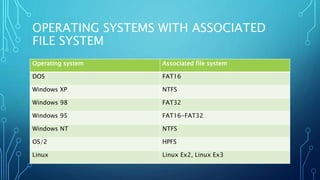
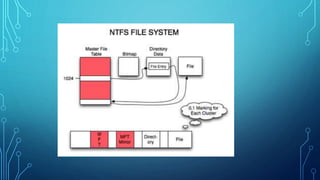
Partitioning involves dividing a physical disk drive into logical sections called partitions. This allows an operating system like Windows to install files onto a designated partition. There are three types of partitions: primary, extended, and logical drives. Common file systems include FAT32, NTFS, and exFAT. NTFS supports larger file sizes, quotas, and encryption while FAT32 is better for compatibility and smaller file sizes. The allocation unit size determines the minimum space a file occupies on the disk.