit – Flaky / Platy
2. Colour – Colourless/ Transparent
3. Streak – Absent
4. Lustre – Pearly/ Vitreous
5. Cleavage – Perfect
6. Fracture – Even
7. Hardness – Can be scratched by Fingernail (2.7 to 3)
8. Specific gravity – Low
D] Diagnostic character – Colourless, Flaky form, Perfect cleavage,
Pearly lustre,
On the basis of above physical properties , the mineral may be
identified as MUSCOVITE
Dr. S. V. Kulkarni](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/physicalproperties-210210134818/85/Physical-properties-13-320.jpg)
![Specimen No. :-
A] Chemical composition :- K(Mg Fe)3 AlSi3O10 (OH)2
B ] Crystal System :- MONOCLINIC
C ] Physical properties :-
1. Form / Habit – Flaky
2. Colour – Deep Brown / Black
3. Streak – Absent
4. Lustre – Pearly/ Vitreous
5. Cleavage – Perfect
6. Fracture – Even
7. Hardness – Can be scratched by Fingernail (2.7 to 3)
8. Specific gravity – Medium
D] Diagnostic character – Brownish Black colour, Perfect cleavage,
Vitreous lustre, Flaky Form
On the basis of above physical properties , the mineral may
be identified as BIOTITE
Dr. S. V. Kulkarni](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/physicalproperties-210210134818/85/Physical-properties-14-320.jpg)
![Specimen No. :-
A] Chemical composition :- Al2SiO5
B ] Crystal System :- TRICLINIC
C ] Physical properties :-
1. Form / Habit – Bladed
2. Colour – Brownish red
3. Streak – Absent
4. Lustre – Vitreous to Subvitreous
5. Cleavage – Perfect
6. Fracture – -
7. Hardness – Variable hardness(Lenghtwise 5 – Across 7)
8. Specific gravity – Medium
D] Diagnostic character – Bladed form, Perfect cleavage,
Variable hardness
On the basis of above physical properties , the mineral may be
identified as KYANITE
Dr. S. V. Kulkarni](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/physicalproperties-210210134818/85/Physical-properties-15-320.jpg)
![Specimen No. :-
A] Chemical composition :- Ca2Na (Mg,Fe)4 (AlFeTi)(AlSi)8O22(OH)2
Complex Silicate of Ca,Mg,Fe,Al & Na
B ] Crystal System :- MONOCLINIC
C ] Physical properties :-
1. Form / Habit – Crystalline ( Prismatic)
2. Colour – Black / Dark Green
3. Streak – Absent
4. Lustre – Vitreous
5. Cleavage – Present
6. Fracture – Uneven
7. Hardness – Can be scratched by knife (5-5.5)
8. Specific gravity – Medium
D] Diagnostic character – Dark colour, Perfect cleavage,
Vitreous lustre, Hardness 5, Prismatic form
On the basis of above physical properties , the mineral may be
identified as HORNBLENDE
Dr. S. V. Kulkarni](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/physicalproperties-210210134818/85/Physical-properties-16-320.jpg)
![Specimen No. :-
A] Chemical composition :- (Ca,Na)(Mg,Fe++,Fe+++,Al)(Si,Al)2O6
B ] Crystal System :- MONOCLINIC
C ] Physical properties :-
1. Form / Habit – Crystalline/ Tabular
2. Colour – Black / Dark Green
3. Streak – Greyish White
4. Lustre – Vitreous
5. Cleavage – Present
6. Fracture – Uneven
7. Hardness – Can be scratched by knife (5-5.5)
8. Specific gravity – Medium
D] Diagnostic character – Dark black colour, Perfect cleavage,
Vitreous lustre, Hardness 5.5, Prismatic
form
On the basis of above physical properties , the mineral may
be identified as AUGITE
Dr. S. V. Kulkarni](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/physicalproperties-210210134818/85/Physical-properties-17-320.jpg)
![Specimen No. :-
A] Chemical composition :- Al2O3
B ] Crystal System :- HEXAGONAL
C ] Physical properties :-
1. Form / Habit – Crystalline/ Tabular
2. Colour – Reddish brown
3. Streak – Greyish White
4. Lustre – Admantine
5. Cleavage – Present
6. Fracture – Uneven
7. Hardness – Can not be scratched by knife (9)
8. Specific gravity – High
D] Diagnostic character – Reddish brown colour, Perfect cleavage,
Admantine lustre, Hardness 9,
On the basis of above physical properties , the mineral may
be identified as CORUNDUM
Dr. S. V. Kulkarni](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/physicalproperties-210210134818/85/Physical-properties-18-320.jpg)
![Specimen No. :-
A] Chemical composition :- Complex Silicate of Ca, Mg, Fe, Al.
B ] Crystal System :- CUBIC/ISOMETRIC
C ] Physical properties :-
1. Form / Habit – Crystalline/ Dodecahedron
2. Colour – Reddish brown/ Wine Red
3. Streak – Absent
4. Lustre – Resinous
5. Cleavage – Indistinct
6. Fracture – Uneven
7. Hardness – Can not be scratched by knife (6.5-7)
8. Specific gravity – High
D] Diagnostic character – Wine red colour, Crystalline form,
Resinous lustre, Hardness,
On the basis of above physical properties , the mineral may
be identified as GARNET
Dr. S. V. Kulkarni](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/physicalproperties-210210134818/85/Physical-properties-19-320.jpg)
![Specimen No. :-
A] Chemical composition :- (Mg,Fe)2 SiO4
B ] Crystal System :- ORTHORHOMBIC
C ] Physical properties :-
1. Form / Habit – Crystalline/ Granular
2. Colour – Olive Green
3. Streak – White
4. Lustre – Vitreous/ Subvitreous
5. Cleavage – Absent
6. Fracture – Uneven
7. Hardness – Can be scratched by knife (6.5)
8. Specific gravity – Medium
D] Diagnostic character – Olive Green colour, Absence of cleavage,
Vitreous lustre, Crystalline form
On the basis of above physical properties , the mineral may
be identified as OLIVINE
Dr. S. V. Kulkarni](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/physicalproperties-210210134818/85/Physical-properties-20-320.jpg)
![Specimen No. :-
A] Chemical composition :- Mg3 Si4 O10(OH)2
B ] Crystal System :- ORTHORHOMBIC
C ] Physical properties :-
1. Form / Habit – Foliated /Massive
2. Colour – White/ pale yellow
3. Streak – White
4. Lustre – Pearly
5. Cleavage – present
6. Fracture – Uneven
7. Hardness – Can be scratched by fingernail (1-1.5)
8. Specific gravity – Medium
D] Diagnostic character – Soapy / very soft , Low hardness
Pearly lustre,
On the basis of above physical properties , the mineral may
be identified as TALC
Dr. S. V. Kulkarni](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/physicalproperties-210210134818/85/Physical-properties-21-320.jpg)
![Specimen No. :-
A] Chemical composition :- Complex Silicate of Boron and aluminum
B ] Crystal System :- HEXAGONAL
C ] Physical properties :-
1. Form / Habit – Crystalline /Prismatic
2. Colour – Jet Black
3. Streak – Greyish white
4. Lustre – Vitreous
5. Cleavage – Present
6. Fracture – Uneven
7. Hardness – Can not be scratched by fingernail (7-7.5)
8. Specific gravity – Medium
D] Diagnostic character – Jet black colour, Prismatic form
On the basis of above physical properties , the mineral may be
identified as TOURMALINE
Dr. S. V. Kulkarni](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/physicalproperties-210210134818/85/Physical-properties-22-320.jpg)
![Specimen No. :-
A] Chemical composition :- Ca SO4.2H2O
B ] Crystal System :- MONOCLINIC
C ] Physical properties :-
1. Form / Habit – Crystalline
2. Colour – White/ Colourless
3. Streak – White
4. Lustre – Vitreous/ Pearly
5. Cleavage – Present
6. Fracture – Uneven
7. Hardness – Can be scratched by fingernail (2-2.5)
8. Specific gravity – Medium
D] Diagnostic character – Crystalline form, Low hardness
On the basis of above physical properties , the mineral may be
identified as GYPSUM
Dr. S. V. Kulkarni](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/physicalproperties-210210134818/85/Physical-properties-23-320.jpg)
![Specimen No. :-
A] Chemical composition :- Fe2O3
B ] Crystal System :- HEXAGONAL
C ] Physical properties :-
1. Form / Habit – Massive/ Granular
2. Colour – Reddish brown / Dark brown/ Black
3. Streak – Cherry Red
4. Lustre – Metallic / Submetallic
5. Cleavage – Absent
6. Fracture – Uneven
7. Hardness – Can be scratched by penknife (5-5.5)
8. Specific gravity – Medium to high
D] Diagnostic character – Metallic Lustre, Cherry red streak,
High Sp. gravity
On the basis of above physical properties , the mineral may be
identified as HEMATITE
Dr. S. V. Kulkarni](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/physicalproperties-210210134818/85/Physical-properties-24-320.jpg)
![Specimen No. :-
A] Chemical composition :- FeCr2O4
B ] Crystal System :- CUBIC/ ISOMETRIC
C ] Physical properties :-
1. Form / Habit – Crystalline/ Granular
2. Colour – Greyish black/ Dark greenish
3. Streak – Brownish black
4. Lustre – Submetallic / Dull
5. Cleavage – Absent
6. Fracture – Uneven
7. Hardness – Can be scratched by penknife (5-5.5)
8. Specific gravity – High
D] Diagnostic character – Submetallic Lustre, Greyish black Colour,
High Sp. gravity
On the basis of above physical properties , the mineral may be
identified as CHROMITE
Dr. S. V. Kulkarni](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/physicalproperties-210210134818/85/Physical-properties-25-320.jpg)
![Specimen No. :-
A] Chemical composition :- MgCO3
B ] Crystal System :- HEXAGONAL
C ] Physical properties :-
1. Form / Habit – Massive
2. Colour – Chalk White
3. Streak – White
4. Lustre – Dull
5. Cleavage – Absent
6. Fracture – Uneven
7. Hardness – Can be scratched by penknife (4)
8. Specific gravity – Medium
D] Diagnostic character – White Colour, Absence of Cleavage
On the basis of above physical properties , the mineral may be
identified as MAGNESITE
Dr. S. V. Kulkarni](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/physicalproperties-210210134818/85/Physical-properties-26-320.jpg)
![Specimen No. :-
A] Chemical composition :- Cu Fe S2
B ] Crystal System :- TETRAGONAL
C ] Physical properties :-
1. Form / Habit – Crystalline/ Massive
2. Colour – Brass yellow Colour
3. Streak – Greenish black
4. Lustre – Submetallic
5. Cleavage – Absent
6. Fracture – Uneven
7. Hardness – Can be scratched by penknife (4-4.5)
8. Specific gravity – High
D] Diagnostic character – Brass Yellow Colour, Greenish black
High Sp. gravity
On the basis of above physical properties , the mineral may be
identified as CHALCOPYRITE
Dr. S. V. Kulkarni`](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/physicalproperties-210210134818/85/Physical-properties-27-320.jpg)
![Specimen No. :-
A] Chemical composition :- CaCO3.MgCO3
B ] Crystal System :- HEXAGONAL
C ] Physical properties :-
1. Form / Habit – Crystalline/ Massive
2. Colour – White/ Grey
3. Streak – White
4. Lustre – Dull
5. Cleavage – Perfect
6. Fracture – Uneven
7. Hardness – Can be scratched by penknife (3.5-4)
8. Specific gravity – Medium
D] Diagnostic character – Greyish Colour, Reacts with HCl.
Medium Sp. gravity
On the basis of above physical properties , the mineral may be
identified as DOLOMITE
Dr. S. V. Kulkarni](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/physicalproperties-210210134818/85/Physical-properties-28-320.jpg)
![Specimen No. :-
A] Chemical composition :- C
B ] Crystal System :- CUBIC/ ISOMETRIC
C ] Physical properties :-
1. Form / Habit – Crystalline/ Granular
2. Colour – Greyish black/Black
3. Streak – Black
4. Lustre – Metallic
5. Cleavage – Perfect
6. Fracture – Uneven
7. Hardness – Can be scratched by penknife (2)
8. Specific gravity – Low to medium
D] Diagnostic character – Metallic Lustre, Greyish black Colour,
Black shining streak
On the basis of above physical properties , the mineral may be
identified as GRAPHITE
Dr. S. V. Kulkarni](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/physicalproperties-210210134818/85/Physical-properties-29-320.jpg)
![Specimen No. :-
A] Chemical composition :- (Mg Fe Al)6(Al Si)4 O10 (OH)8
B ] Crystal System :- Monoclinic
C ] Physical properties :-
1. Form / Habit – Folliated
2. Colour – Greenish
3. Streak – Brownish black
4. Lustre – Vitreous
5. Cleavage – Perfect
6. Fracture – Uneven
7. Hardness – Can be scratched by penknife (5-5.5)
8. Specific gravity – High
D] Diagnostic character – Vitreous Lustre, Greyish black Colour,
High Sp. gravity
On the basis of above physical properties , the mineral may be
identified as CHLORITE
Dr. S. V. Kulkarni](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/physicalproperties-210210134818/85/Physical-properties-30-320.jpg)
![Specimen No. :-
A] Chemical composition :- CaF2
B ] Crystal System :- CUBIC/ ISOMETRIC
C ] Physical properties :-
1. Form / Habit – Crystalline/ Granular
2. Colour – Yellow/ White
3. Streak – Brownish black
4. Lustre – Vitreous
5. Cleavage – Perfect
6. Fracture – Uneven
7. Hardness – Can be scratched by penknife (4)
8. Specific gravity – Medium to High
D] Diagnostic character – Crystalline form,
High Sp. gravity
On the basis of above physical properties , the mineral may be
identified as FLUORITE
Dr. S. V. Kulkarni](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/physicalproperties-210210134818/85/Physical-properties-31-320.jpg)
![Specimen No. :-
A] Chemical composition :- Mg3Si2O5 (OH)4
B ] Crystal System :- MONOCLINIC
C ] Physical properties :-
1. Form / Habit – Fibrous
2. Colour – Greenish
3. Streak – White
4. Lustre – Pearly
5. Cleavage – Perfect
6. Fracture – Uneven
7. Hardness – Can be scratched by penknife (3)
8. Specific gravity – High
D] Diagnostic character – Fibrous form, Pearly lustre
On the basis of above physical properties , the mineral may be
identified as ASBESTOS
Dr. S. V. Kulkarni](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/physicalproperties-210210134818/85/Physical-properties-32-320.jpg)