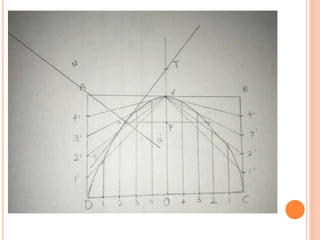
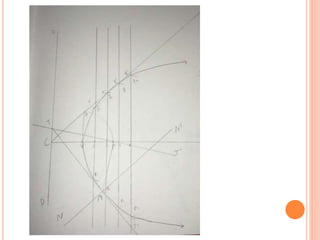
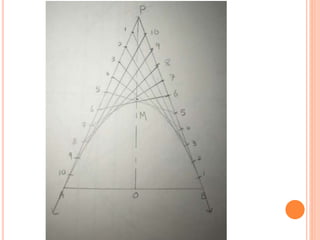
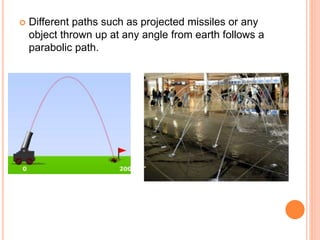
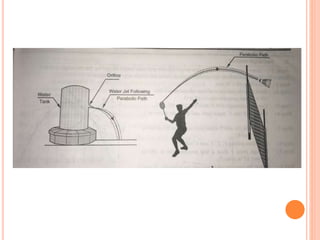
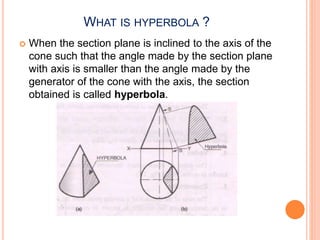
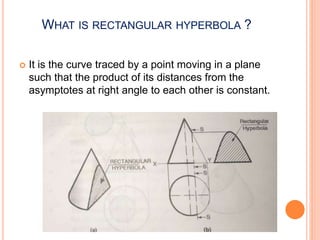
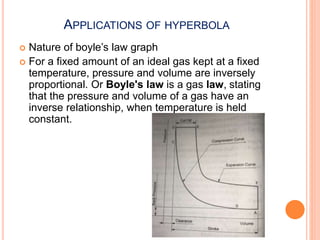
The document introduces various methods for drawing parabolas and hyperbolas, including techniques such as the rectangle method, directrix-focus method, and tangent/triangle method. It discusses the applications of these conic sections in fields like engineering graphics, mentioning specific uses like bridge arches, light reflectors, and gas law representations. Additionally, it covers hyperbolas, their characteristics, and applications, highlighting their relevance in structures like water tanks and cooling towers.