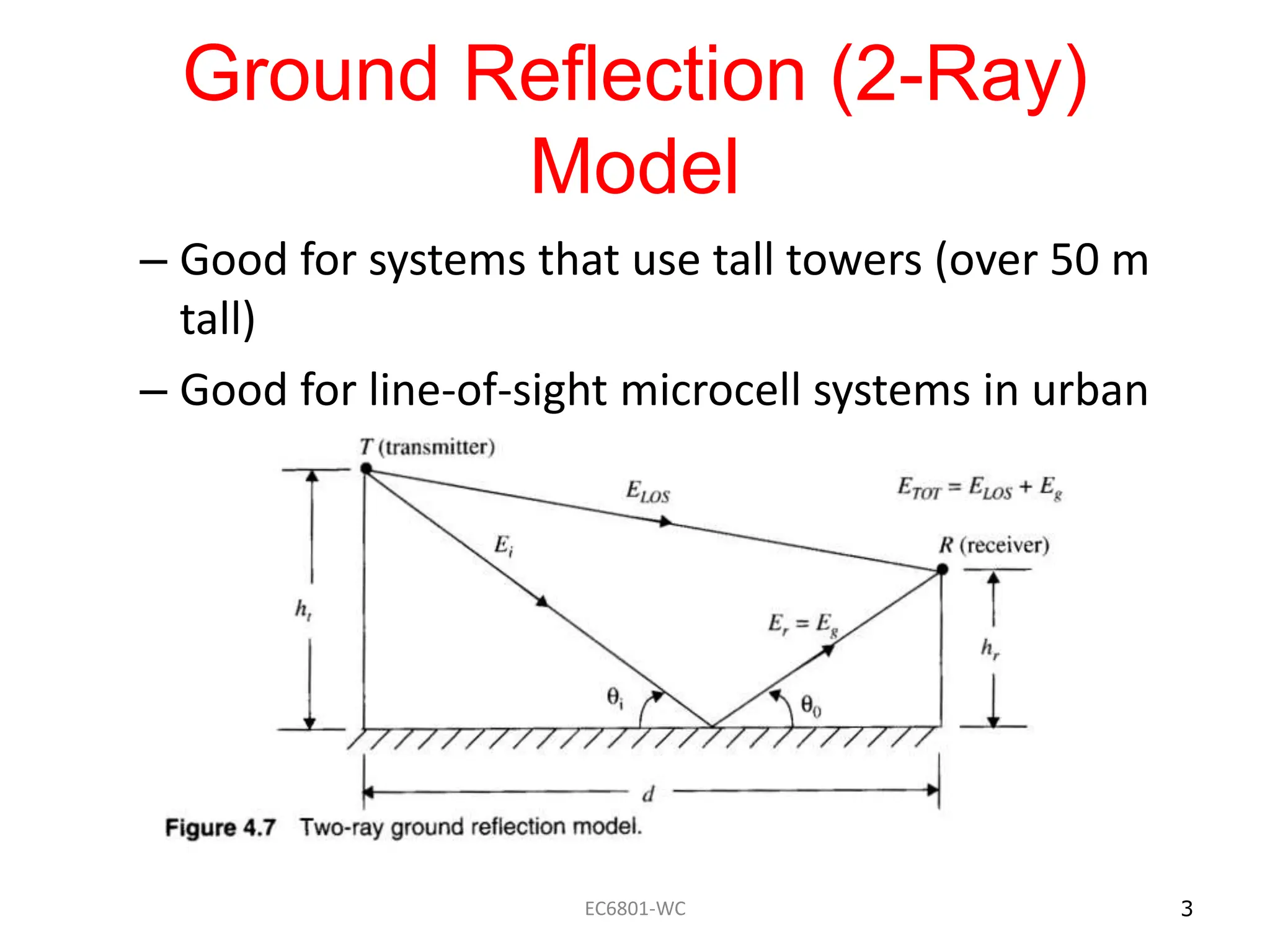
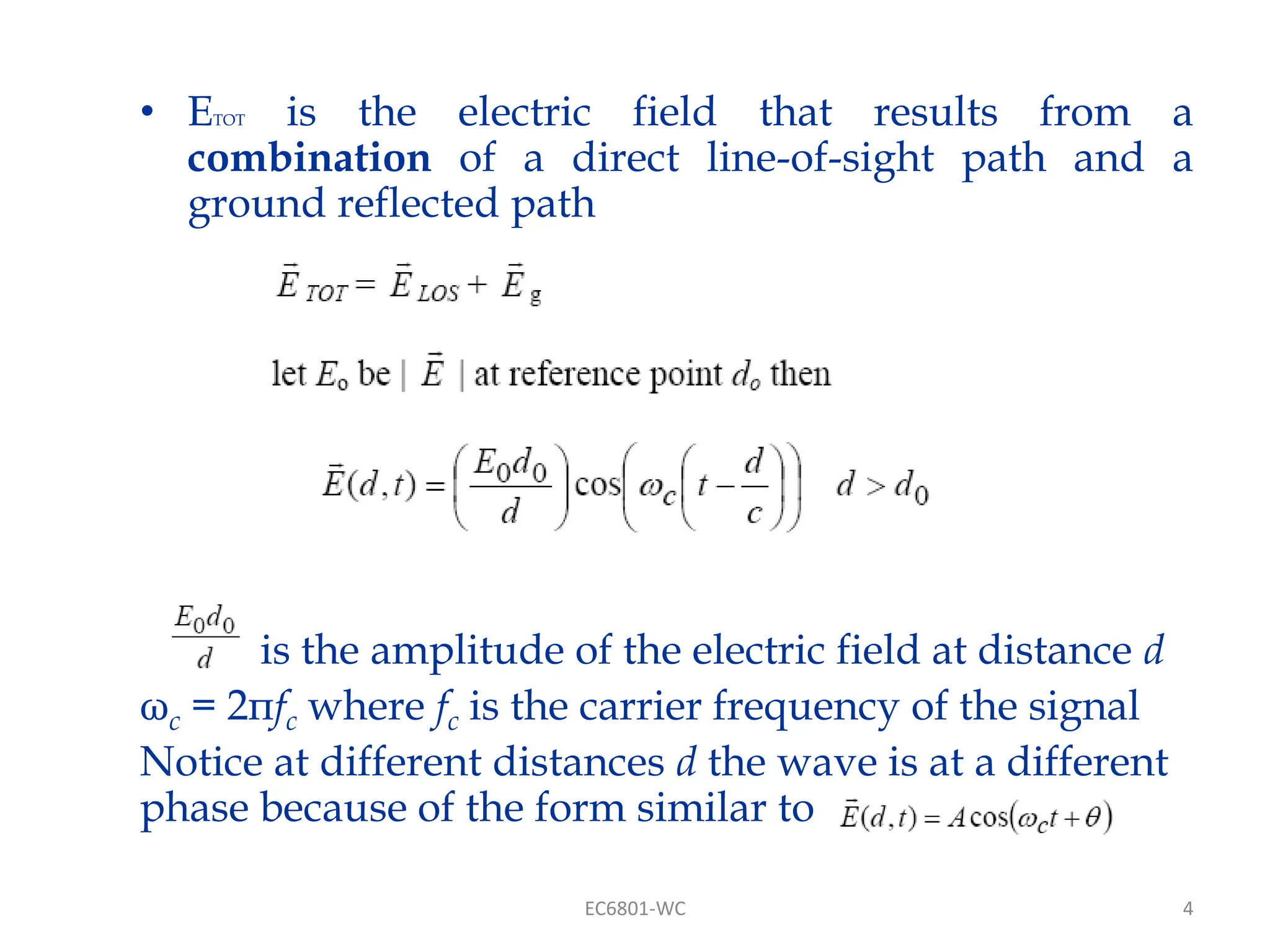
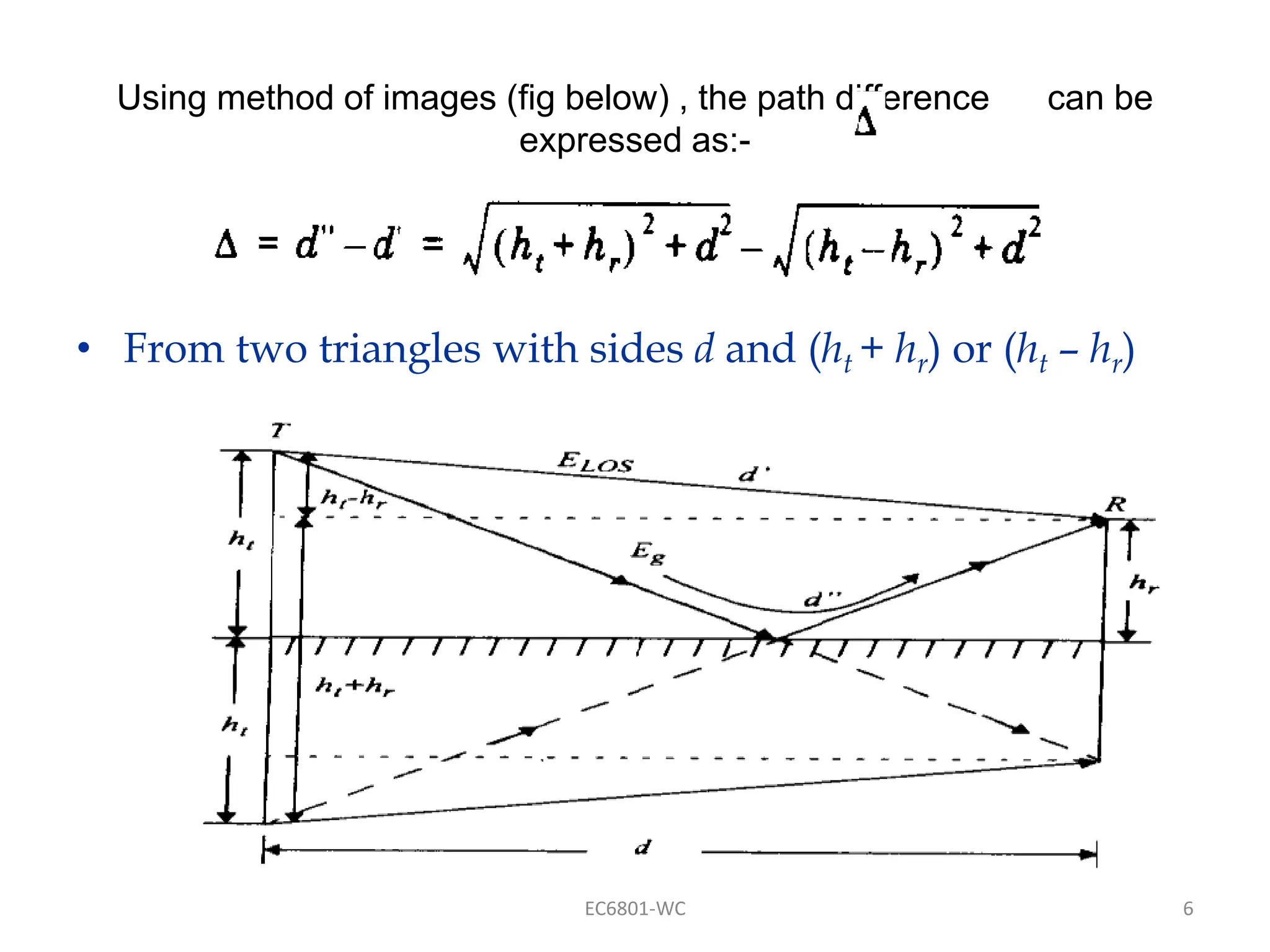
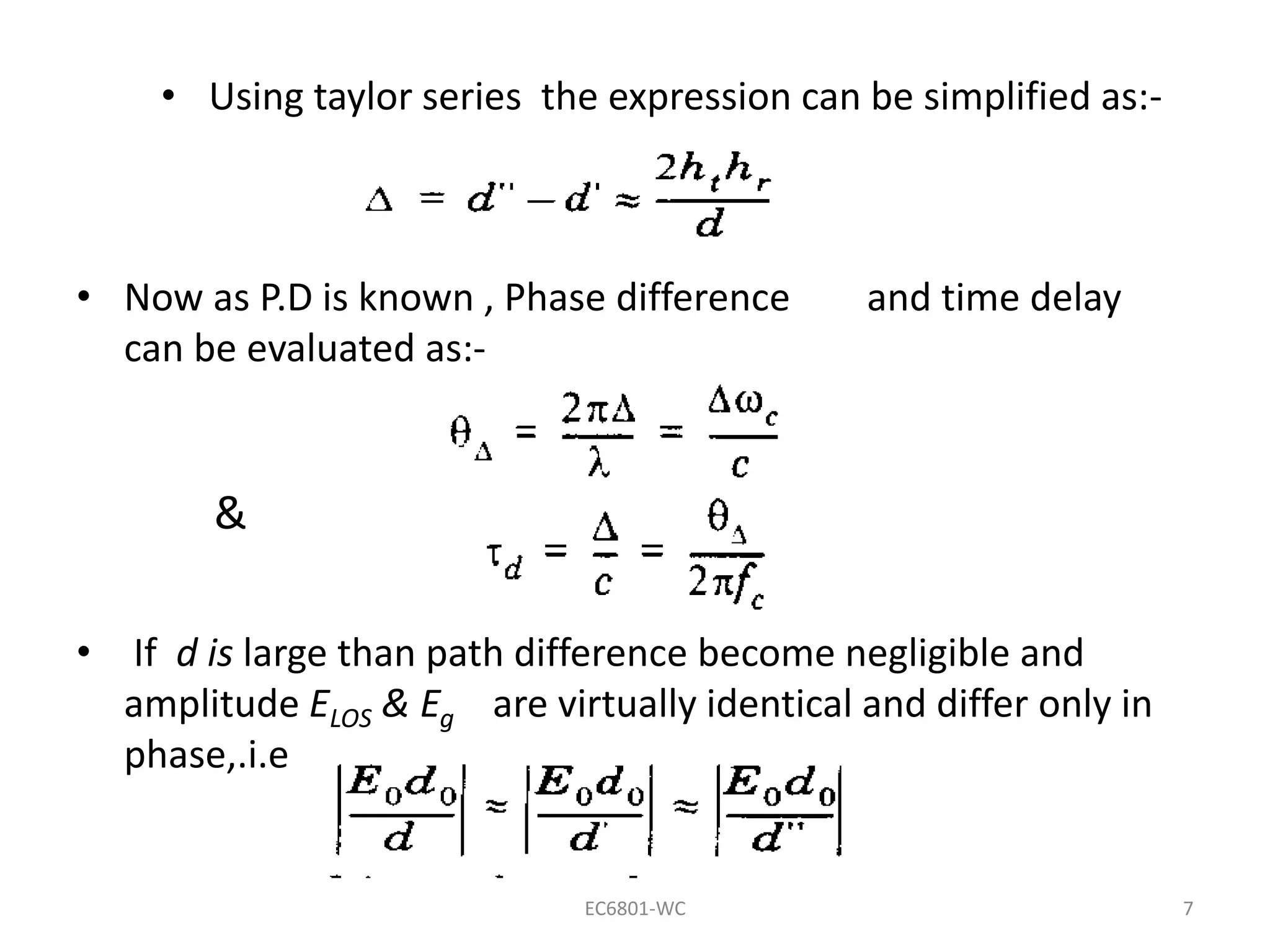
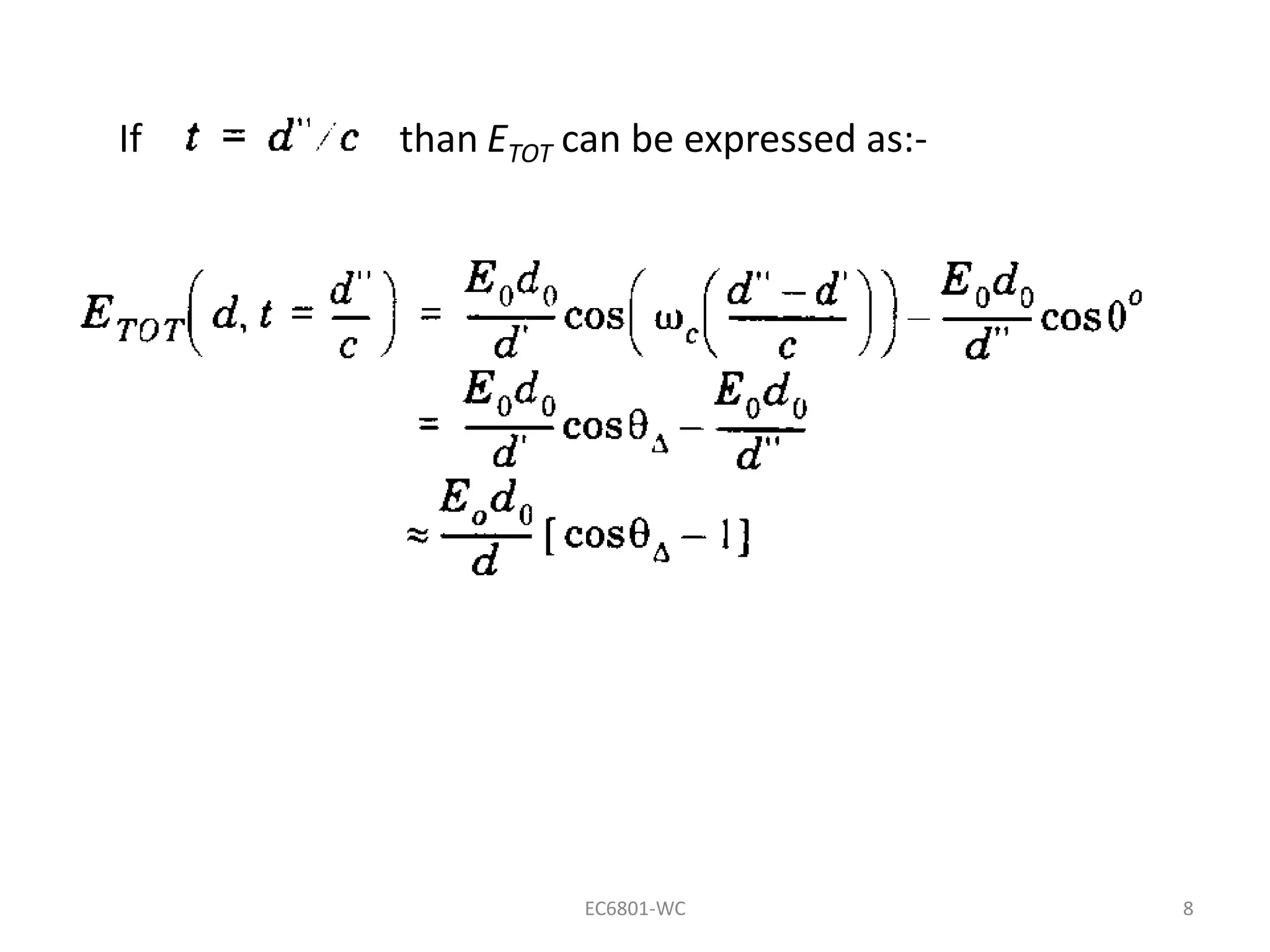
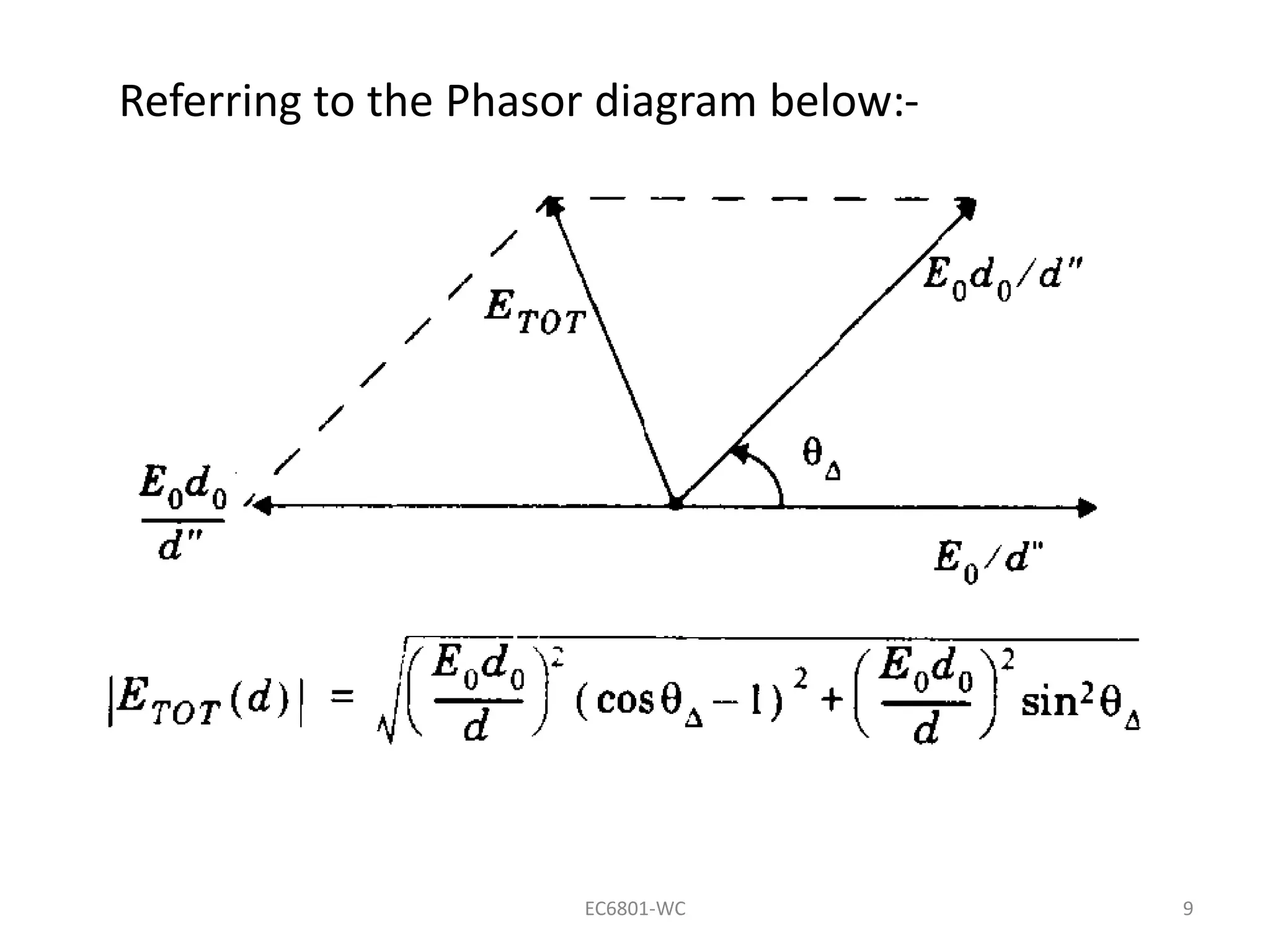
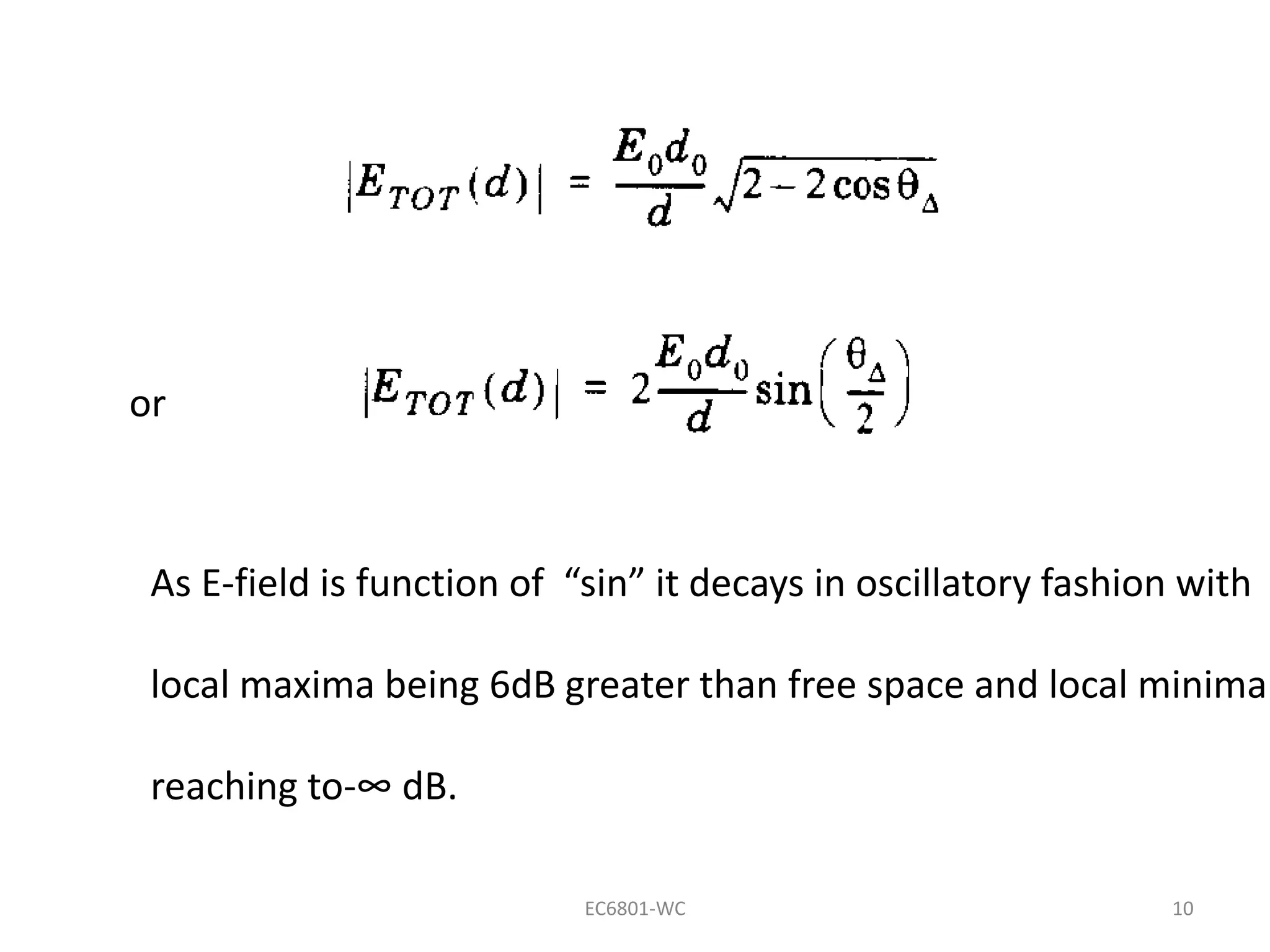
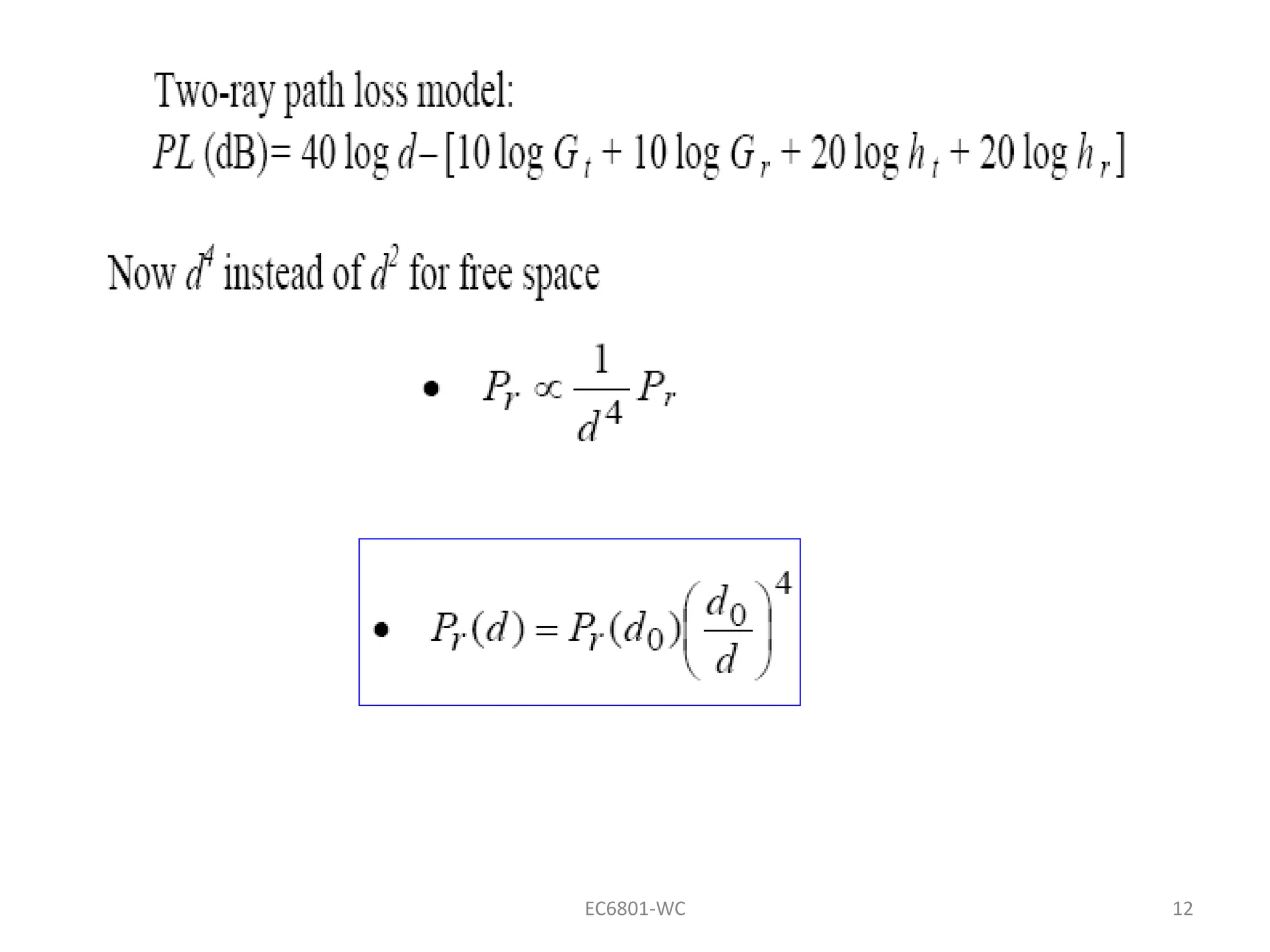
Dr. S. Mary Praveena discusses path loss models related to electromagnetic wave propagation, focusing on reflection, diffraction, and scattering as the three basic mechanisms. The ground reflection model is effective for tall towers in urban settings, emphasizing the phase differences between direct and reflected paths. The document explains the impact of these factors on signal strength and wave behavior at varying distances.