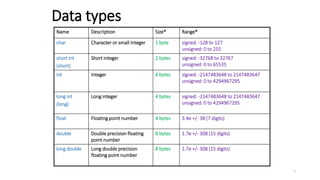
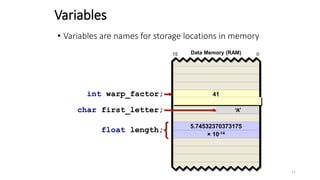
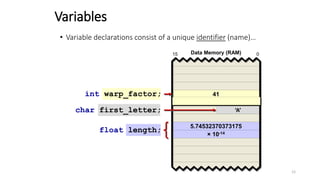
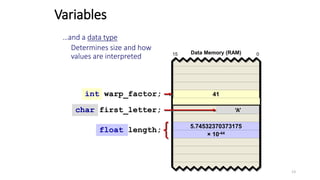
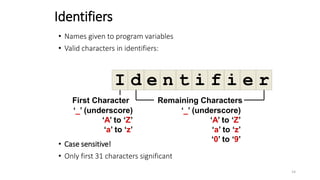
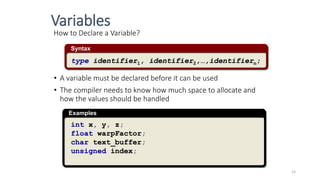
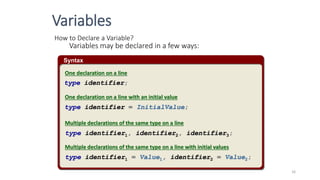
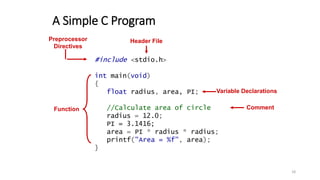
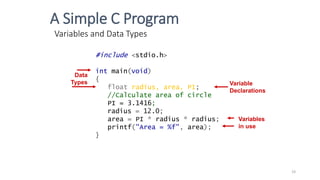
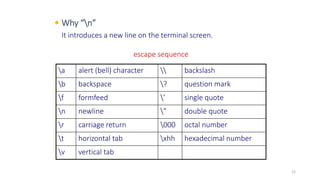
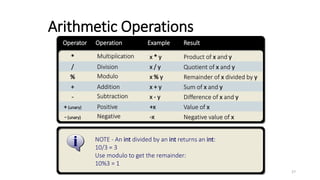
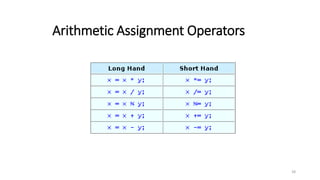
The document provides an overview of the C programming language. It discusses that C is commonly used for embedded systems and systems programming tasks like operating systems and compilers. It was developed between 1969-1973 along with Unix. The "Hello World" example program is shown to demonstrate the basic structure of a C program with main() as the entry point. Data types, variables, and basic I/O functions like printf() and scanf() are described. Operators for arithmetic, comparison, logic, and assignment are also covered.








![An example
int global = 10; //global variable
int func (int x)
{
static int stat_var; //static local variable
int temp; //(normal) local variable
int name[50]; //(normal) local variable
……
}
10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationcbasics1589366177381682-221110160600-07142fc6/85/presentation_c_basics_1589366177_381682-pptx-10-320.jpg)

![printf()
The printf() function can be instructed to print
integers, floats and string properly.
The general syntax is
printf( “format”, variables);
An example
int stud_id = 5200;
char name[20] = “Mike”; // array discussed in LO4
printf(“%s ‘s ID is %d n”, name, stud_id);
20](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationcbasics1589366177381682-221110160600-07142fc6/85/presentation_c_basics_1589366177_381682-pptx-20-320.jpg)



![Example: The following example shows the usage of scanf() function to read strings.
Note: in scanf, we do not use & with array names
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
char str1[20], str2[30];
printf("Enter name: ");
scanf("%s", str1);
printf("Enter your website name: ");
scanf("%s", str2);
printf("Entered Name: %sn", str1);
printf("Entered Website:%s", str2);
}
scanf()
Enter name: admin
Enter your website name: www.tutorialspoint.com
Entered Name: admin
Entered Website: www.tutorialspoint.com
25](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationcbasics1589366177381682-221110160600-07142fc6/85/presentation_c_basics_1589366177_381682-pptx-25-320.jpg)

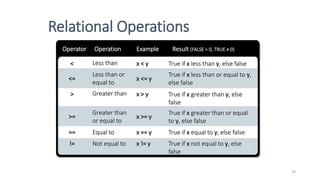
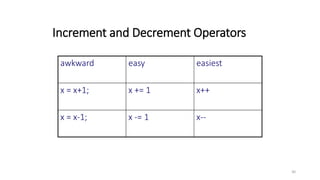





![Precedence and Associativity of C Operators
Symbol Type of Operation Associativity
[ ] ( ) . –> postfix ++ and postfix –– Expression Left to right
prefix ++ and prefix –– sizeof
& * + – ~ !
Unary Right to left
typecasts Unary Right to left
* / % Multiplicative Left to right
+ – Additive Left to right
<< >> Bitwise shift Left to right
< > <= >= Relational Left to right
== != Equality Left to right
& Bitwise-AND Left to right
^ Bitwise-exclusive-OR Left to right
| Bitwise-inclusive-OR Left to right
&& Logical-AND Left to right
|| Logical-OR Left to right
? : Conditional-expression Right to left
= *= /= %=
+= –= <<= >>= &=
^= |=
Simple and compound
assignment
Right to left
, Sequential evaluation Left to right
OPERATOR PRECEDENCE
36](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationcbasics1589366177381682-221110160600-07142fc6/85/presentation_c_basics_1589366177_381682-pptx-36-320.jpg)

