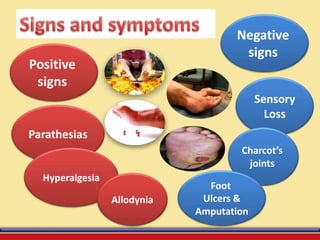
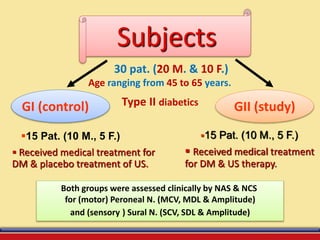
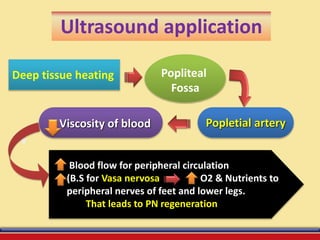
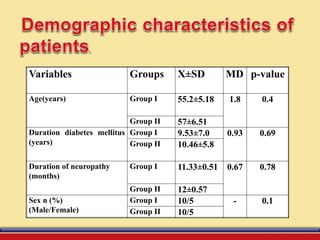
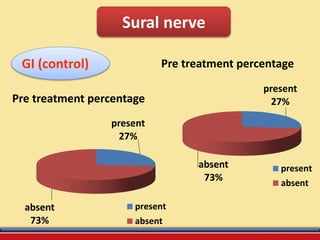
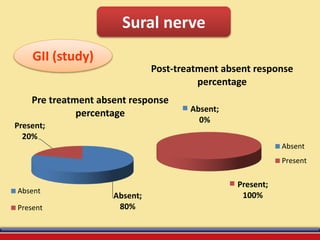
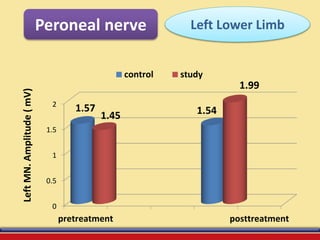
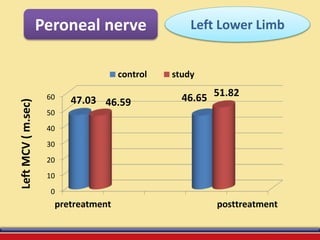
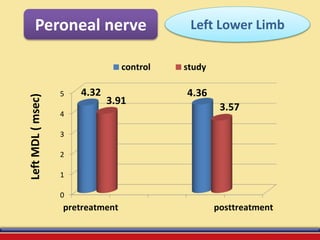
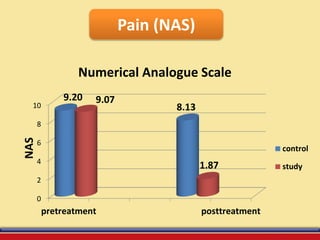
The document discusses the efficacy of ultrasound therapy for treating diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN), a common complication associated with diabetes affecting a significant portion of the population. It highlights the methodology and results of a study comparing standard medical treatment with ultrasound therapy, finding that the latter shows promise as a safe and cost-effective option for improving nerve conduction and overall patient outcomes. The findings suggest that ultrasound therapy might help alleviate symptoms and address the underlying pathophysiology of DPN.