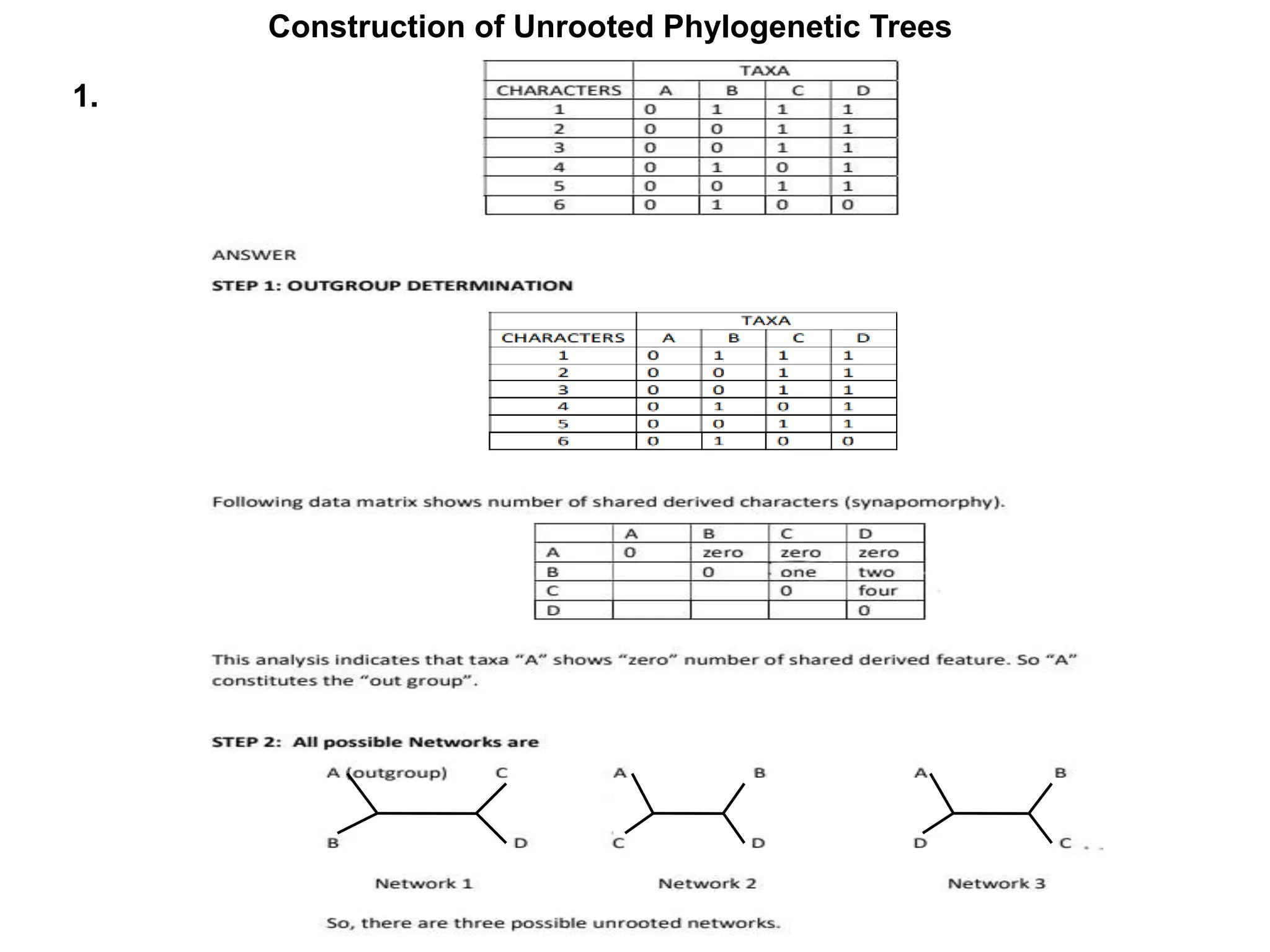
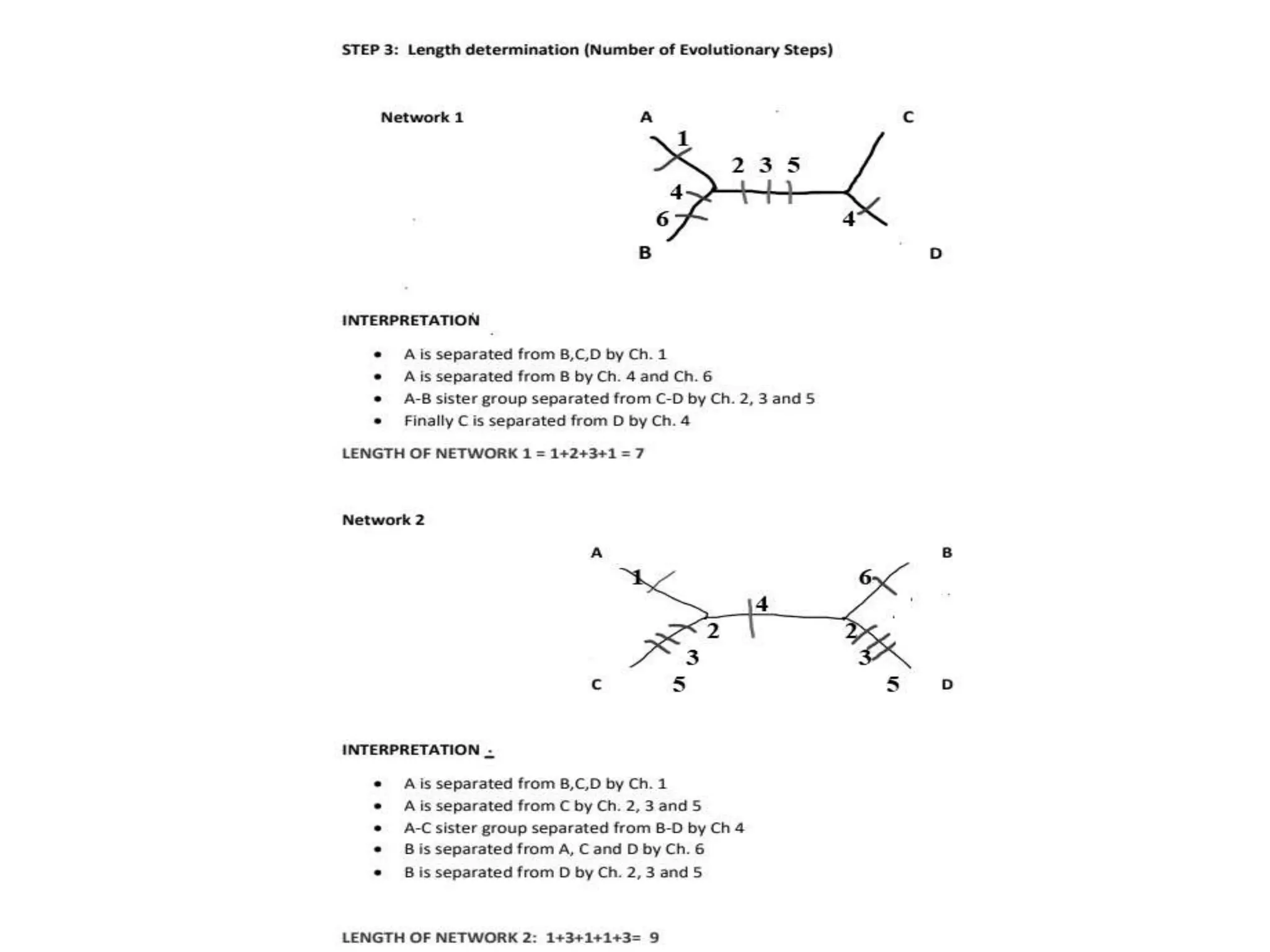
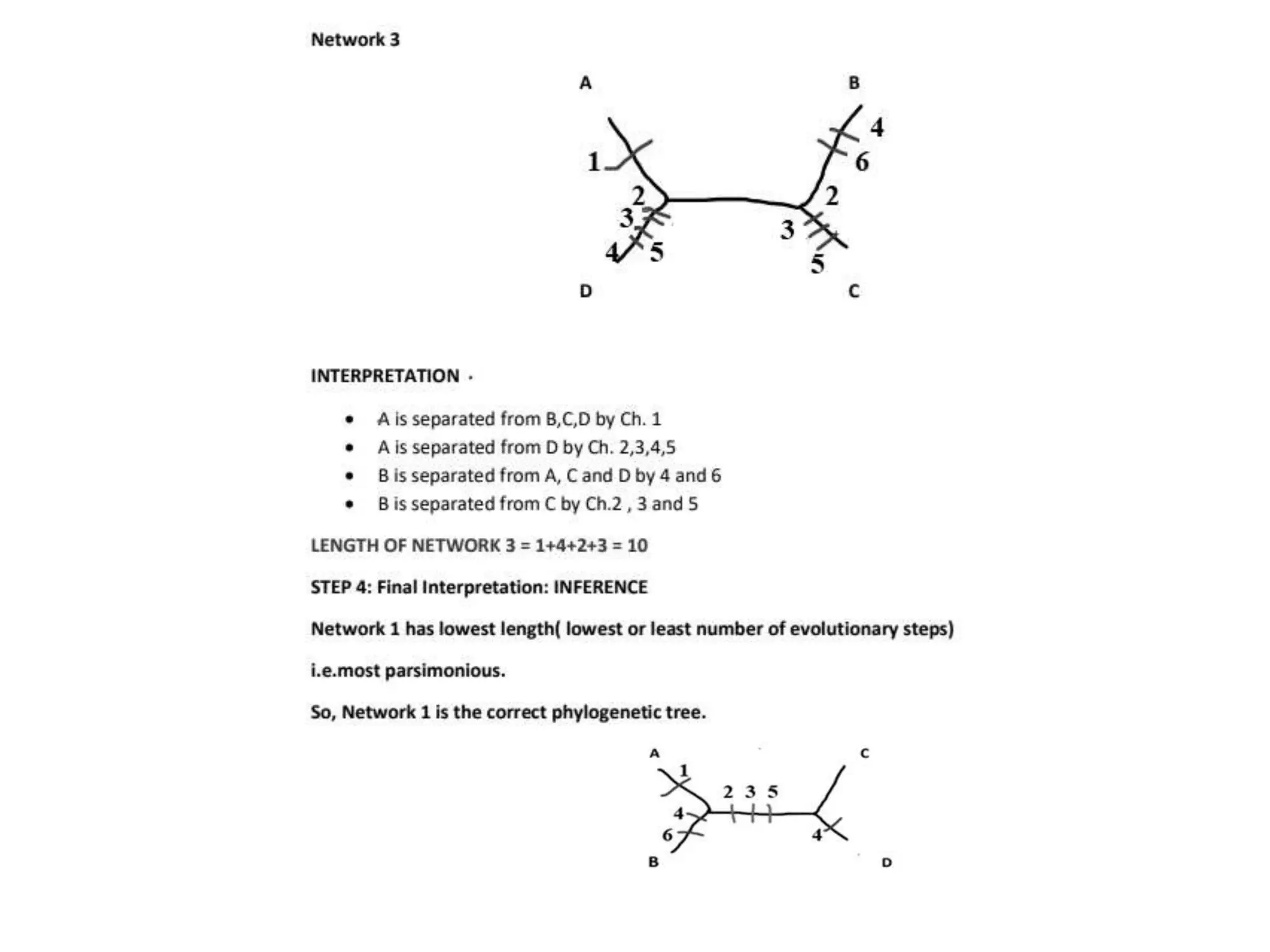
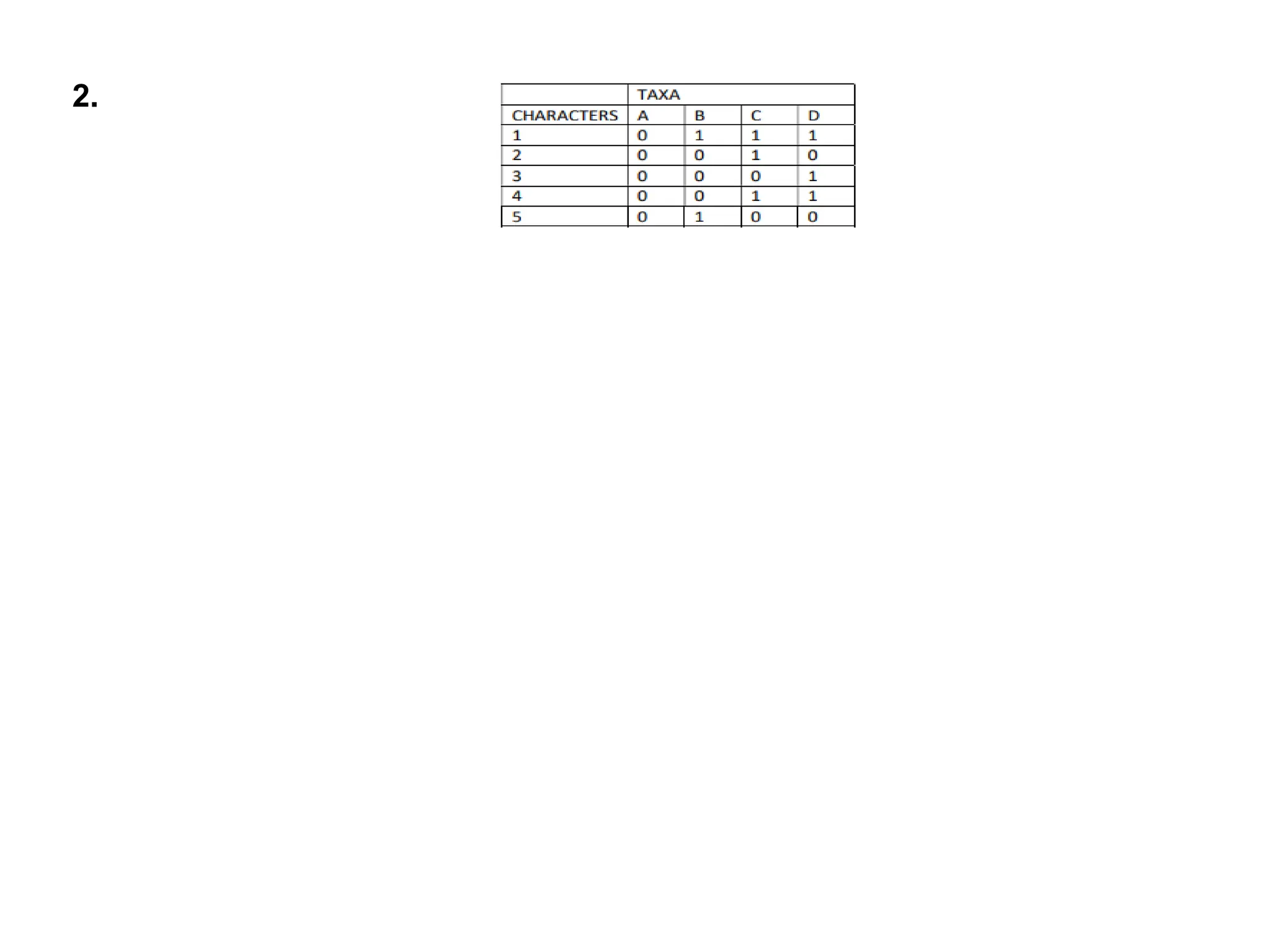
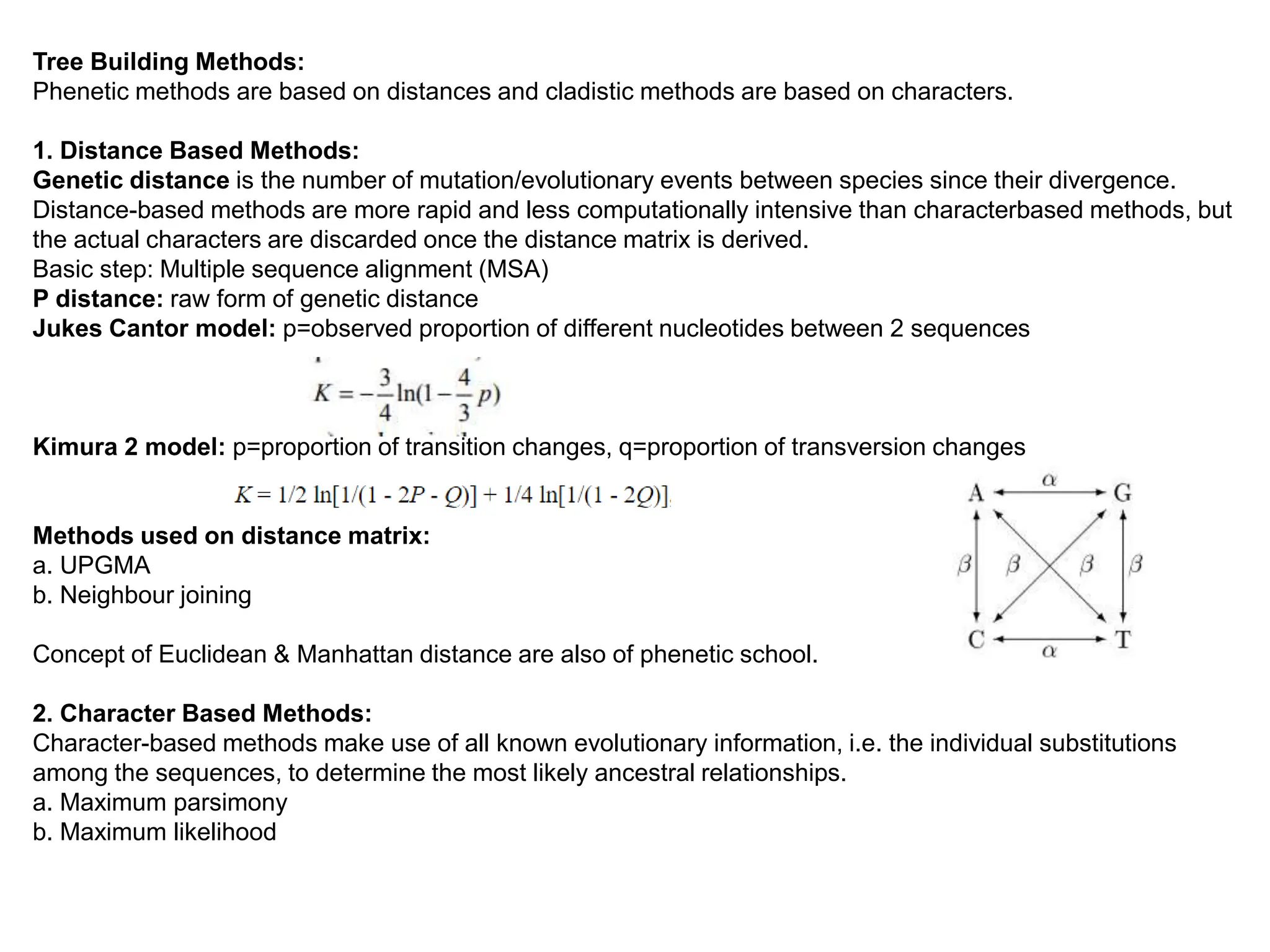
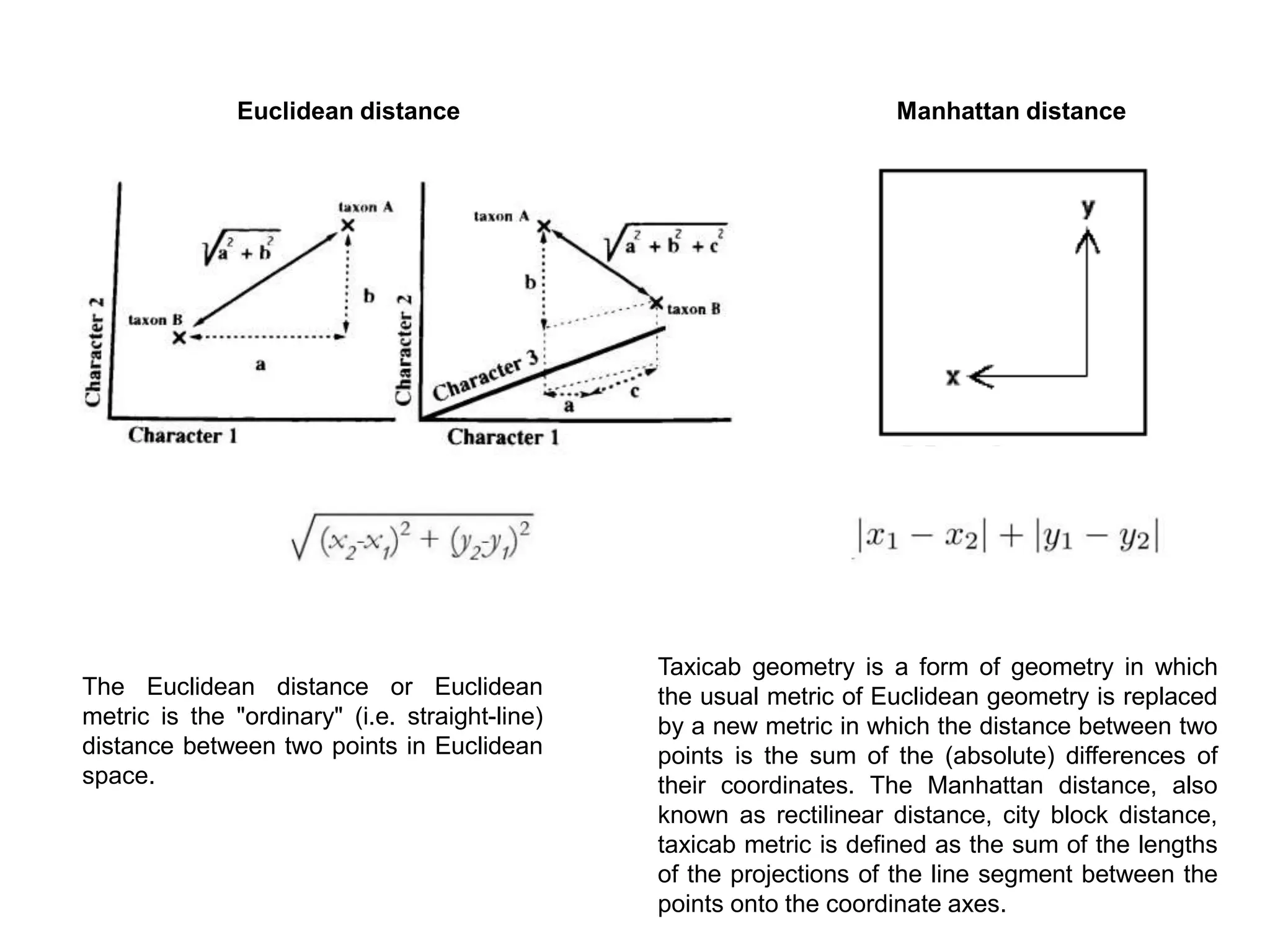
The document describes methods for constructing unrooted phylogenetic trees, distinguishing between phenetic methods based on genetic distances and cladistic methods using character data. Distance-based methods are quicker and less computationally intensive but discard character-level information, while character-based methods leverage all available evolutionary information for more accurate ancestral relationships. Key topics include distance metrics like Euclidean and Manhattan distances, and methods such as UPGMA, neighbor joining, maximum parsimony, and maximum likelihood.