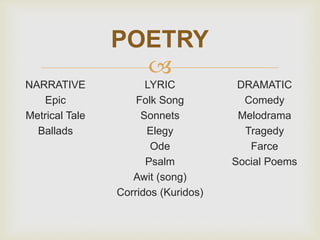
Literature is defined as any printed material found in books, magazines, or pamphlets that deals with human ideas, thoughts, and emotions, telling the story of humanity. Studying Philippine literature helps people appreciate, understand, realize, and truly love and take pride in their own culture. Some key differences between literature and history are that literature can include fictional events while history recounts things that actually occurred. Pre-Spanish Philippine literature included forms like legends, folk tales, riddles, chants, and proverbs.