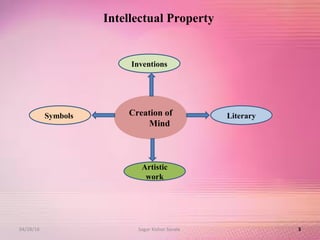
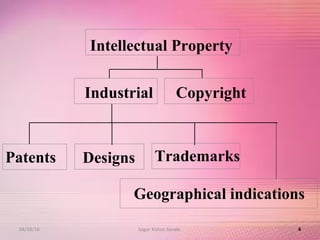
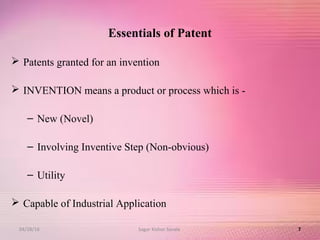
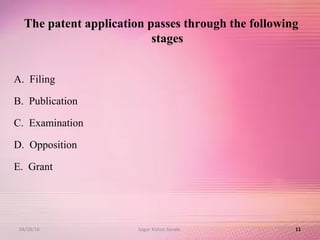
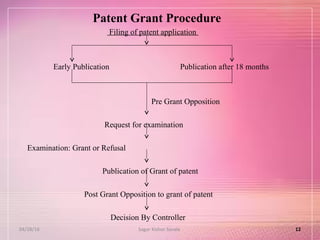
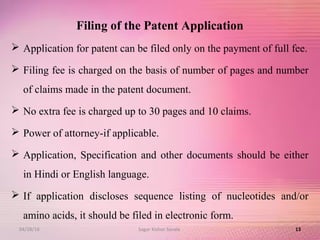
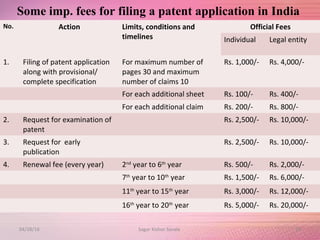
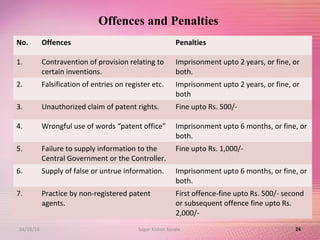
The document provides an overview of the patent filing process in India. It discusses the types of patent applications that can be filed, including ordinary, convention, patent of addition, and divisional applications. The key stages of the patent process are described, including filing, publication, examination, opposition, and grant. Requirements for documents, fees, and timelines at different stages of the process are also outlined.