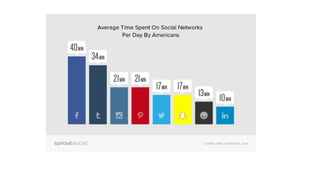
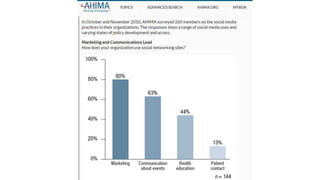
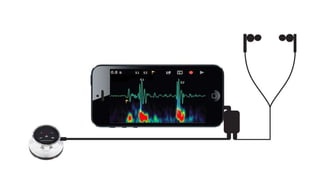
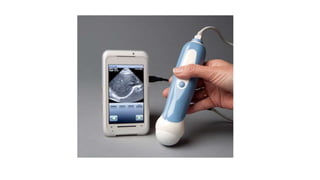
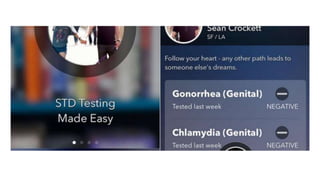
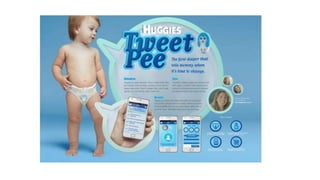
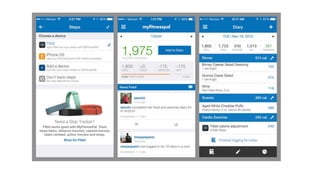
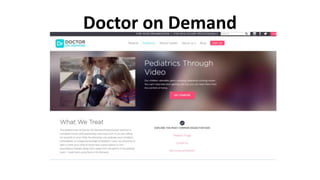
The speaker has no disclosures to make. The presentation will illustrate current uses of health apps, demonstrate critical appraisal of apps, and analyze benefits and legal issues related to health apps. It will provide an overview of topics like social media usage, appropriate professional uses of social media, risks of social media use, and examples of popular health apps. The presentation concludes with a discussion of cautions and policies around social media use in healthcare.