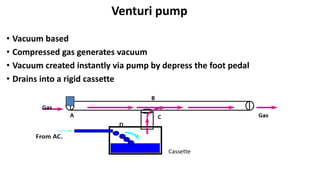
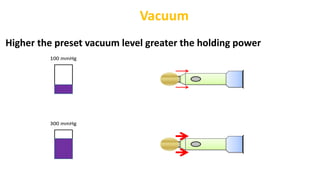
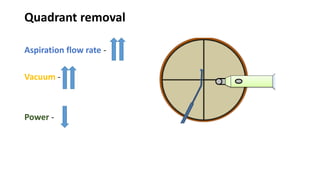
This document discusses the fundamentals of phacodynamics, which refers to the interrelationship between the various functions of a phacoemulsification machine. It provides a history of phacoemulsification and defines the key components and parameters of phaco machines. These include ultrasound energy, fluidics systems for irrigation and aspiration, and parameters like power, vacuum, and aspiration flow rate. The document explains how these components and parameters work together to perform different surgical techniques like sculpting, chopping, and quadrant removal during cataract surgery.