The document provides an overview of PHP, including:
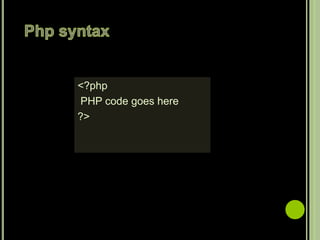
- PHP is an open source scripting language widely used for web development. PHP scripts are executed on the server and output HTML.
- PHP files can contain text, HTML, CSS, JavaScript and PHP code. PHP code generates dynamic page content and can interface with databases.
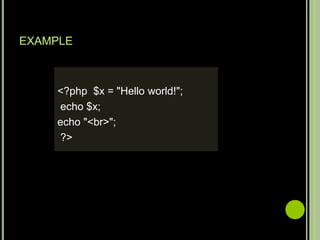
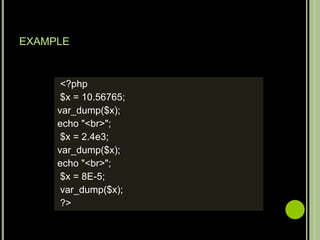
- To use PHP, a web server, PHP and a database like MySQL need to be installed. Core PHP data types include strings, integers, floats, booleans, arrays and objects. Comments start with //, # or /* */.