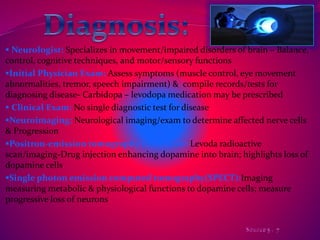
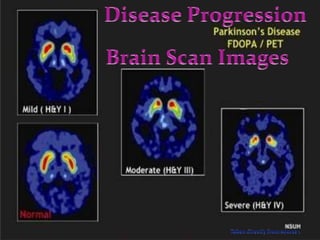
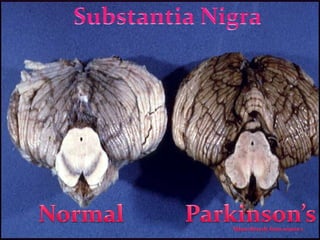
This document discusses Parkinson's disease, which is caused by degeneration of dopamine-producing neurons in the substantia nigra region of the brain. This leads to a loss of dopamine signaling and results in motor symptoms like tremors, rigidity, and impaired movement. The disease progresses as more dopamine neurons are lost over time. It can be diagnosed through neurological exams and imaging tests, and is typically treated with medications like levodopa and carbidopa or therapies like deep brain stimulation. Recent research also suggests weight gain from deep brain stimulation may help improve cognitive and sensory symptoms in Parkinson's patients.