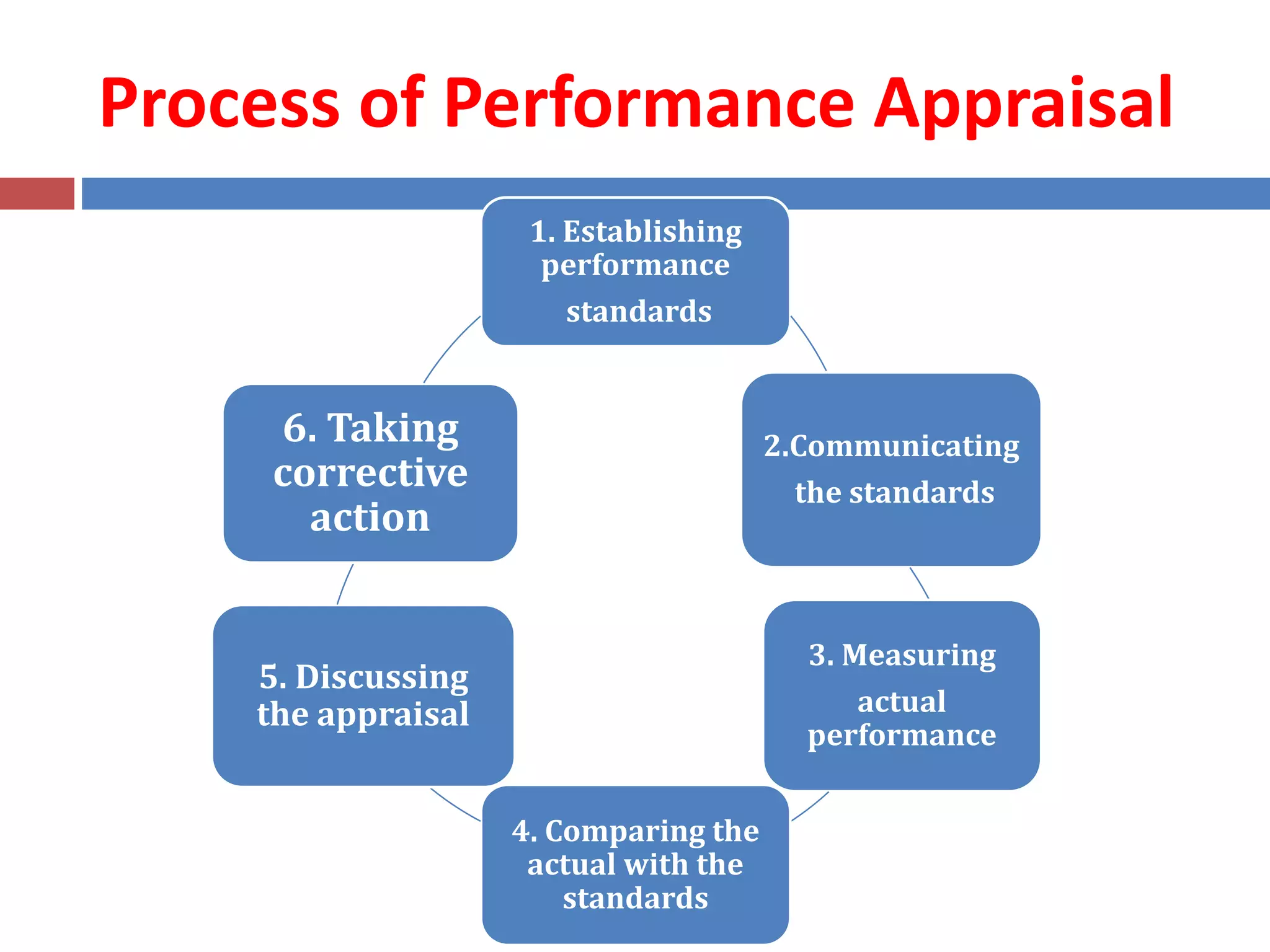
The document provides a comprehensive overview of performance appraisal, highlighting its evolution, definitions, objectives, methods, and processes. Performance appraisal is described as a systematic evaluation of employee performance against defined benchmarks to inform decisions on promotions, training needs, and overall employee development. Various traditional and modern appraisal methods are discussed, including graphic rating scales, 360-degree appraisal, and behaviorally anchored rating scales (BARS), each with its own advantages and limitations.