The document discusses promoting individual excellence through the Personal Excellence Pathway (PEP) program at Taibah University.
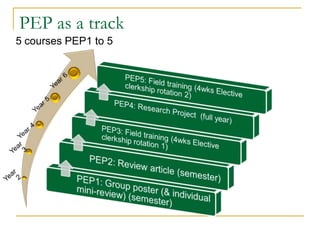
PEP allows students to study a range of topics within and beyond medicine through a series of 5 modular courses. It aims to help students develop skills like communication, information technology use, and continuing education of lay people.
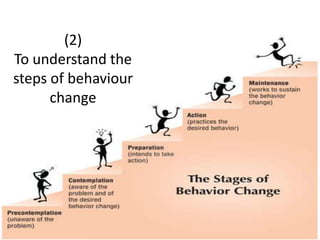
Students can complete projects related to topics like behavioral and social sciences in medicine and medical ethics. Examples shown include a group project on obesity and behavioral treatment, and a presentation by psychiatry professors on the importance of behavioral and social sciences.


















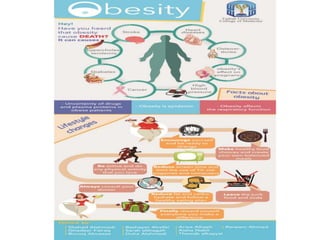





![OBESITY AND BEHAVIORAL TREATMENT
Definition:
It is a complex disorder involving an excessive
amount of body fat. Obesity isn't just a
cosmetic concern. It increases your risk of
diseases and health problems such as heart
disease, diabetes and high blood pressure.
Abdullah Essa – Abdulmanan alem – Turki albouq – alhosam alsinani – Abdullah alhojaili-Ahmed aljohani -
mohammed Qarh - bandar alfohidi – mohammed bakheet – Ali alshareef
Causes:
•Lack of Energy Balance
•A lack of energy balance most often causes
overweight and obesity. Energy balance means
that your energy IN equals your energy OUT.
•An Inactive Lifestyle
•Many people aren't very physically active. One
reason for this is that many people spend
hours in front of TVs and computers doing
work, schoolwork, and leisure activities. In
fact, more than 2 hours a day of regular TV
viewing time has been linked to overweight
and obesity.
•Genes and Family History
•Studies of identical twins who have been
raised apart show that genes have a strong
influence on a person's weight. Overweight
and obesity tend to run in families. Your
chances of being overweight are greater if one
or both of your parents are overweight or
obese.
•Smoking
•Some people gain weight when they stop
smoking. One reason is that food often tastes
and smells better after quitting smoking.
Treatment:
•For Adults
•Try to lose 5 to 10 percent of your current
weight over 6 months. This will lower your
risk for coronary heart disease (CHD) and other
conditions.
•For Children and Teens
•If your child is overweight or at risk for
overweight or obesity, the goal is to maintain
his or her current weight and to focus on
eating healthy and being physically active.
This should be part of a family effort to make
lifestyle changes.
•Lifestyle Changes
•Lifestyle changes can help you and your
family achieve long-term weight-loss success.
Example of lifestyle changes include:
•Following a healthy eating plan
•Learning how to adopt healthy lifestyle habits
•Over time, these changes will become part of
your everyday life.
World obesityprevalence among males (left) and females (right).[168]
•World obesity prevalence among males (up) and
females (down)
•The darker the higher.
• References:
1-http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/health-
topics/topics/obe/causes.html
2- Wikipedia](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/06pepandstudentswork-150121185447-conversion-gate01/85/PBL-Personal-Excellence-Pathway-PEP-29-320.jpg)