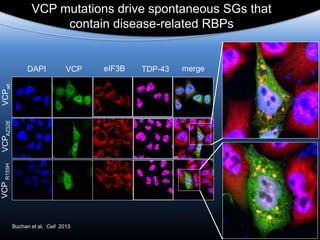
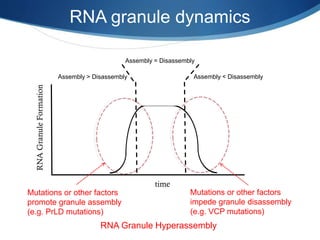
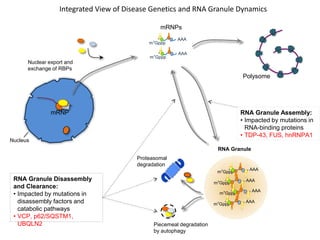
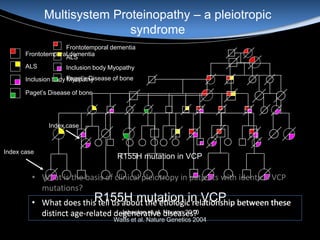
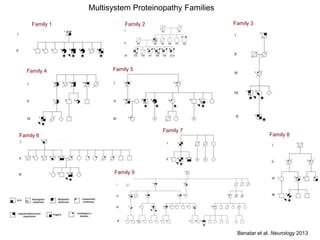
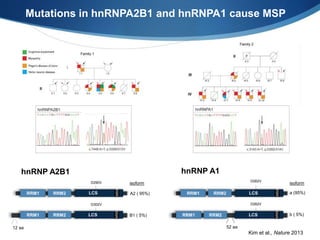
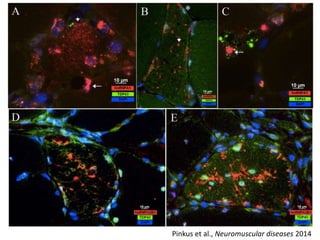
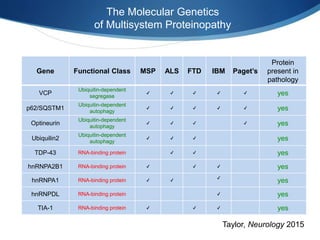
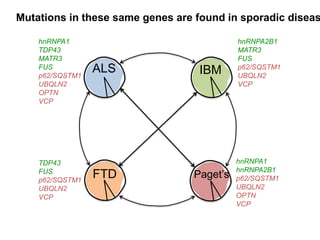
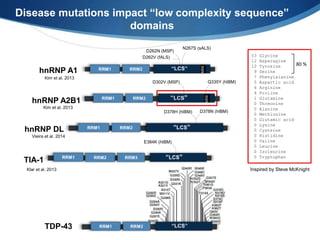
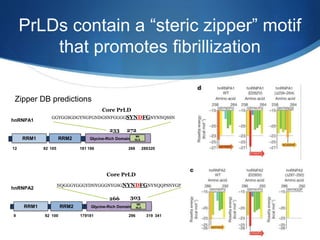
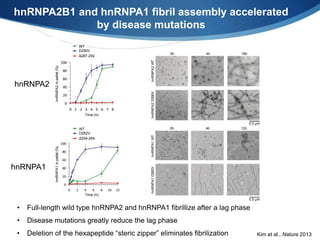
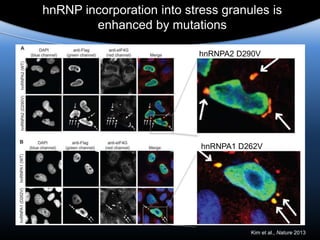
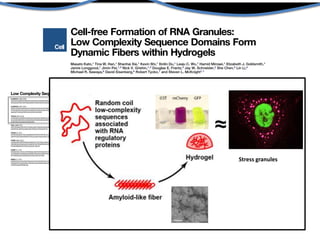
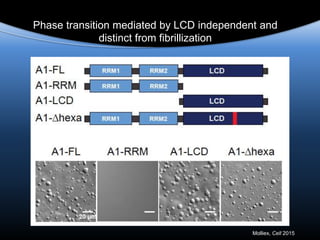
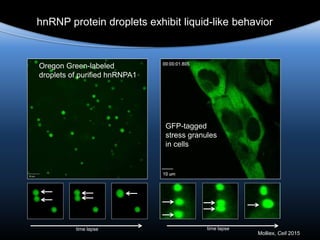
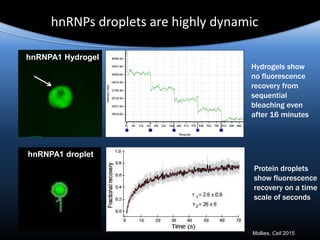
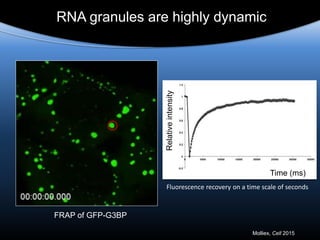
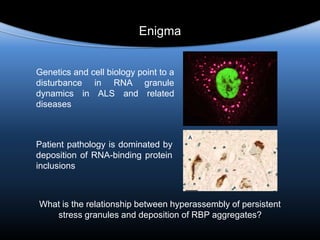
The document discusses dynamic RNA-protein assemblies in neurological diseases, focusing on multisystem proteinopathy and mutations in various RNA-binding proteins like hnrnpa1 and hnrnpa2b1. It explores the clinical pleiotropy in patients with identical VCP mutations and the implications of these mutations on age-related degenerative diseases, highlighting the relationships among amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), frontotemporal dementia (FTD), and other related conditions. Additionally, it emphasizes the disturbance in RNA granule dynamics in these diseases, driven by factors such as phase separation and fibrillization tendencies of mutant proteins.



![T [°C]
time
33
20
35
[A1-FL] (μM)
50 100 150 200 250 300
Temperature(⁰C)
10
15
20
25
30
35
150 100 75
[Ficoll] (mg/ml)
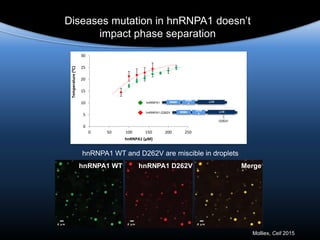
hnRNPA1 is poised at the phase boundary as we
approach physiological conditions of temperature,
concentration, salt and intracellular molecular
crowding
Mapping the phase diagram of liquid-liquid
phase separation
Individual mRNPs
m7Gppp
AAA
m7Gppp
AAA
m7Gppp
AAA
m7Gppp
AAA
m7Gppp
AAA
RNA granule
m7Gppp
AAA
m7Gppp
AAA
m7Gppp
AAA
LLPS
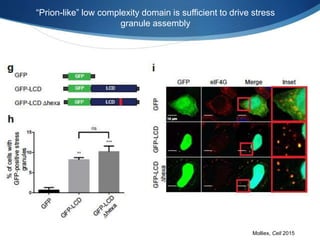
Hypothesis: phase separation by LCD-containing
RBPs underlies the formation of RNA granules and
related RNA-protein assemblies as well as their
liquid properties
Molliex, Cell 2015](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tayloralzforum-151102152031-lva1-app6891/85/Paul-Taylor-20-320.jpg)

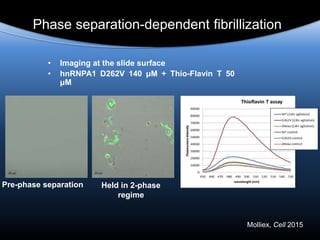
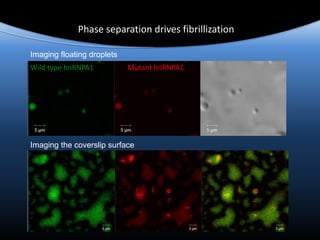
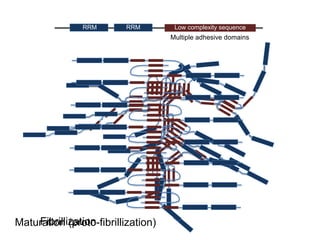
![Persistent Granule Assembly Promotes Amyloid
Formation
m7Gppp
AAA
m7Gppp
AAA
m7Gppp
AAA
m7Gppp
AAA
Individual mRNPs
(one phase)
AAA
m7Gppp
RNA Granule
(two phases)
Pathological
inclusions
Reversible
phase
separation
AAA
m7Gppp
m7Gppp
AAA
m7Gppp
AAA
m7Gppp
AAA
m7Gppp
AAA
Amyloid
formation
AAA AAA
AAA AAA
m7Gppp m7Gppp
m7Gpppm7Gppp
m7Gppp
AAA
m7Gppp
AAA
m7Gppp
AAA
m7Gppp
AAA
[hnRNP]low = low risk
of amyloid formation
[hnRNP]high = high risk
of amyloid formation
time
Insoluble residua
formed from the
most
amyloidogenic
constituents of
granules](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tayloralzforum-151102152031-lva1-app6891/85/Paul-Taylor-27-320.jpg)