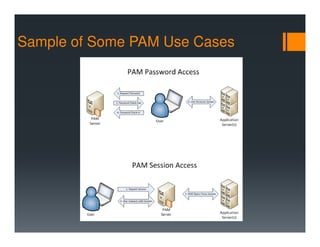
This document discusses privileged access management (PAM). PAM is defined as securing and managing privileged accounts, which hold special permissions like administrator access. The document outlines why PAM is important given recent data breaches from compromised privileged accounts. It also discusses how identity is the new security perimeter and that PAM is a collaborative effort involving technology, people and processes. Examples of PAM use cases and an adoption approach emphasizing the need for leadership support and prioritizing critical systems are also provided.