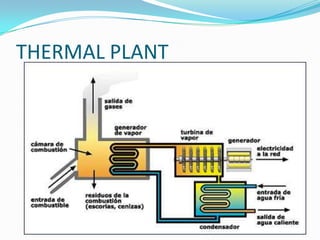
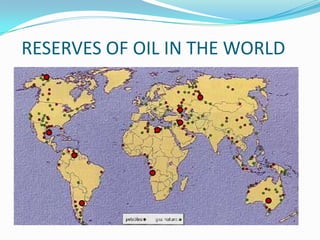
The document discusses oil, including its formation, composition, transformation into energy, and global reserves. It is formed from the remains of organisms over millions of years underground without oxygen. It replaced coal as a major energy source in the 20th century and can be refined into fuels like gasoline and diesel. The document outlines the process of extracting oil, transporting it to refineries, and generating energy by burning it to heat water and power turbines at thermal power plants.