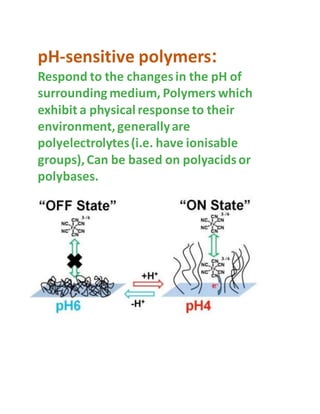
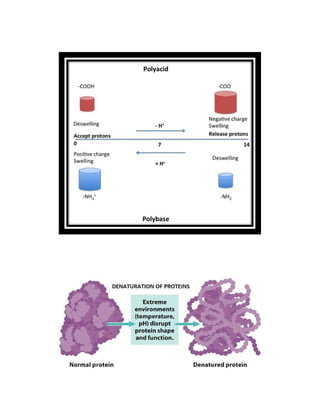
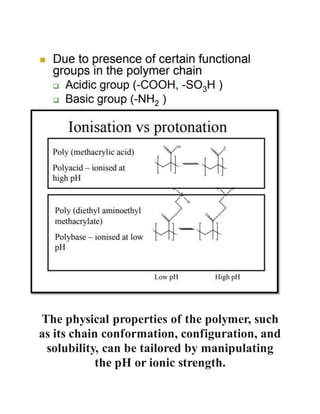
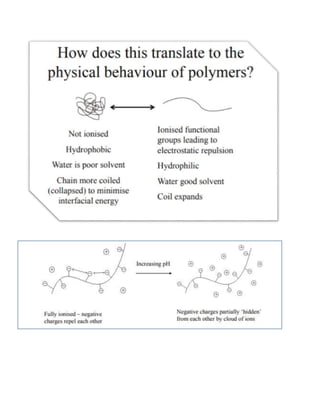
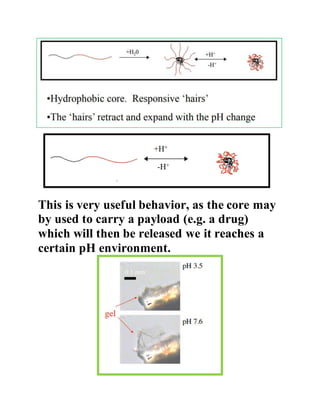
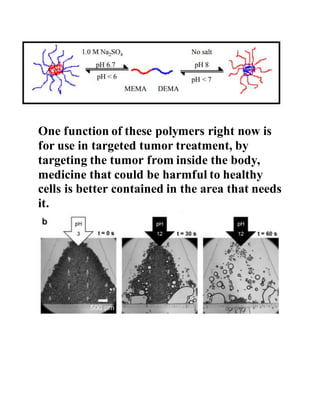
pH-sensitive polymers are polymers that change their physical properties in response to changes in pH. They include polyelectrolytes that have ionizable groups that become charged or uncharged depending on the pH. The properties that change include chain conformation, configuration, and solubility. This makes pH-sensitive polymers useful for applications like targeted drug delivery where a drug core can be released when the polymer reaches a certain pH. Examples of uses include insulin delivery systems and tumor treatment by targeting medicine specifically to tumor sites. Living polymerization is often used to control the molecular weight of these polymers.