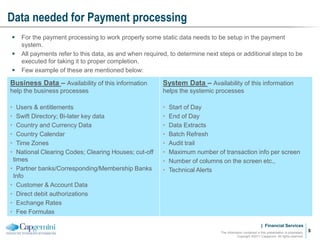
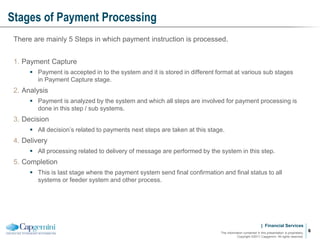
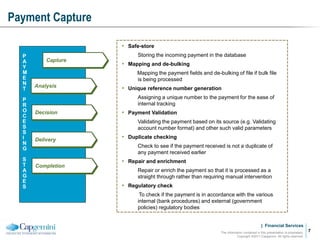
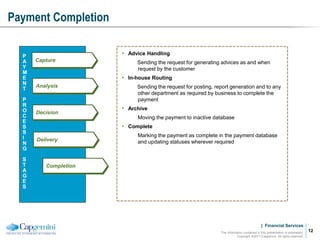
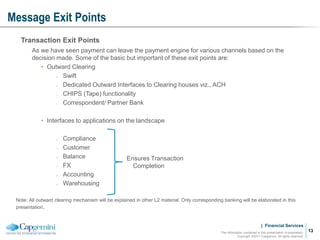
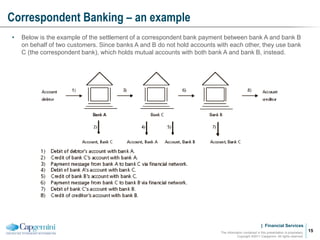
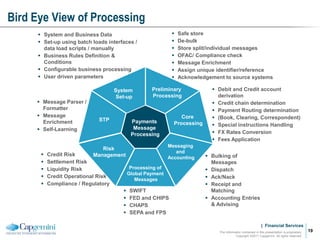
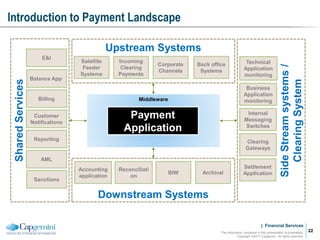
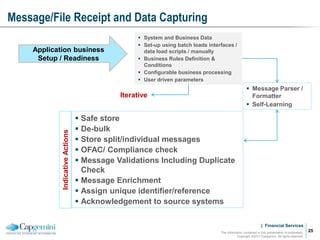
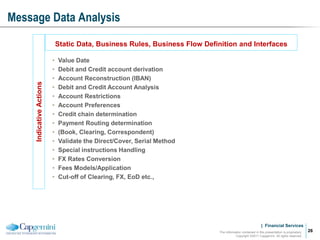
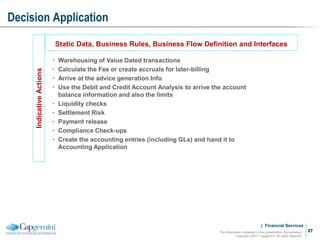
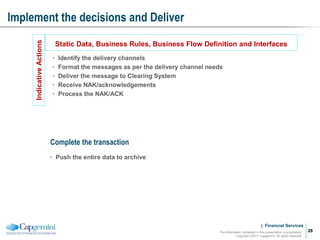
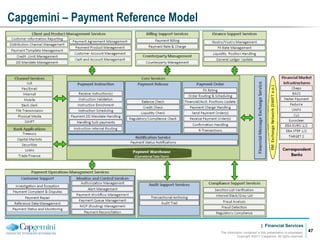
Payment processing involves multiple stages from when a payment enters a payment processor until it is completed. It includes capturing the payment details, analyzing it to determine accounts and processing steps, making decisions about how it will be processed and delivered, and completing the processing. Key aspects of payment processing discussed in the document include various entry and exit points, static data needed, the five main processing stages, correspondent banking, and end-of-day and start-of-day tasks and uploads.