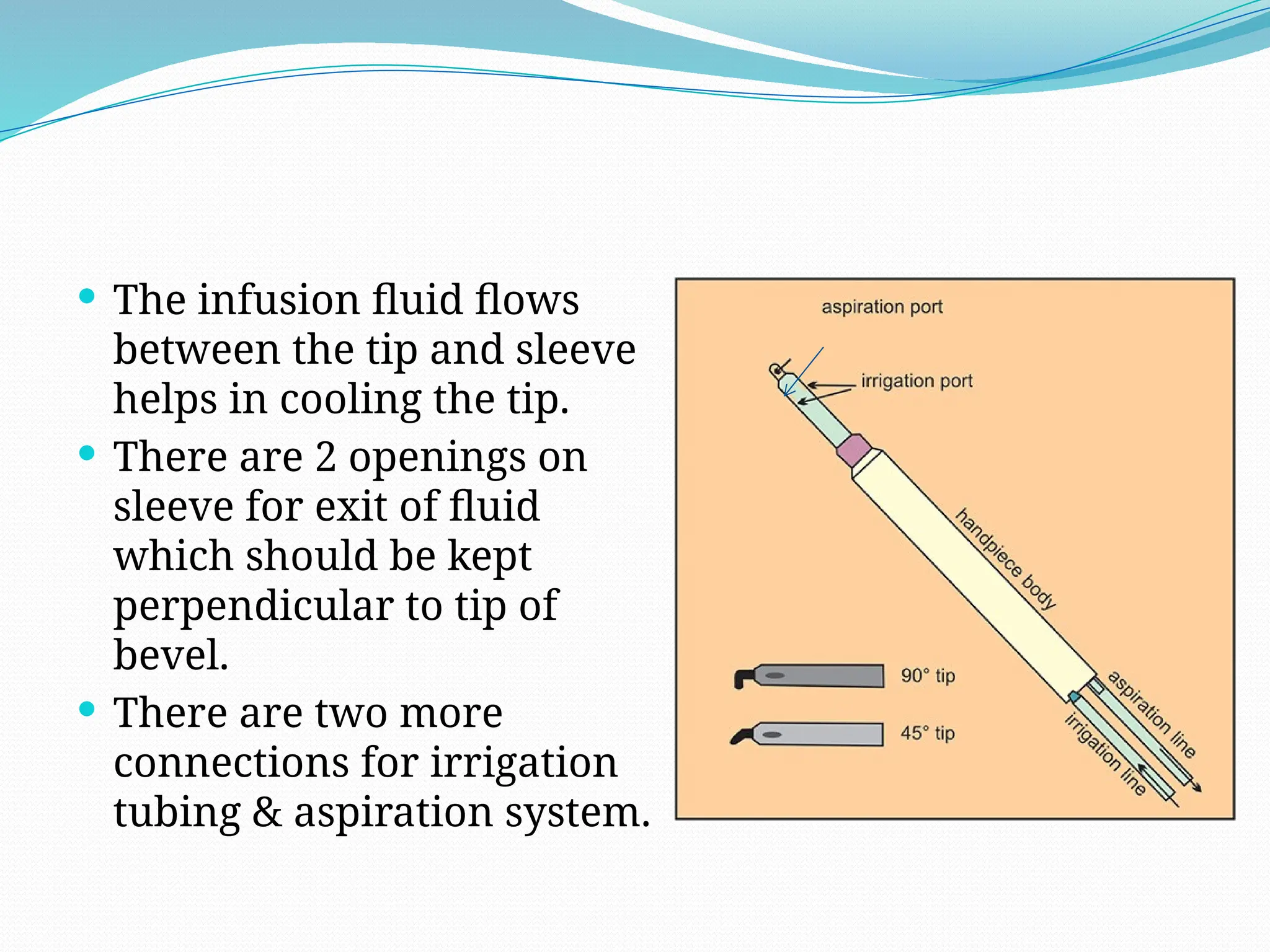
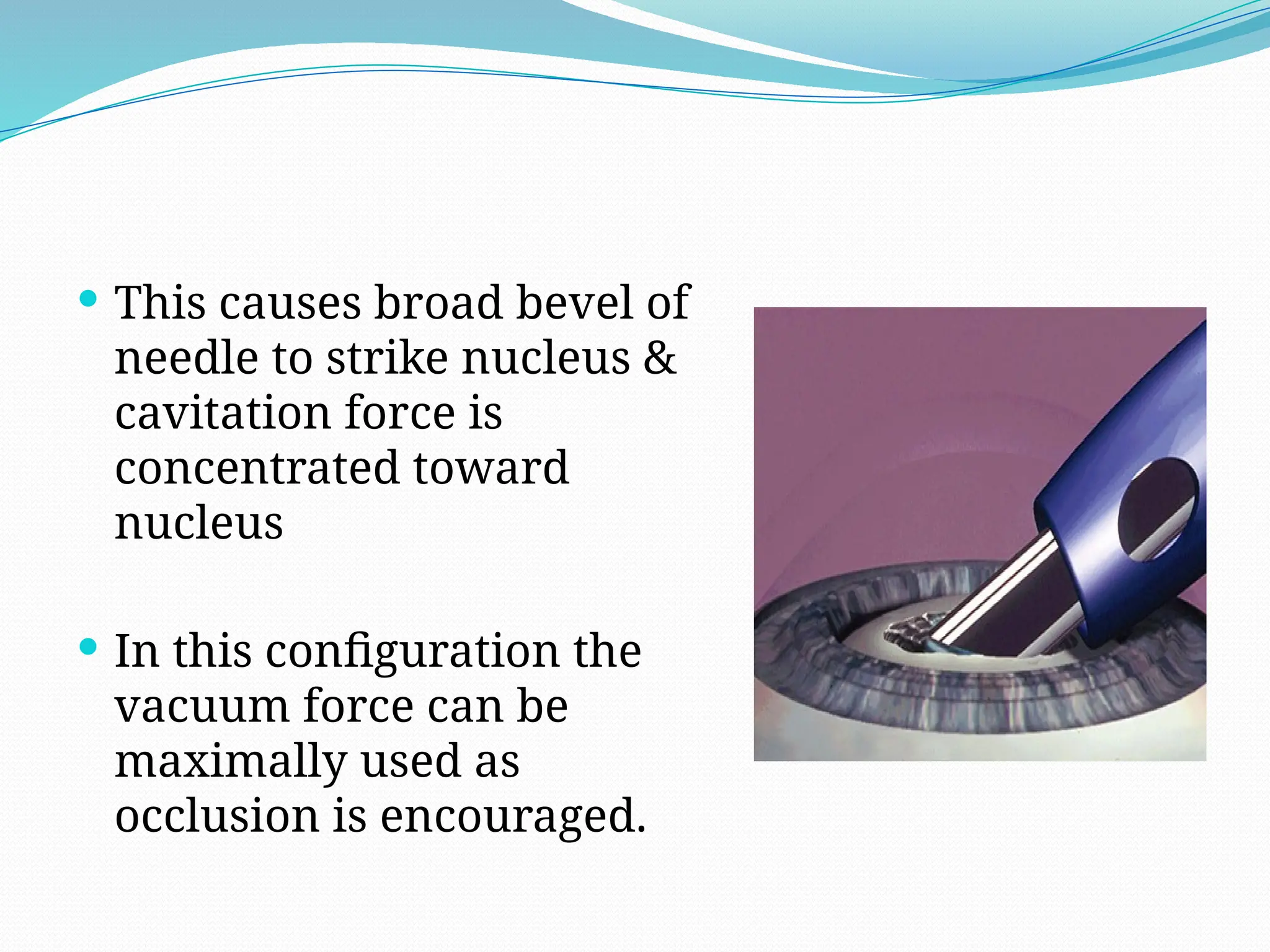
Phacoemulsification is a cataract surgery technique developed by Dr. Charles Kelman in 1962, utilizing ultrasound energy to emulsify and aspirate lens materials through smaller incisions, thereby reducing complications and improving recovery times. The surgery involves complex machinery including a console, handpiece, and foot pedal to control various parameters, with functions based on fluidics and the dynamics of power delivery. Key steps in the procedure include eye marking, incision creation, capsulorrhexis, hydrodissection, nucleus disassembly, and cortical aspiration to ensure a thorough removal of lens material.