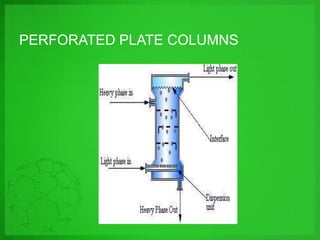
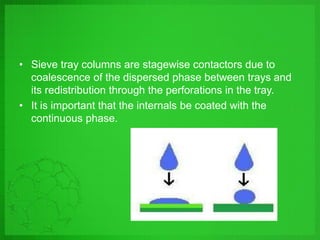
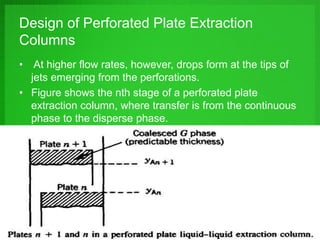
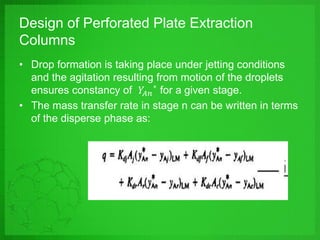
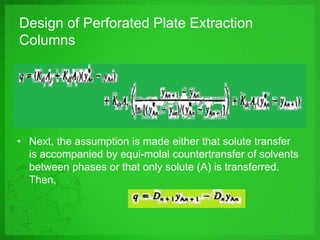
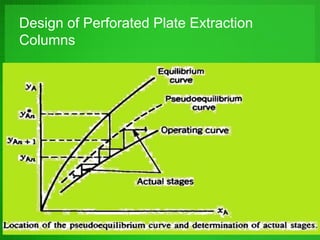
Perforated plate columns are used for liquid-liquid extraction. They consist of several perforated plates along with downcomers or upcomers for the continuous phase. Mass transfer occurs as the dispersed phase forms droplets on the plates and moves countercurrently between stages. Engineers can design perforated plate columns using rate equations to model mass transfer and locate a pseudoequilibrium curve, which is then used with an operating line to determine the required number of stages. The design procedure involves iteratively guessing composition values to calculate flow rates and ensure they match at equilibrium.