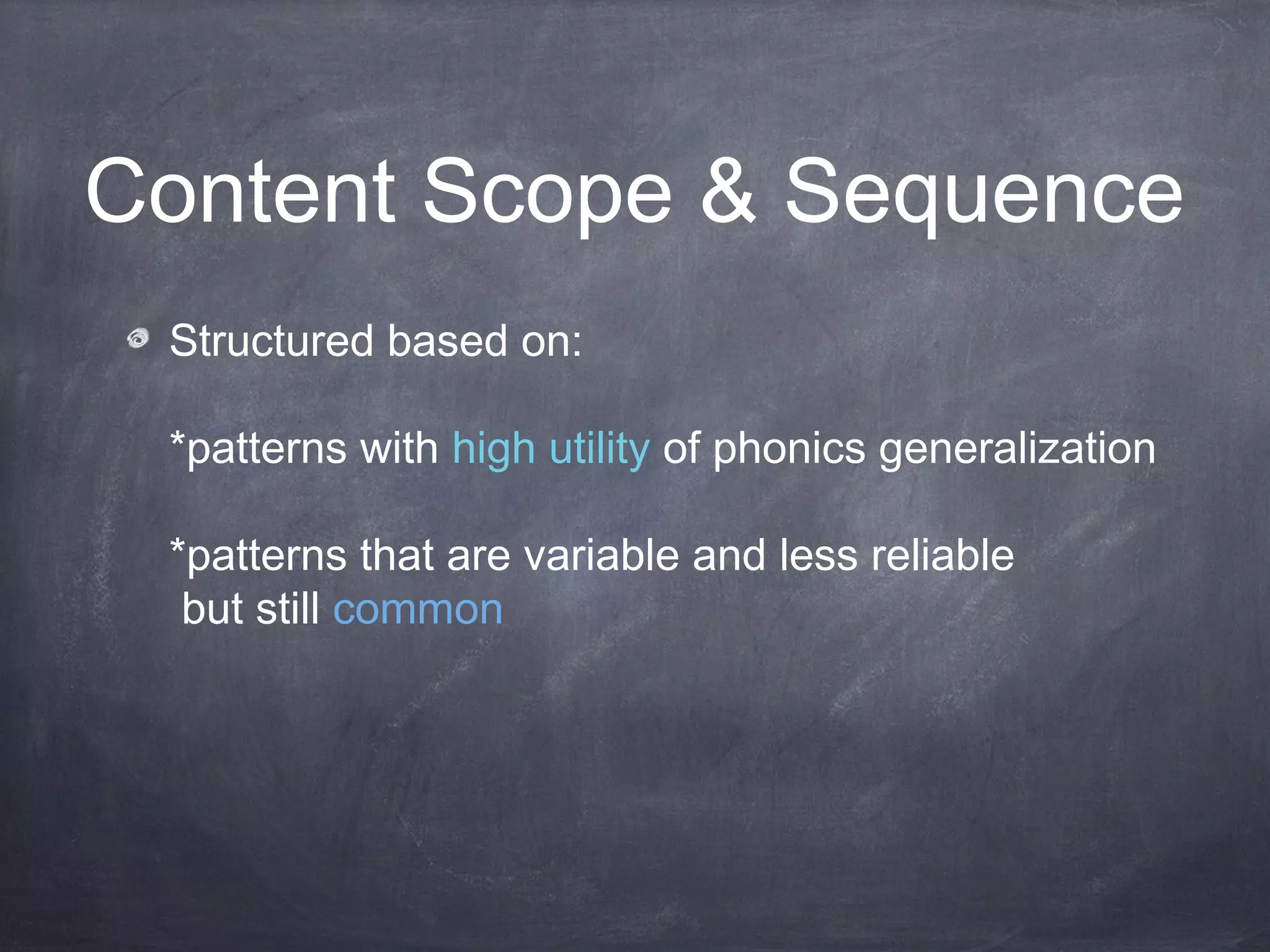
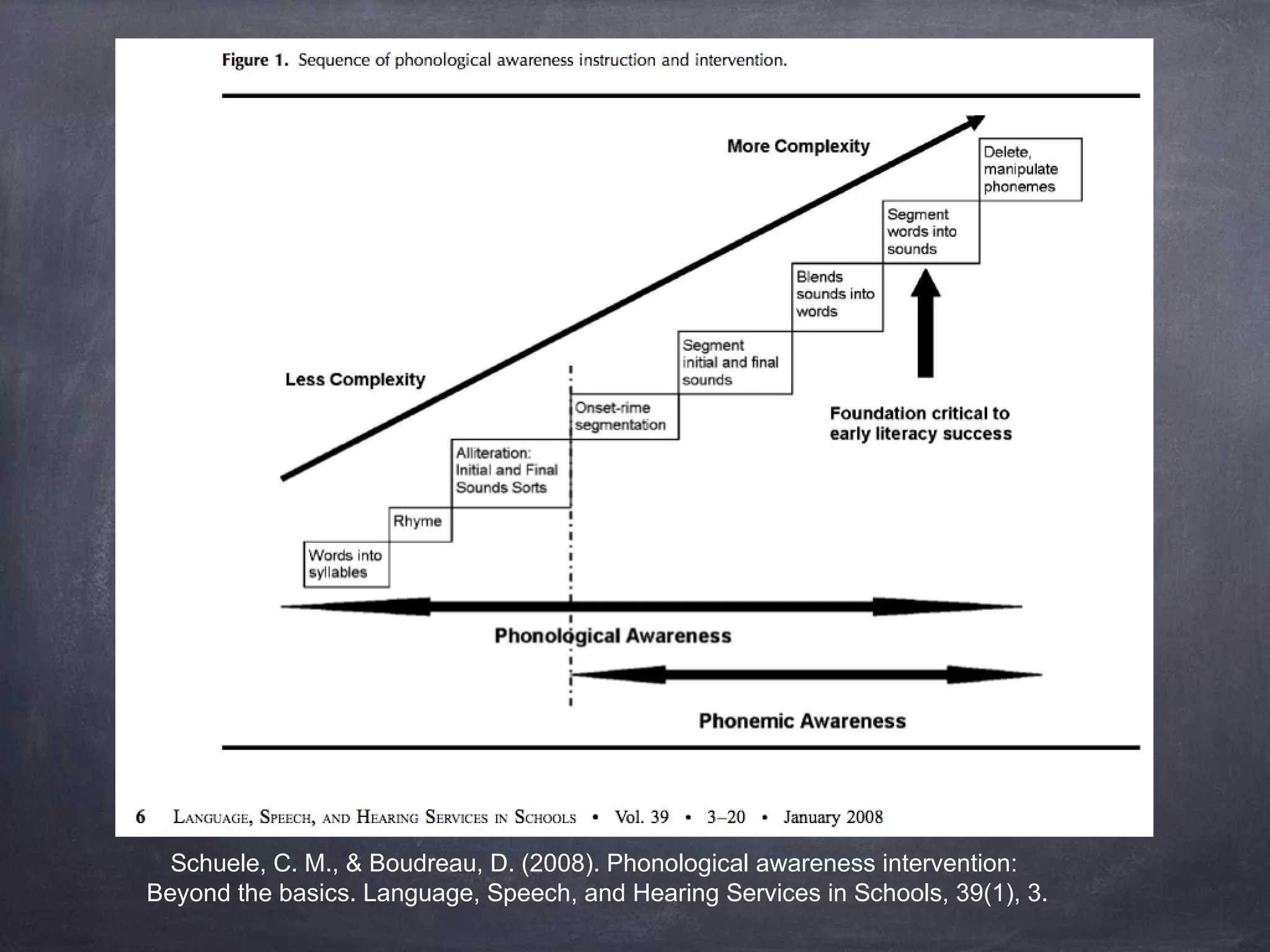
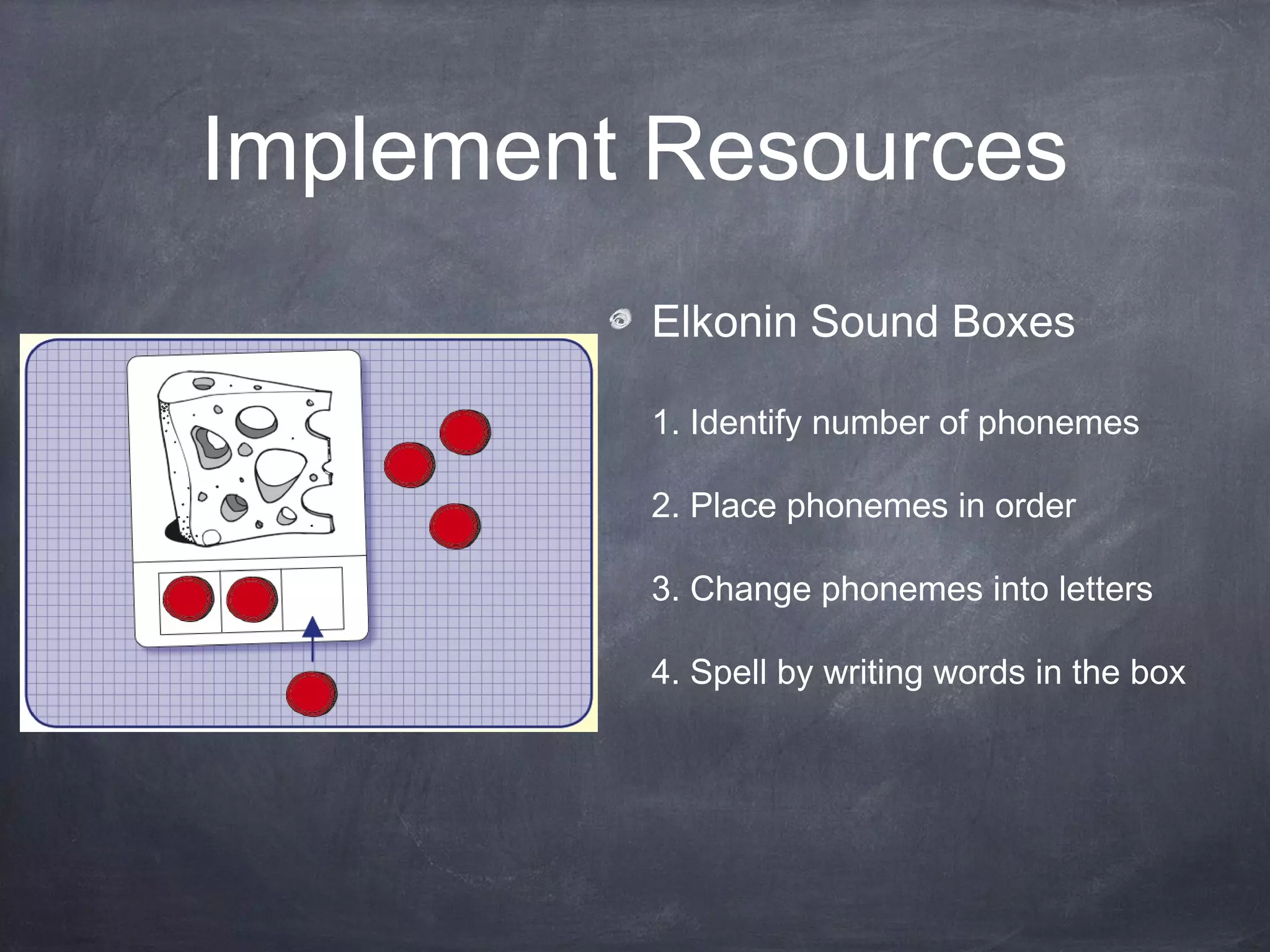
This curriculum aims to teach 4th-5th grade EFL students phonics skills like r-controlled vowels and vowel pairs over 5 weekly lessons. The objectives are for students to read words with these phonics patterns correctly on an individual assessment. The curriculum follows a synthetic phonics approach and uses resources like Elkonin sound boxes, videos, and readers. Assessment involves a word reading test to evaluate decoding of targeted phonics patterns.





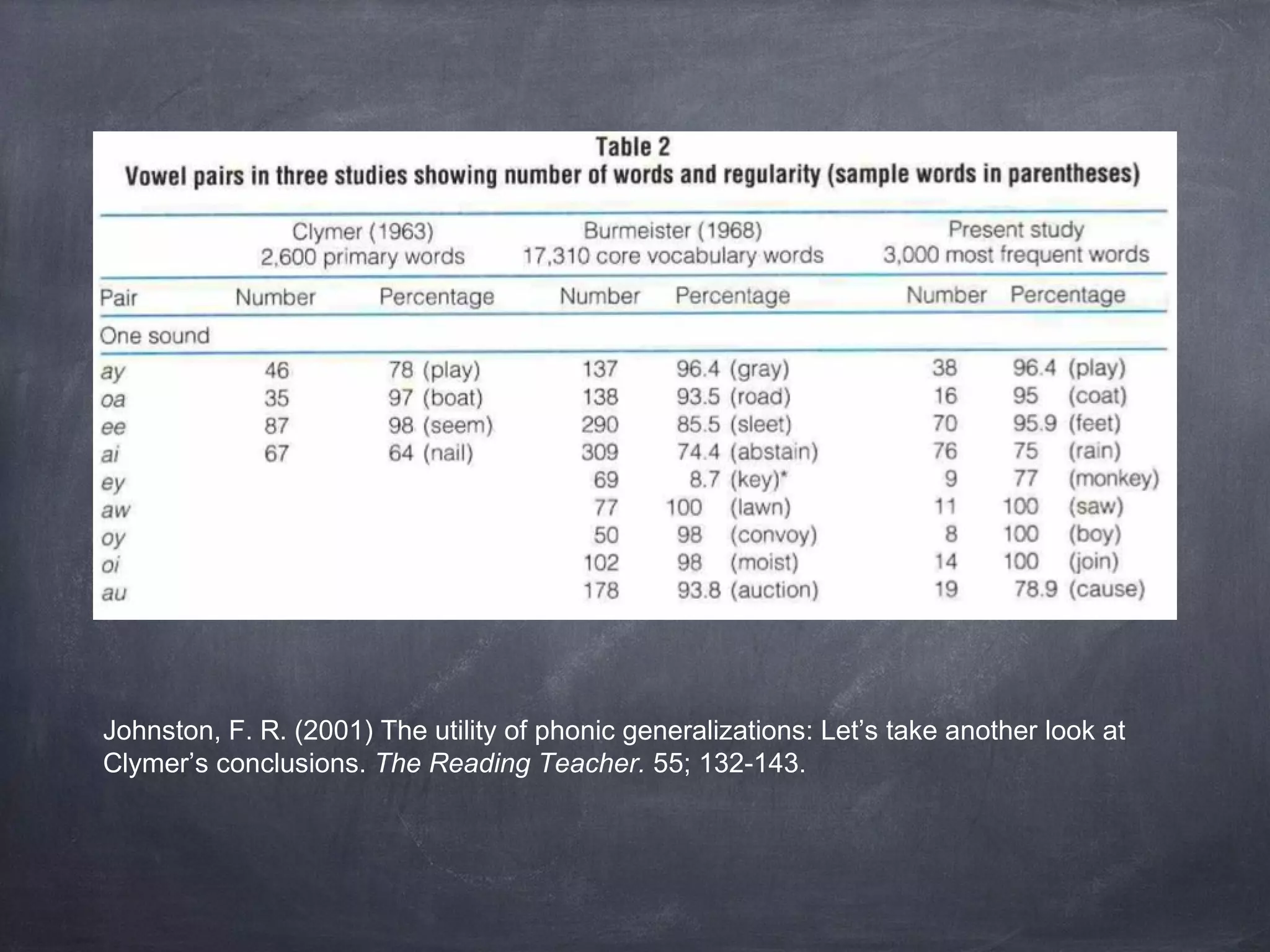
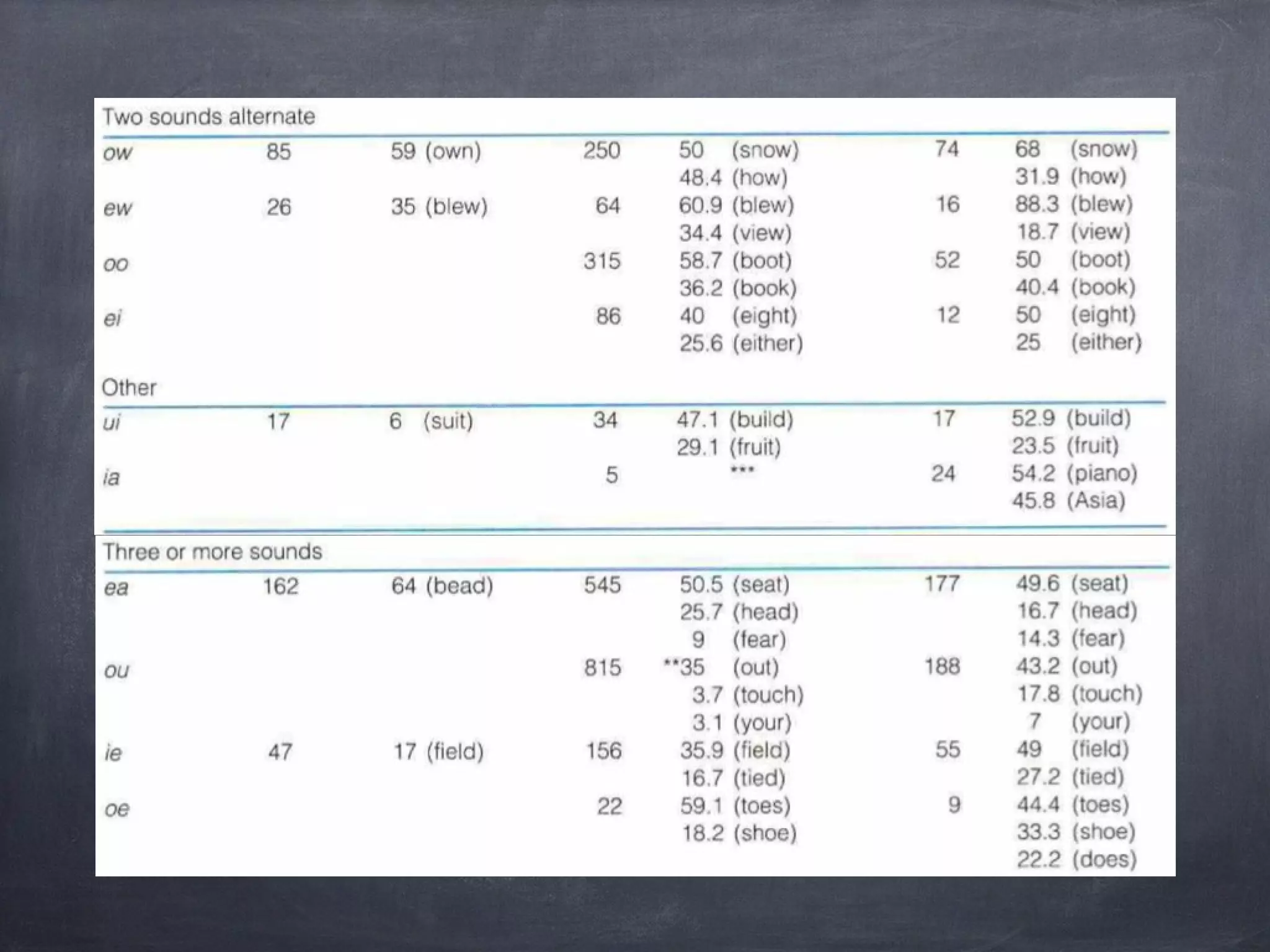
![What rules to teach?
Clymer, T. (1963). The Utility of Phonic Generalizations in the Primary Grades [with Comment].
The Reading Teacher, 16(4), 252-258.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalproject-140311110754-phpapp01/75/Phonics-Based-Curriculum-Design-6-2048.jpg)