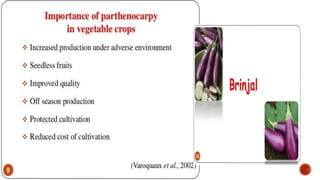
The document discusses seedless fruits and the concept of parthenocarpy, which is the formation of fruit without fertilization, categorized into natural and induced forms. Factors influencing parthenocarpy include genetic mutations, environmental conditions, and the application of hormones such as auxin and gibberellins. It highlights the significance of parthenocarpic fruits in agriculture, food preservation, and consumer preference due to the absence of seeds.