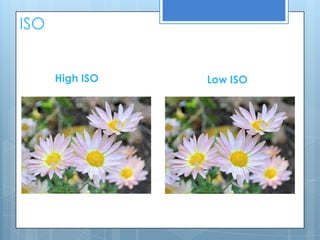
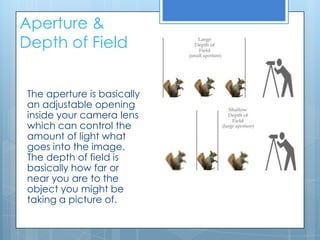
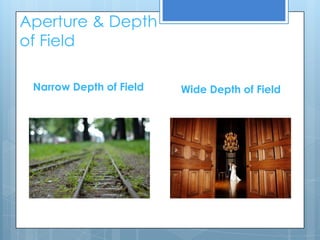
This document provides an overview of key photographic terminology used in photography and photographic practice. It defines shutter speed as the duration that the camera shutter is open, exposing the image sensor to light. It also explains ISO as a measure of the camera sensor's light sensitivity and how it affects image grain. Aperture and depth of field are discussed, with aperture controlling the amount of light entering through the lens and depth of field referring to the distance between the nearest and farthest objects that appear acceptably sharp. The document also touches on manual and automatic exposure settings, color balance, white balance, composition techniques like the rule of thirds, analogous and complementary colors, and macro photography.