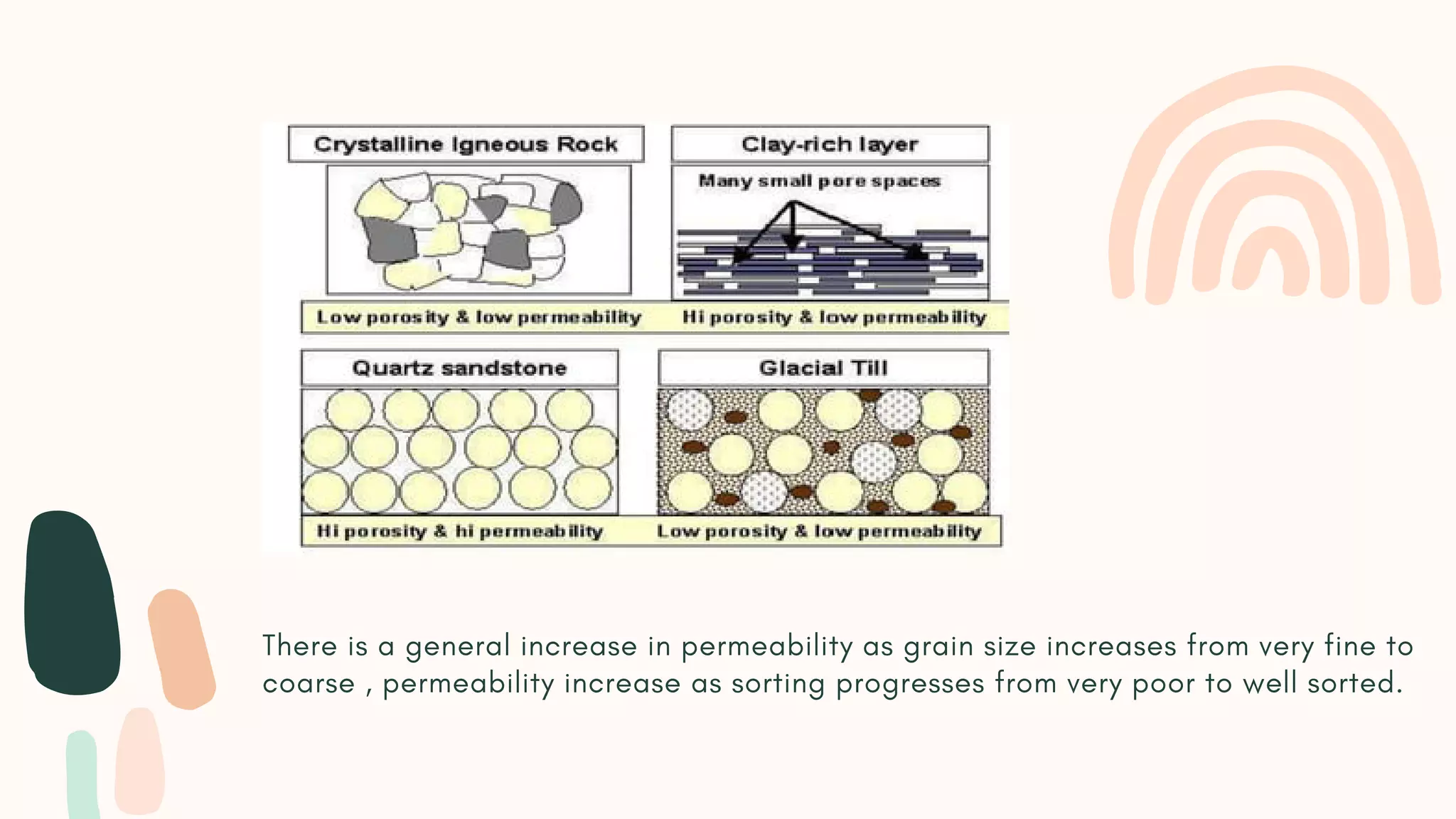
Permeability is a measure of how easily a rock allows fluid to pass through it. The Navier-Stokes equation governs fluid flow through rocks, which is assumed to be laminar. Darcy's law provides an empirical formula to calculate permeability based on factors like flow rate, pressure differences, fluid viscosity, sample length and area. There are three types of permeability: absolute, effective, and relative. Absolute permeability depends on the rock properties alone, effective permeability also considers other fluid phases present, and relative permeability is the ratio of effective to absolute permeability. Permeability is affected by pore size, grain size, shape, packing and other textural properties of the rock.