PHP is a server-side scripting language used to build dynamic web applications. It allows developers to add interactivity to websites. Some key points:
- PHP scripts are executed on the server-side and allow generation of dynamic web page content.
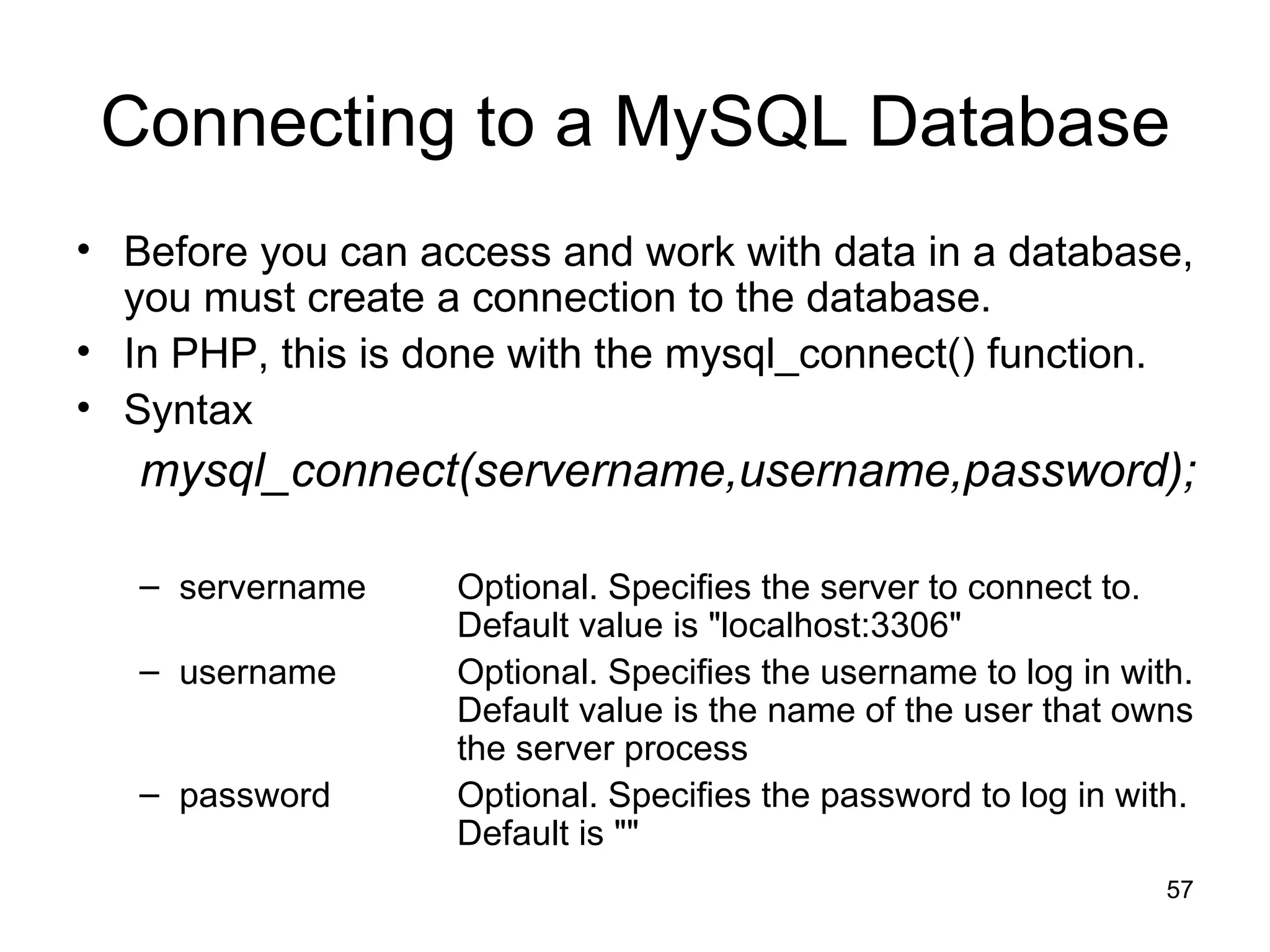
- It supports many databases and is compatible with popular web servers like Apache and IIS.
- Basic PHP syntax involves opening and closing <?php ?> tags to embed PHP code in HTML documents.
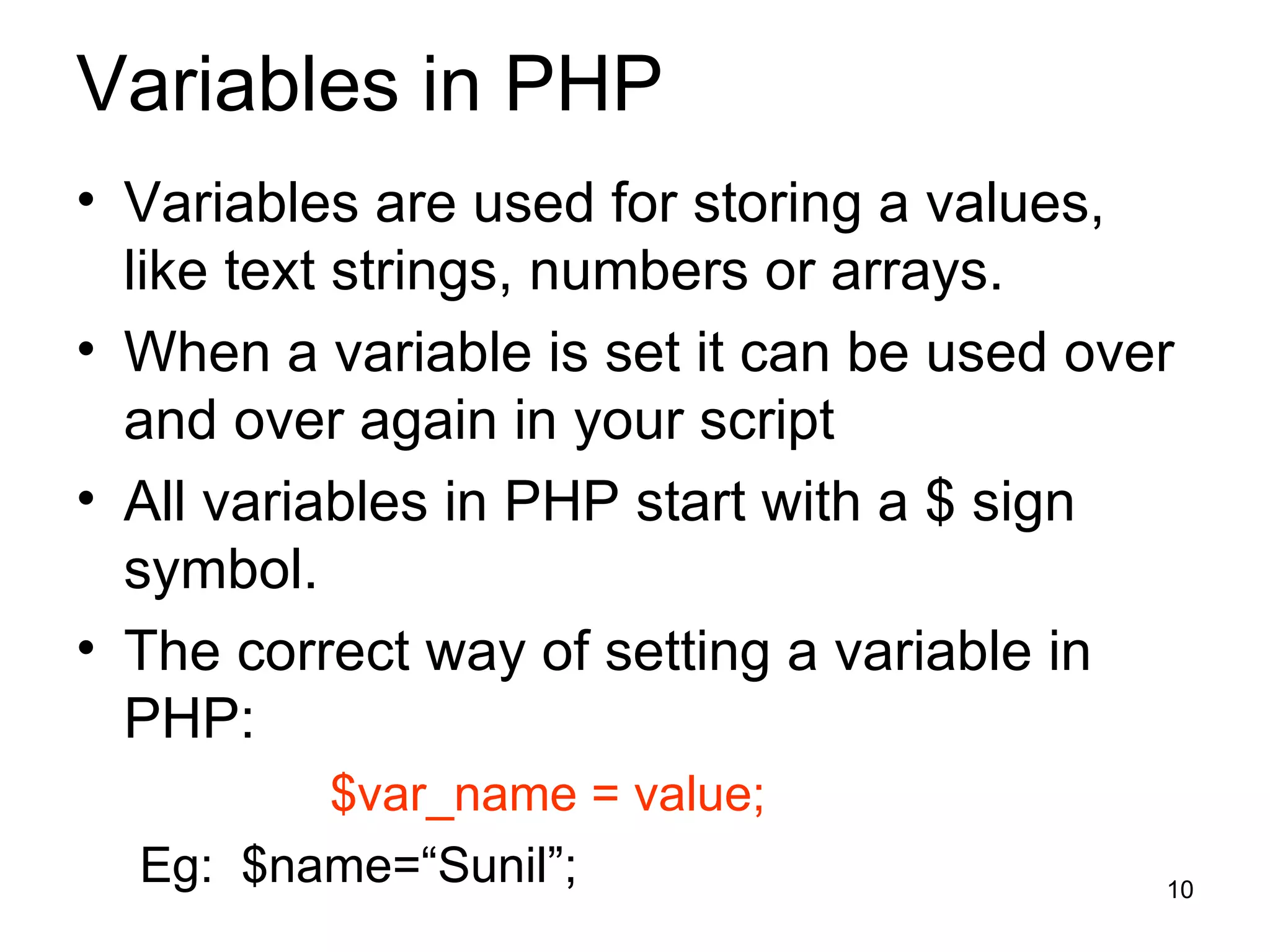
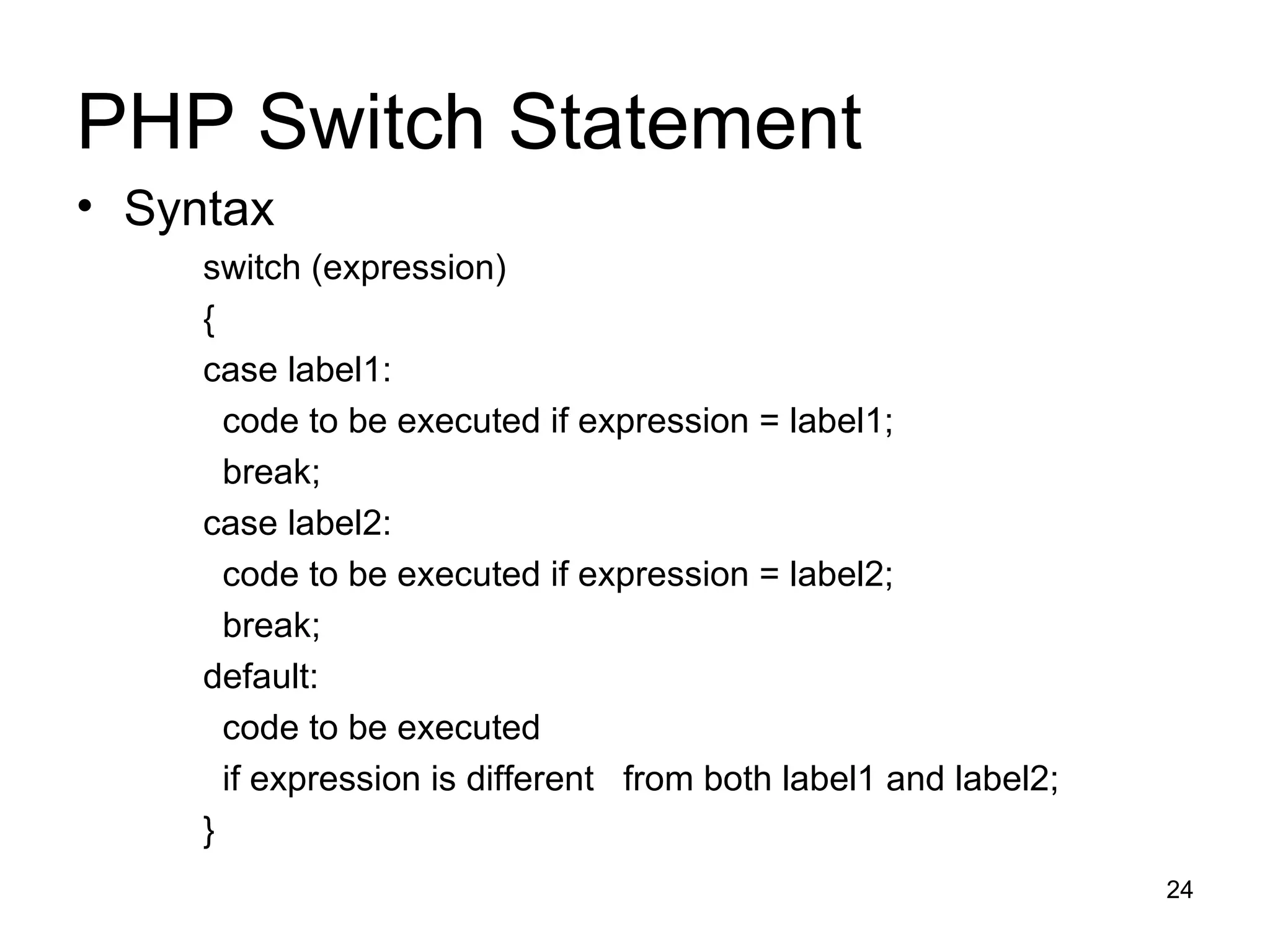
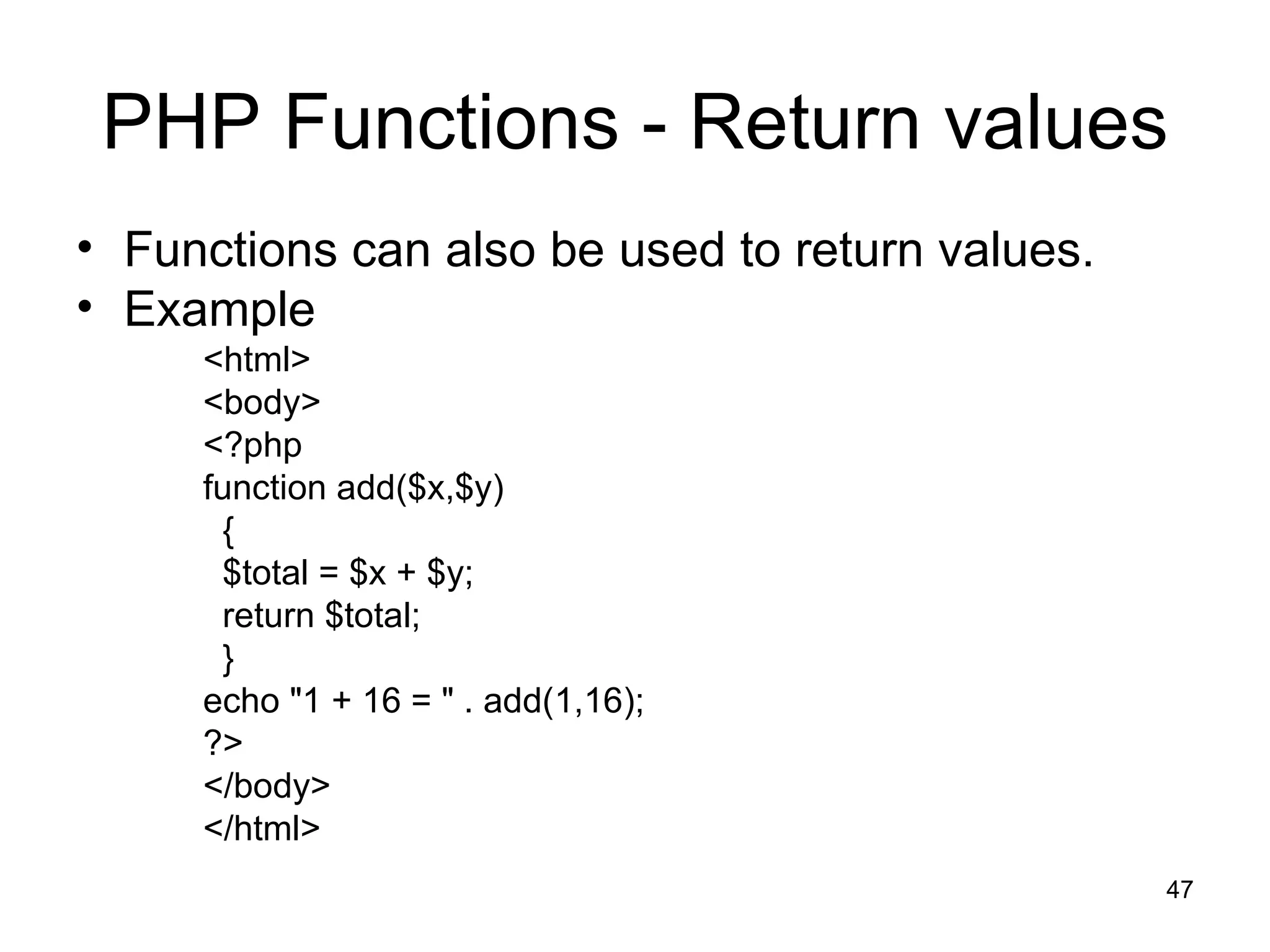
- Variables, conditional statements, loops and functions allow building complex scripts.
- PHP can retrieve and process form data submitted from HTML forms.

























![PHP Arrays : Example 1 <?php $names[0] = "Peter"; $names[1] = "Quagmire"; $names[2] = "Joe"; echo $names[1] . " and " . $names[2] . " are ". $names[0] . "'s neighbors"; ?> The code above will output: Quagmire and Joe are Peter's neighbors](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whatisphp-091225013935-phpapp02/75/What-Is-Php-28-2048.jpg)
![PHP Arrays : Example 2 <?php $names = array("Peter","Quagmire","Joe"); echo $names[1] . " and " . $names[2] . " are ". $names[0] . "'s neighbors"; ?> The code above will output: Quagmire and Joe are Peter's neighbors](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whatisphp-091225013935-phpapp02/75/What-Is-Php-29-2048.jpg)



















![Example welcome.php <html> <body> Welcome <?php echo $_POST["name"]; ?>.<br /> You are <?php echo $_POST["age"]; ?> years old. </body> </html>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whatisphp-091225013935-phpapp02/75/What-Is-Php-50-2048.jpg)

![Example <form action="welcome.php" method="get"> Name: <input type="text" name="name" /> Age: <input type="text" name="age" /> <input type="submit" /> </form> Welcome.php Welcome <?php echo $_GET["name"]; ?>.<br /> You are <?php echo $_GET["age"]; ?> years old!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whatisphp-091225013935-phpapp02/75/What-Is-Php-52-2048.jpg)


![Example <form action="welcome.php" method="post"> Enter your name: <input type="text" name="name" /> Enter your age: <input type="text" name="age" /> <input type="submit" /> </form> Welcome.php Welcome <?php echo $_POST["name"]; ?>.<br /> You are <?php echo $_POST["age"]; ?> years old!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whatisphp-091225013935-phpapp02/75/What-Is-Php-55-2048.jpg)







![Insert Data From a Form Into a Database Example : insert.php <?php $con = mysql_connect("localhost","peter","abc123"); if (!$con) { die('Could not connect: ' . mysql_error()); } mysql_select_db("my_db", $con); $sql="INSERT INTO person (FirstName, LastName, Age) VALUES ('$_POST[firstname]','$_POST[lastname]','$_POST[age]')"; if (!mysql_query($sql,$con)) { die('Error: ' . mysql_error()); } echo "1 record added"; mysql_close($con) ?>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whatisphp-091225013935-phpapp02/75/What-Is-Php-64-2048.jpg)