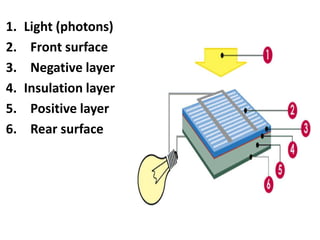
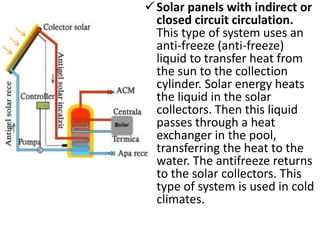
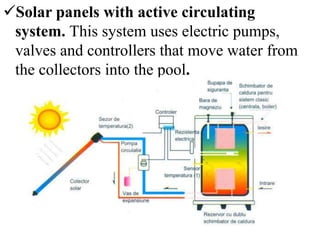
Photovoltaic panels convert photons from sunlight into electricity using photovoltaic cells. When photons are absorbed by solar cells, they release electrons which create a current to produce electricity. Photovoltaic panels can be mounted on roofs, terraces, or the ground and come in monocrystalline, polycrystalline, or amorphous forms. Solar collectors capture solar energy in solar rays and convert it to thermal energy to heat water or antifreeze for storage or use. Thermal solar panel systems use heat from the sun to heat domestic hot water by circulating water or antifreeze through collectors and a storage tank.