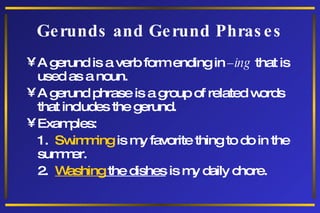
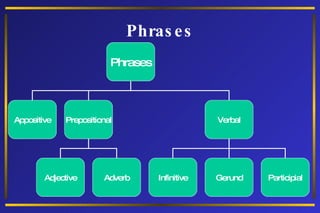
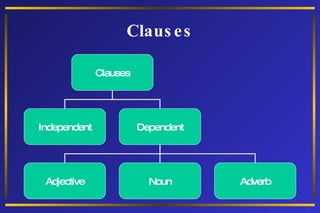
The document discusses different types of phrases and clauses. It defines phrases as groups of related words that do not contain a verb and subject. There are five types of phrases: prepositional, adjective, adverb, verbal, and appositive. It also defines clauses as groups of words containing a subject and verb. Clauses are either independent or dependent, with three types of dependent clauses: adjective, adverb, and noun clauses. Examples are provided to illustrate each type of phrase and clause.