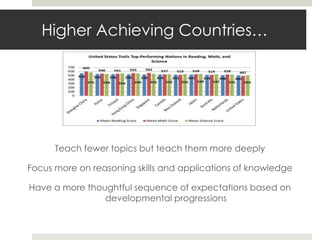
The document discusses skills needed for global competitiveness in the 21st century. It argues that students need to develop skills like critical thinking, problem solving, communication and collaboration. Higher achieving countries teach fewer topics more deeply and focus on reasoning skills. The document recommends changing curriculum to include more science/technology, foreign languages, and knowledge of other cultures. It also suggests assessments focus on higher-order skills and problem solving through open-ended tasks and projects.