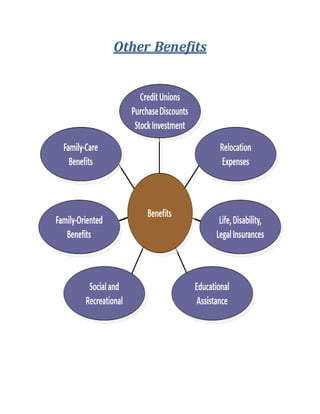
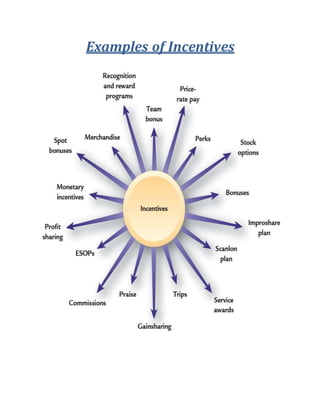
The document discusses performance appraisal and performance-linked compensation (PLC) as vital processes in human resource management that evaluate employee performance and link pay to that performance. PLC is designed to motivate employees, reward high performers, and optimize organizational productivity, while also presenting challenges such as potential demotivation for those not meeting performance criteria. The document outlines advantages and disadvantages of PLC, key criteria for effective performance compensation, and various incentive plans used to enhance employee engagement and productivity.