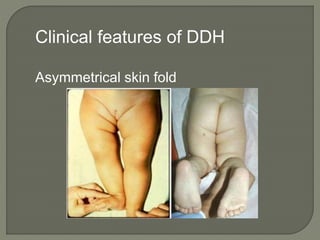
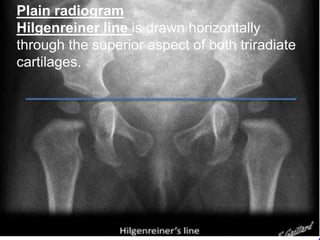
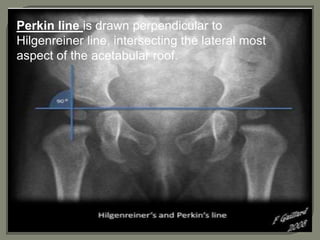
This document discusses radiological imaging of pediatric hip conditions. It begins by defining developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH) as abnormal development of the ball and socket hip joint. Risk factors, clinical features, and imaging findings for DDH are described. Plain radiographs and ultrasound are the main imaging modalities used to evaluate DDH. Hip septic arthritis is also covered, with pathogenesis, clinical presentation, and imaging discussed to differentiate it from transient synovitis. MRI is useful to detect bone marrow signal changes and enhancement patterns that can distinguish between pyogenic and tuberculous septic arthritis.
![Radiological Imaging
of
Pediatric Hip
Dr Girish G [PG]
Moderator : Dr Madan Mohan [MD radiology]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/newmicrosoftofficepowerpointpresentation3-200119134144/75/Pediatric-hip-radiology-1-2048.jpg)






![Imaging Findings
Plain radiogram : Gold standerd
Ultrasonography : in first 2week
of life [ beast before 4-6m when
femoral head cartilaginous]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/newmicrosoftofficepowerpointpresentation3-200119134144/85/Pediatric-hip-radiology-10-320.jpg)
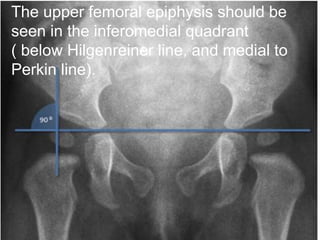
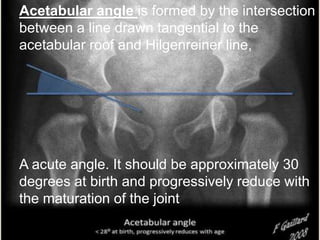
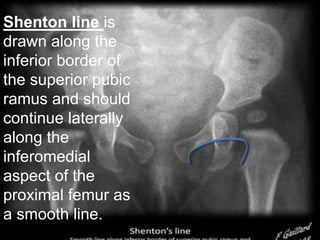
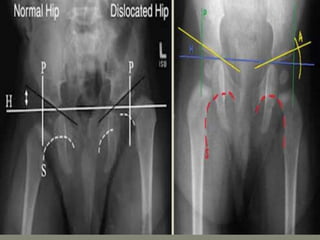
![Ultrasonography : in first 2week of life
[ beast before 4-6m when femoral head
cartilaginous]
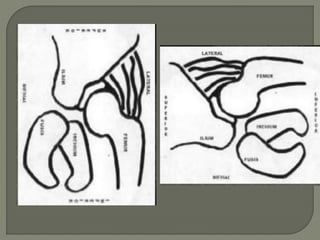
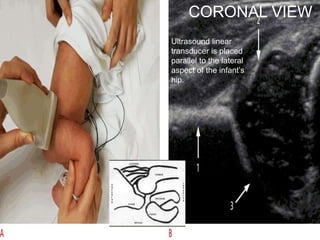
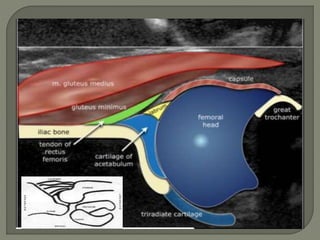
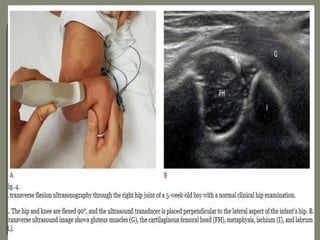
ultrasound examination be performed in
coronal view
Transverse view
7-5 mhz in < 7month
5 mhz in < 7-12 month](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/newmicrosoftofficepowerpointpresentation3-200119134144/85/Pediatric-hip-radiology-21-320.jpg)
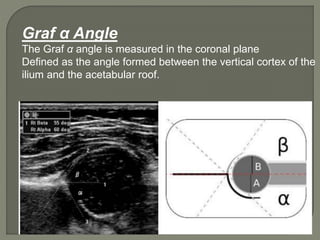
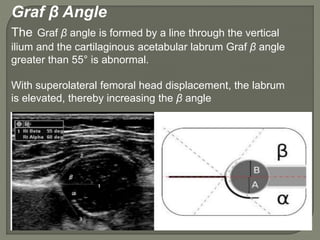
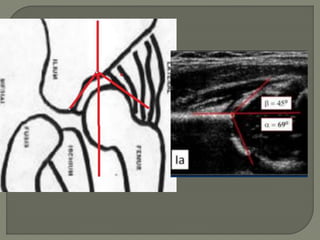
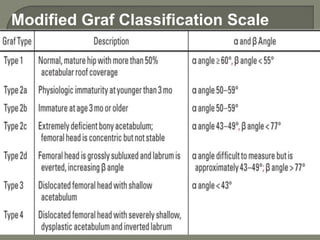
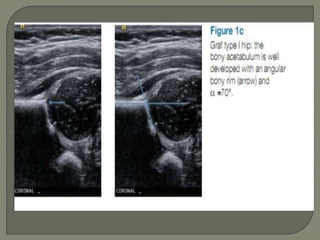
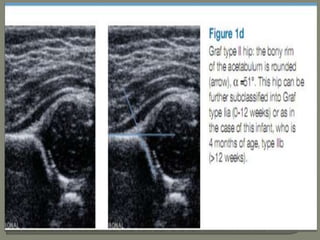
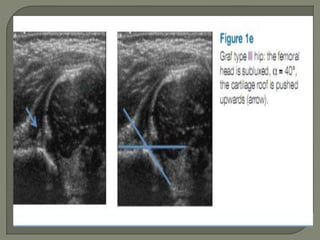
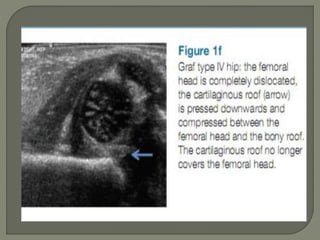
![Method depends on Age
1] Birth to 6 months :
Double napkins , Pavlik harness or hip spica cast
2] 6 months – 12 months : Closed reduction and
hip spica casts
3]12 months – 18 months : Possible closed /
possible open reduction
4]Above 18 months : Open reduction and
Acetabuloplasty
5]Above 2 years : Open reduction, acetabulplasty,
and femoral osteotomy](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/newmicrosoftofficepowerpointpresentation3-200119134144/85/Pediatric-hip-radiology-38-320.jpg)
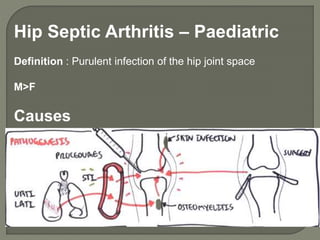

![A] In the early stage, there is an acute synovitis with a purulent
joint effusion
B] Soon the articular cartilage is attacked by bacterial and
cellular enzyme.
C] If infection is not arrested , the cartilage may be completely
destroyed
D] Sequlae include necrosis, sublaxation, dislocation and
ankylosis](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/newmicrosoftofficepowerpointpresentation3-200119134144/85/Pediatric-hip-radiology-42-320.jpg)
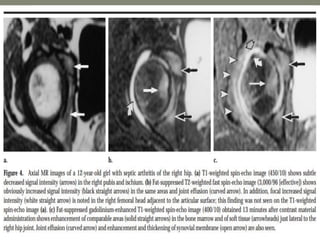
![Imaging
Plain x ray
1]Early Stage – Normal
Look for soft tissue swelling, loss of tissue planes,
widening of joint space and slight subluxation due to fluid in
joint.
2] Late stage – Narrowing and irregularity of joint space,
erosion of epiphysis or metaphysis , ostiporosis
3]Plain film findings of superimposed osteomyelitis may
develop (periosteal reaction, bone destruction, sequestrum
formation).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/newmicrosoftofficepowerpointpresentation3-200119134144/85/Pediatric-hip-radiology-43-320.jpg)
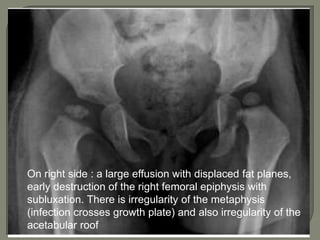
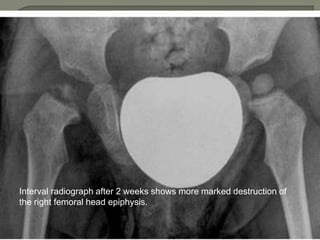
![Radionuleotide scan :
1]Localise the site of infection
2]Positive as early as 2days after onset of symptoms
3]Increased articular activity in blood flow
4] Decreased uptake in the epiphysis as result of
ischemia](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/newmicrosoftofficepowerpointpresentation3-200119134144/85/Pediatric-hip-radiology-47-320.jpg)
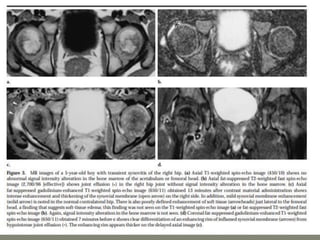
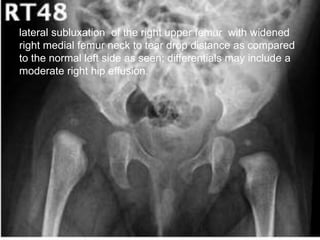
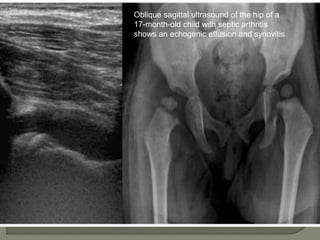
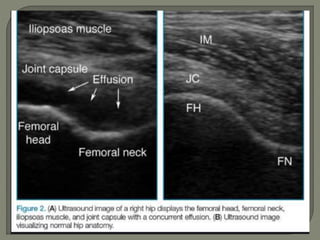
![Ultrasound
1]More reliable in revealing a joint effusion in early cases.
Widening of space between capsule and bone of > 2mm
indicates effusion.
2]Echo-free - transient synovitis
3]Positively echogenic septic arthritis](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/newmicrosoftofficepowerpointpresentation3-200119134144/85/Pediatric-hip-radiology-48-320.jpg)
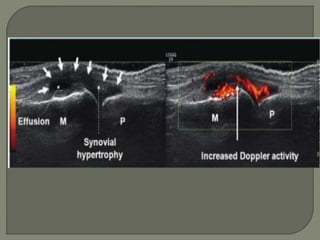
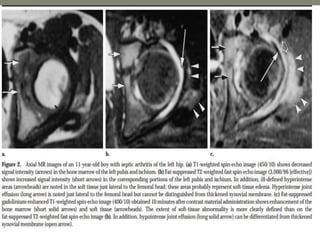
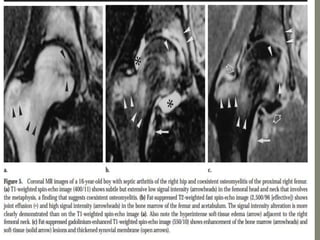
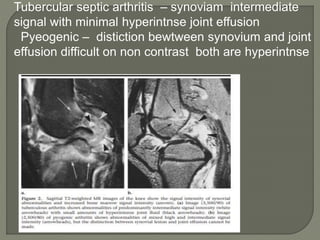
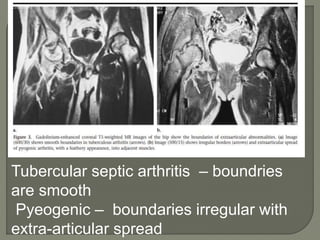
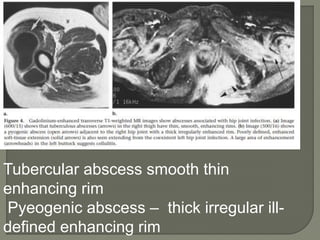
![MRI- both tenosynovities and septic arthritis show
T1 hypo T2 /STIR joint effusion
Contrast enhanced image [T1+C]-
Rim of enhancing hypertrophic synovial membrane
differentiated by hypo intense joint effusion](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/newmicrosoftofficepowerpointpresentation3-200119134144/85/Pediatric-hip-radiology-53-320.jpg)
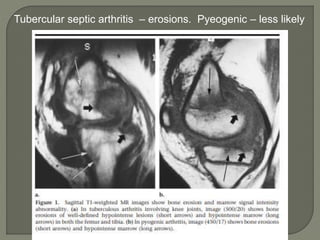
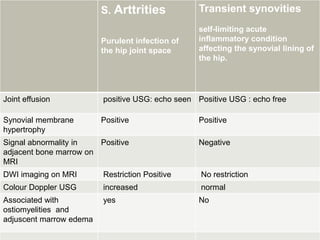
![MRI-
1]septic arthritis show signal intensity alteration in the
bone marrow of affected hip joint
2] In transient synovities cases show no such altered
signal entity in bone marrow
T1- poorly defined low signal intesity
T2-/STIR: hyperintese
Contrast study : show enhancment](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/newmicrosoftofficepowerpointpresentation3-200119134144/85/Pediatric-hip-radiology-54-320.jpg)