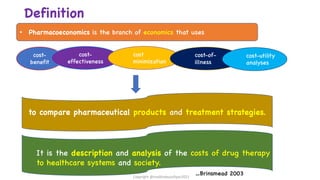
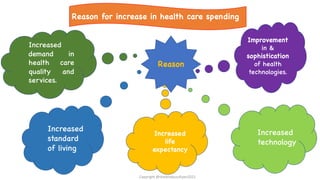
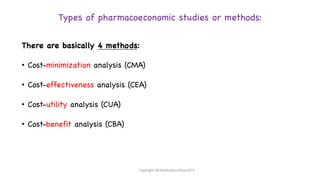
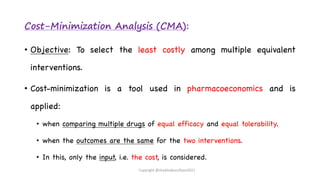
The document discusses pharmacoeconomics, its definitions, aims, and its role in evaluating healthcare spending, drug costs, and health outcomes. It outlines various methods of pharmacoeconomic evaluation including cost-minimization, cost-effectiveness, cost-utility, and cost-benefit analysis, emphasizing the importance of these analyses in clinical decision-making and healthcare policy. The document also highlights challenges in drug pricing and the impact of regulations on pharmaceutical costs, particularly in developing countries.