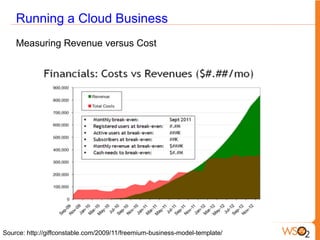
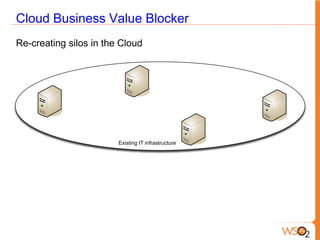
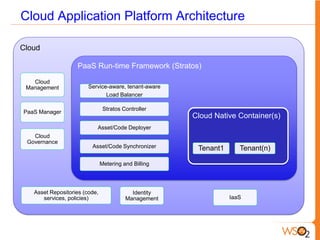
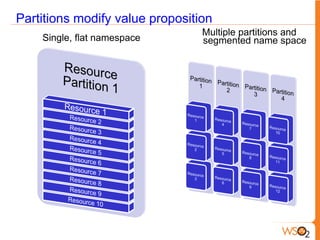
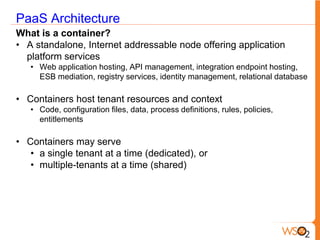
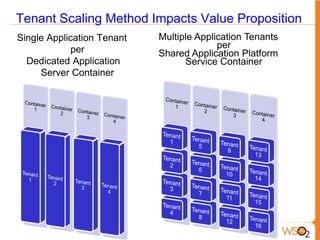
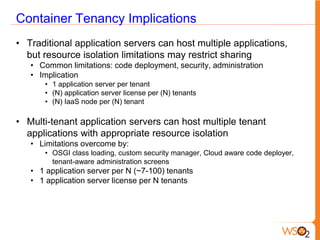
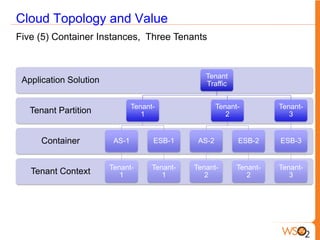
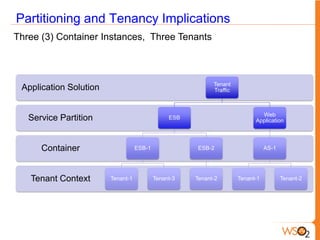
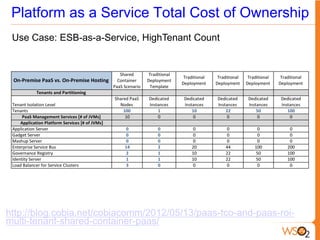
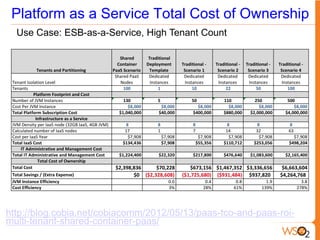
This document discusses measuring the value of Platform as a Service (PaaS) and reducing costs through a multi-tenant shared container approach. It describes how partitioning containers by service and tenant can improve efficiency and lower costs compared to traditional single-tenant models. The document also analyzes how WSO2's shared container PaaS architecture can reduce total cost of ownership through on-demand provisioning and better utilization rates.