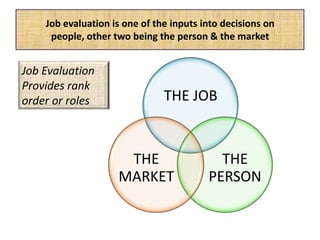
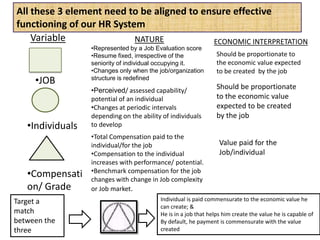
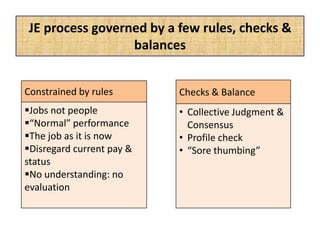
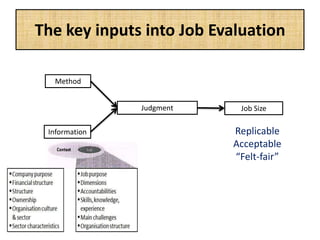
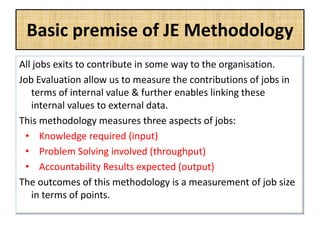
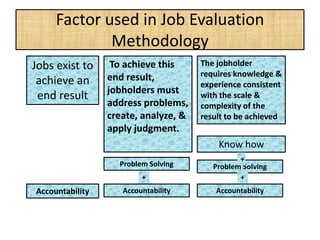
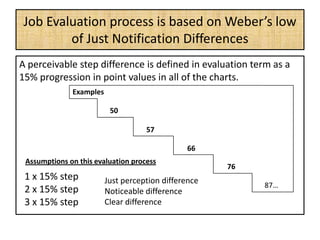
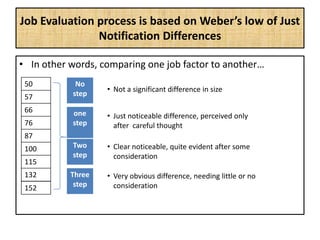
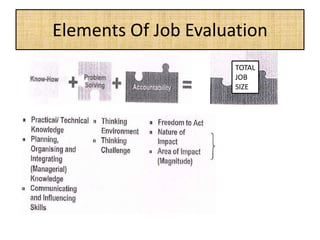
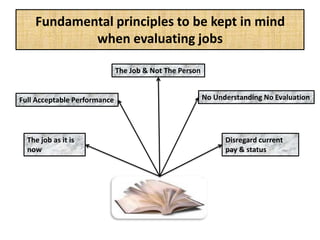
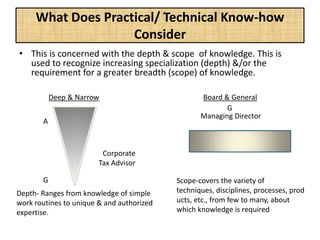
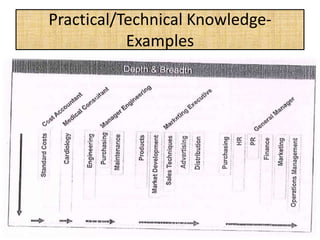
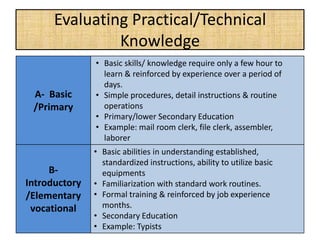
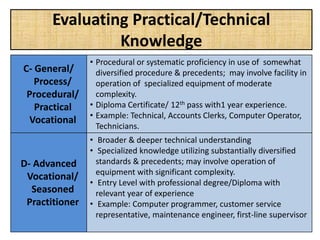
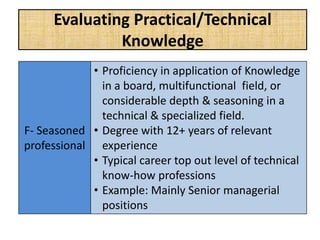
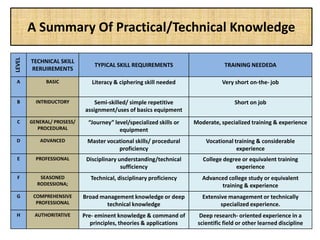
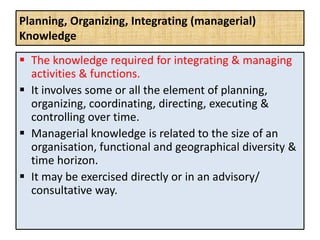
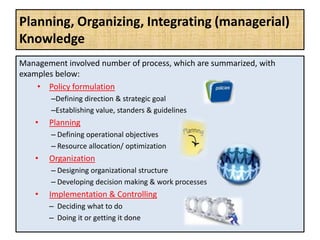
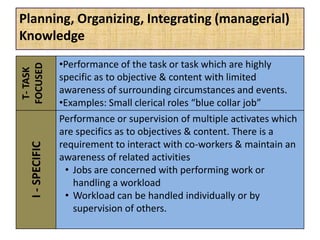
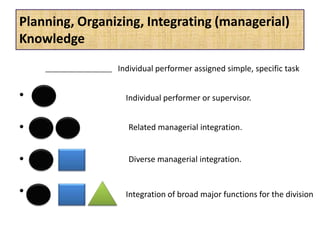
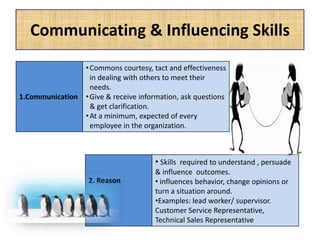
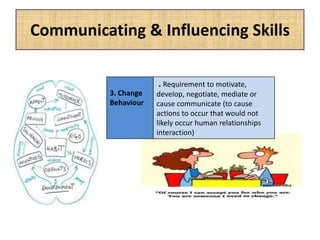
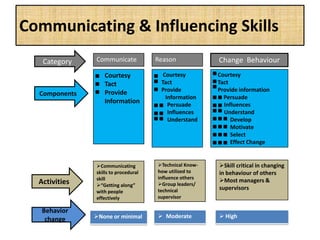
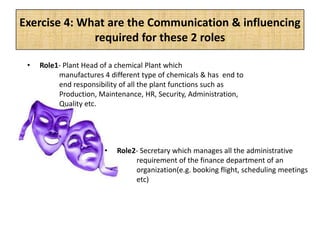
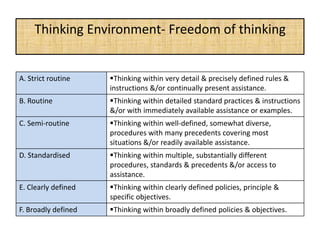
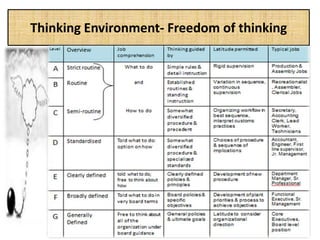
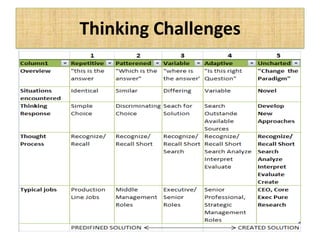
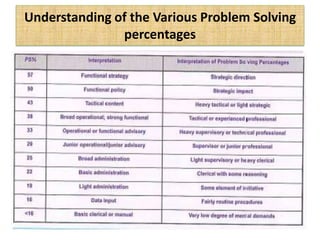
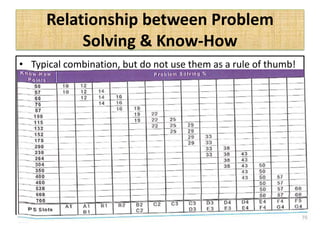
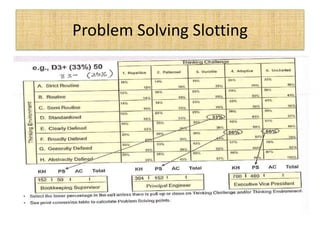
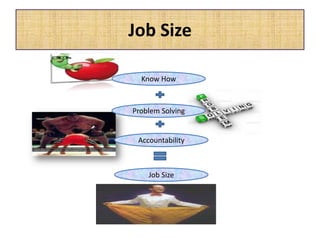
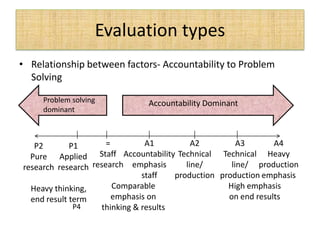
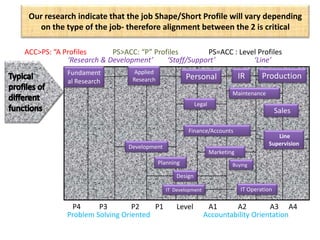
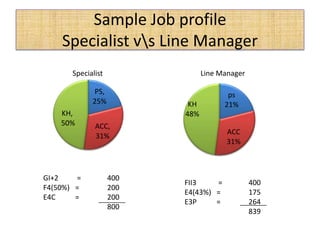
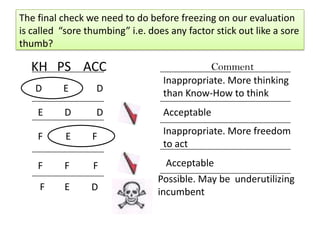
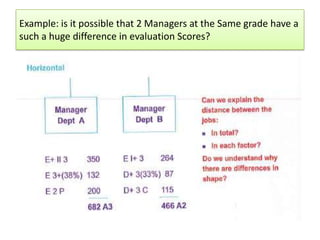
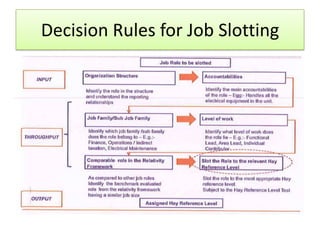
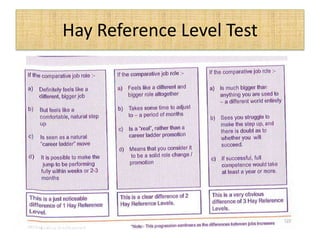
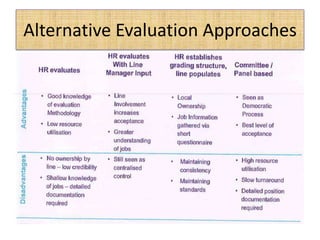
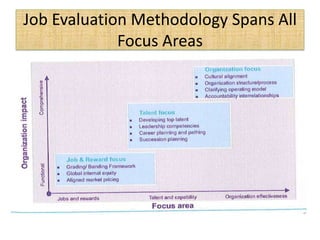
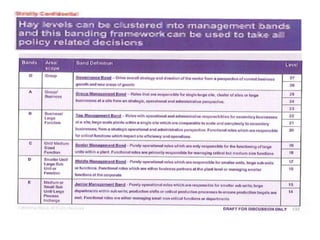
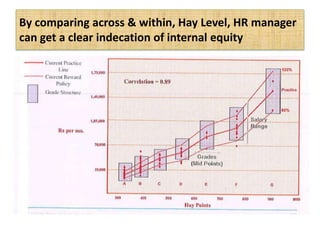
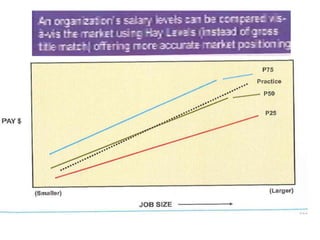
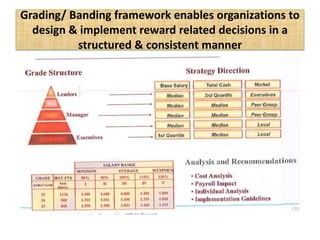
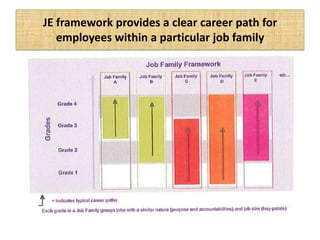
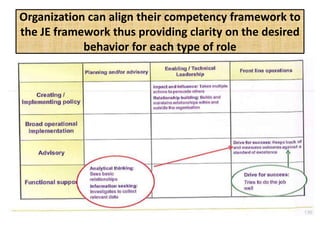
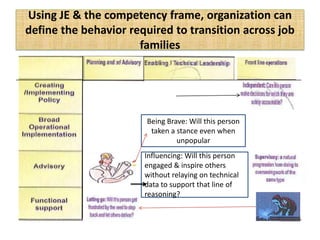
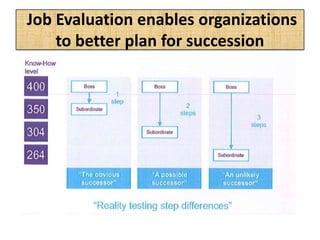
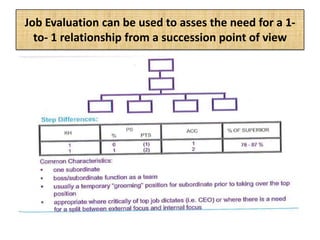
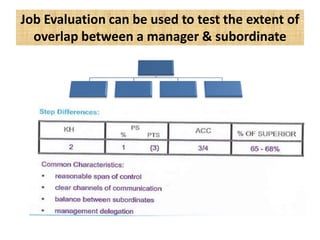
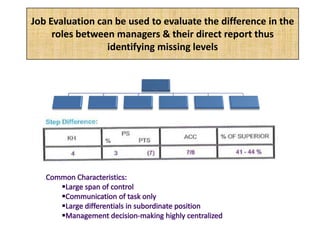
The document outlines job evaluation as a systematic method for assessing the relative importance of jobs within an organization, focusing on understanding job content and organizational context. It provides a structured approach to evaluating jobs based on knowledge required, problem-solving, and accountability, and emphasizes the need for fairness and objectivity in the evaluation process. Key components include methodologies, assumptions, and factors affecting job evaluation, with guidelines to avoid common pitfalls in evaluation practices.