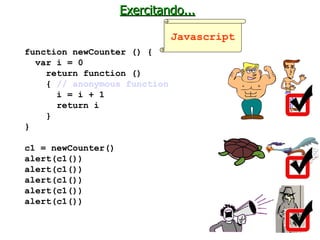
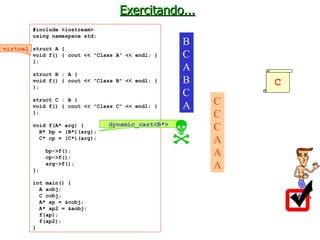
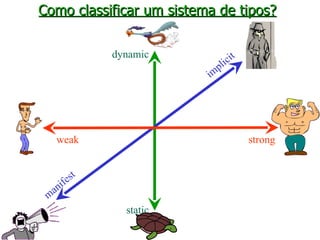
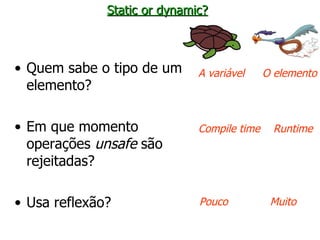
The document discusses type systems in programming languages. It defines a type system as a method for proving the absence of certain program behaviors by classifying phrases based on the values they compute. Type systems can help detect errors, improve security, enable abstraction and verification, and aid in evolution and documentation. The document then discusses different characteristics of type systems such as being static or dynamic, strong or weak, manifest or implicit. It provides examples to illustrate these concepts in different programming languages like C, C#, Pascal, Lua, JavaScript, and Fortran.
![Paradigmas de Linguagens de Programação Paradigma Imperativo [Teoria de Tipos] Aula #5 (CopyLeft)2009 - Ismar Frango ismar@mackenzie.br](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/plp5-090903122311-phpapp01/75/Paradigmas-de-Linguagens-de-Programacao-Aula-5-1-2048.jpg)




![Strong or weak? class Silly: def __init__(self, data): self.data = data def __add__(self, other): return str(self.data) + str(other.data) def double(a): return a + a print double(1) print double('x') print double([1]) print double(Silly({'a':1})) print double({'a':1}) Python 2 xx [1, 1] {'a': 1}{'a': 1} Traceback (most recent call last): File "test.py", line 14, in ? print double({'a':1}) File "test.py", line 8, in double return a + a TypeError: unsupported operand types for +: 'dict' and 'dict'](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/plp5-090903122311-phpapp01/85/Paradigmas-de-Linguagens-de-Programacao-Aula-5-7-320.jpg)
![Strong or weak? var s : array [1..10] of character; s := 'hello'; Pascal ERRO](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/plp5-090903122311-phpapp01/85/Paradigmas-de-Linguagens-de-Programacao-Aula-5-8-320.jpg)

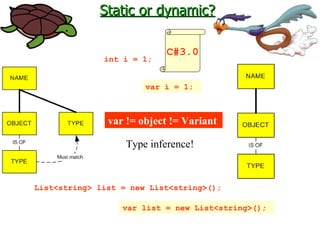
![Static or dynamic? Customer c = GetCustomer(); var d = new { Name = c.Name, City = c.City }; Tipo anônimo public void Linq1() { int[] numbers = { 5, 4, 1, 3, 9, 8, 6, 7, 2, 0 }; var lowNums = from n in numbers where n < 5 select n; Console.WriteLine("Numbers < 5:"); foreach ( var x in lowNums ) { Console.WriteLine(x); } } C#3.0 C#3.0 (LINQ)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/plp5-090903122311-phpapp01/85/Paradigmas-de-Linguagens-de-Programacao-Aula-5-12-320.jpg)