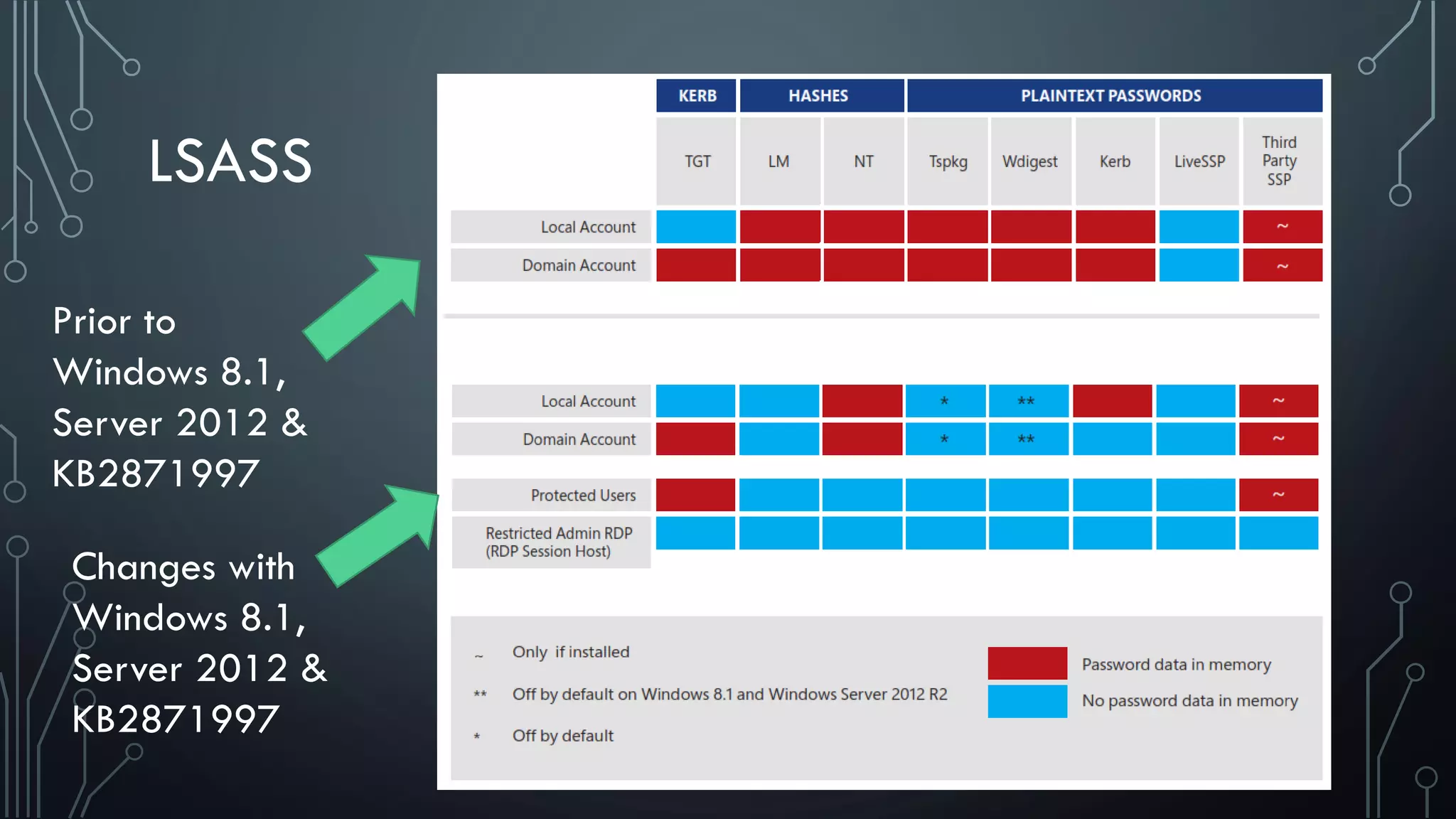
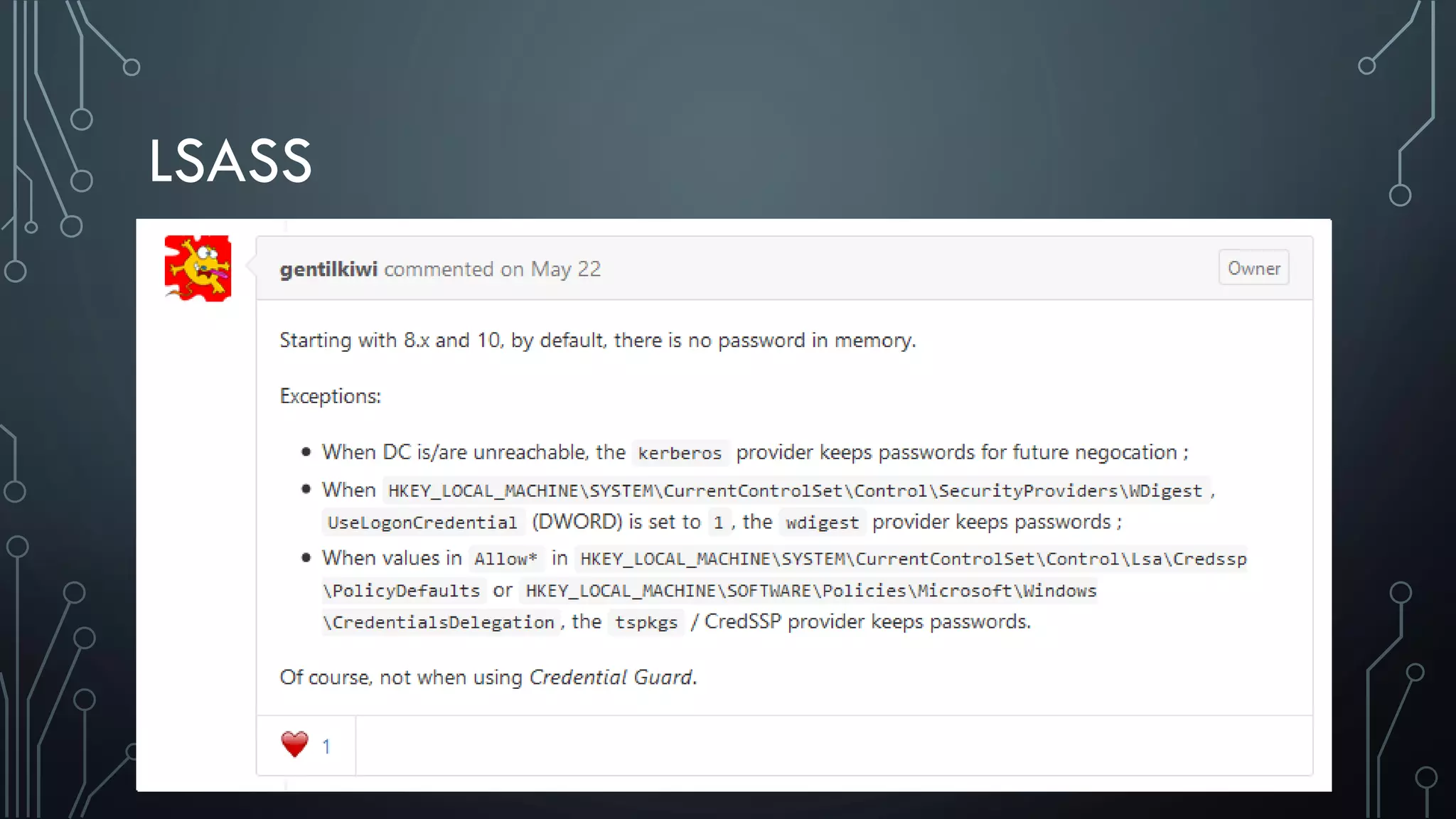
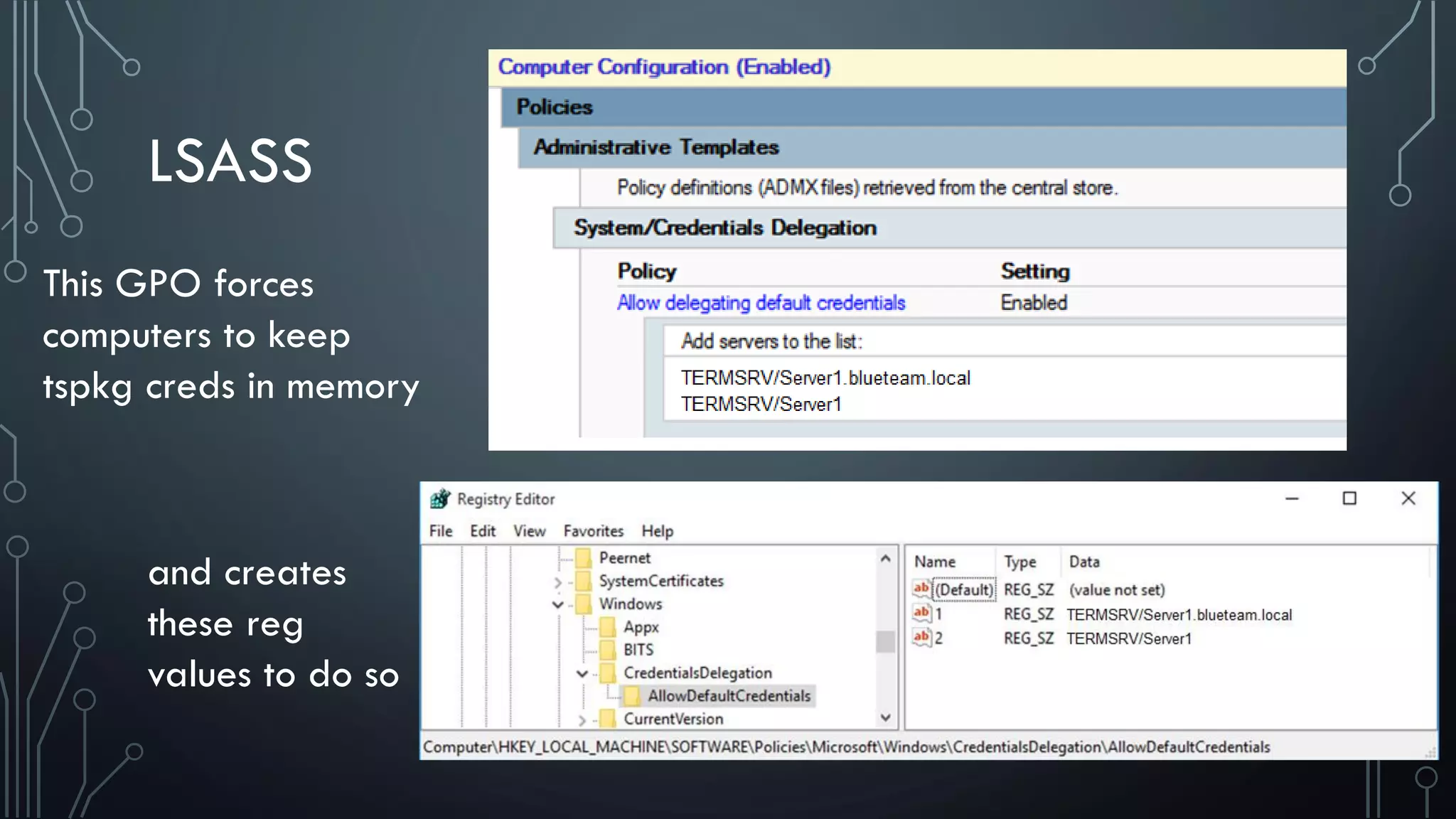
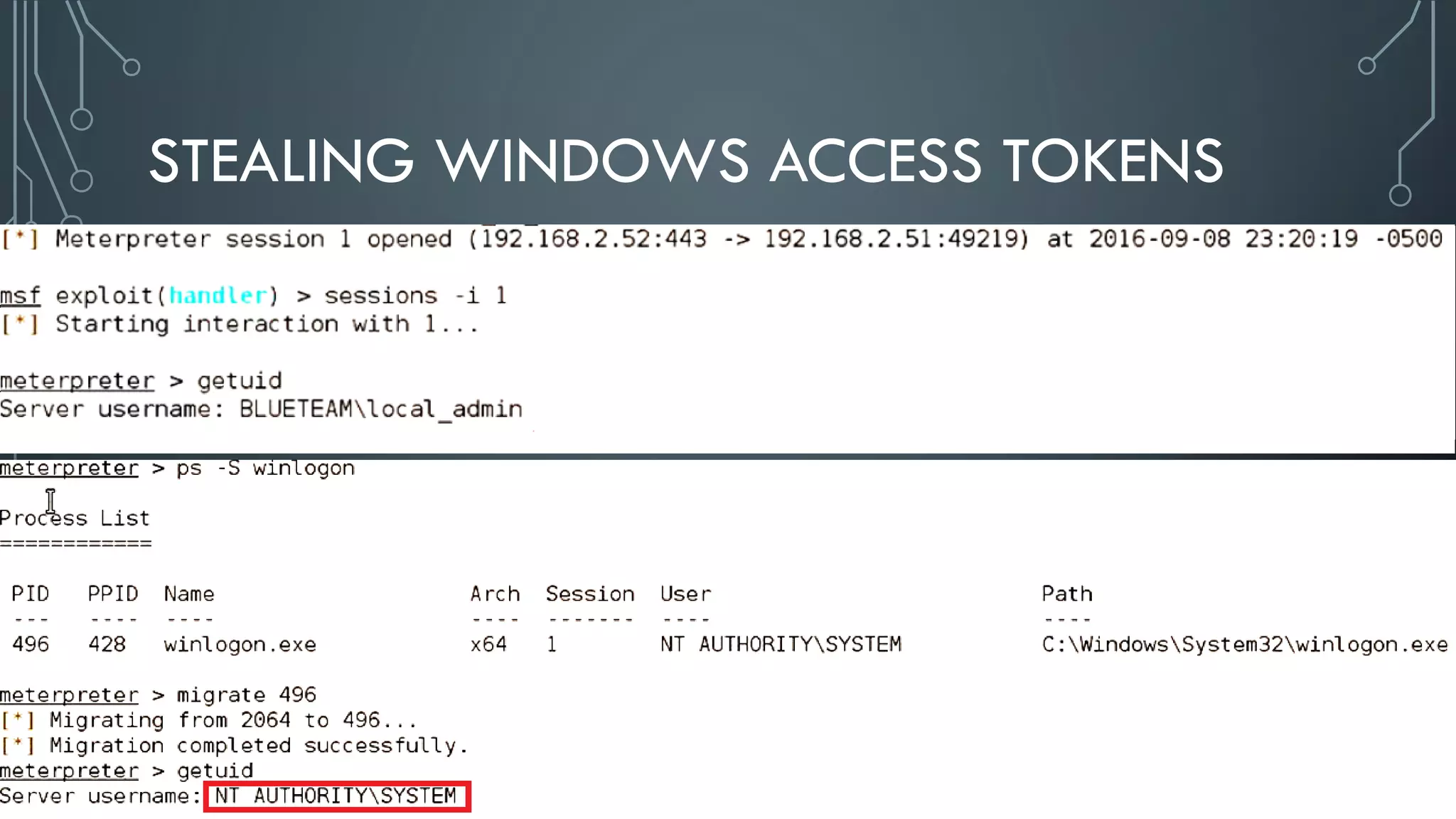
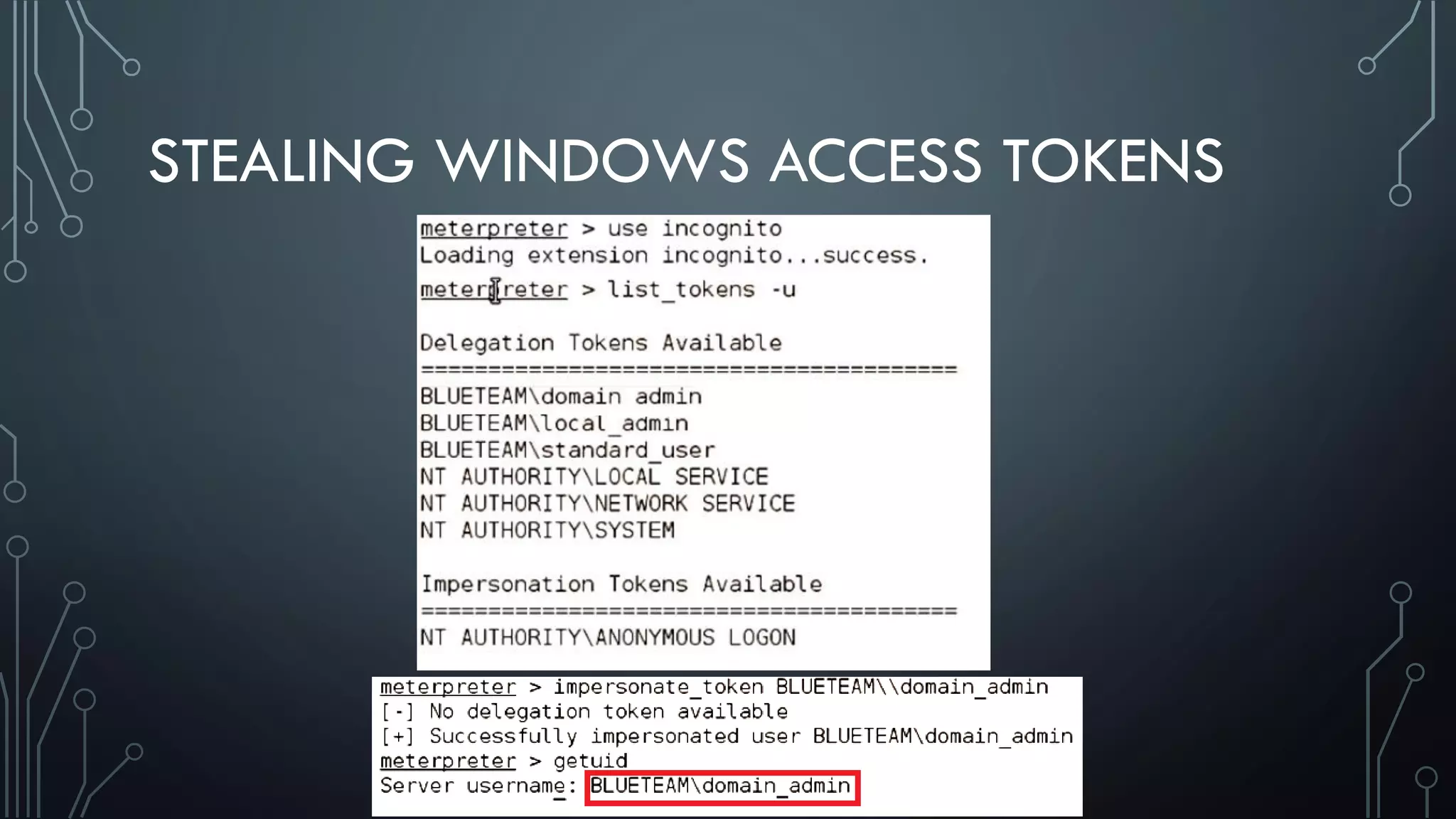
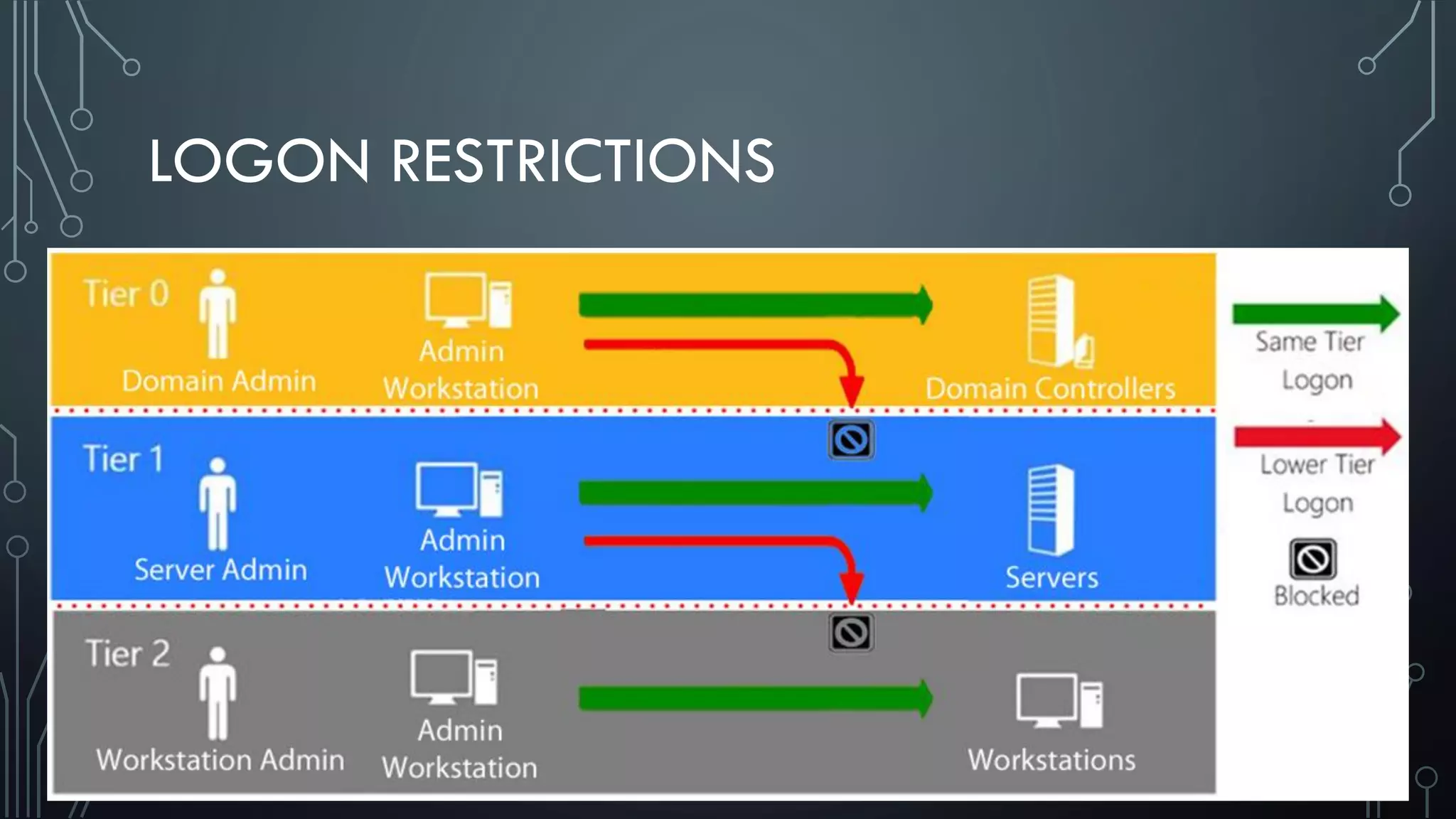
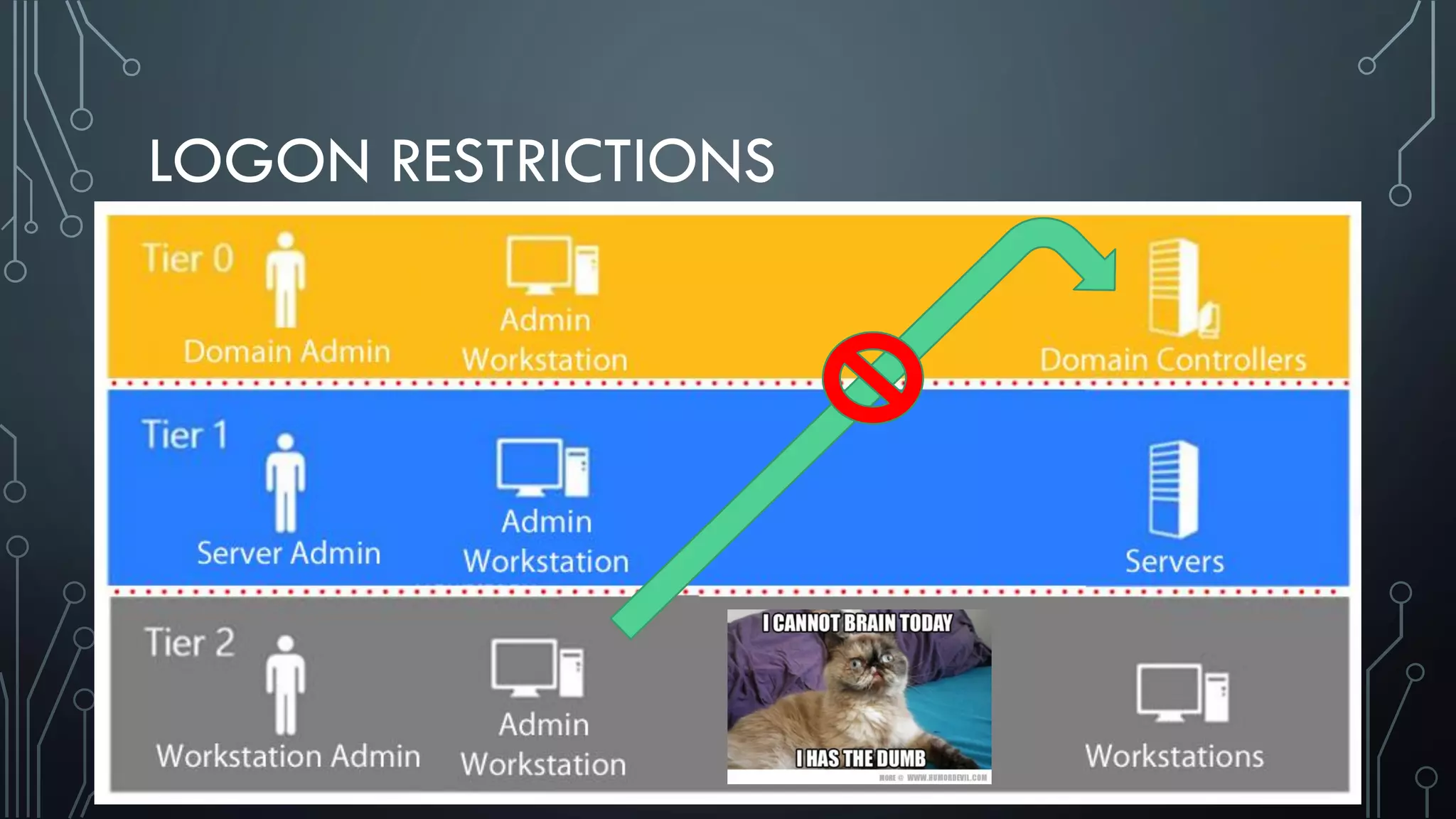
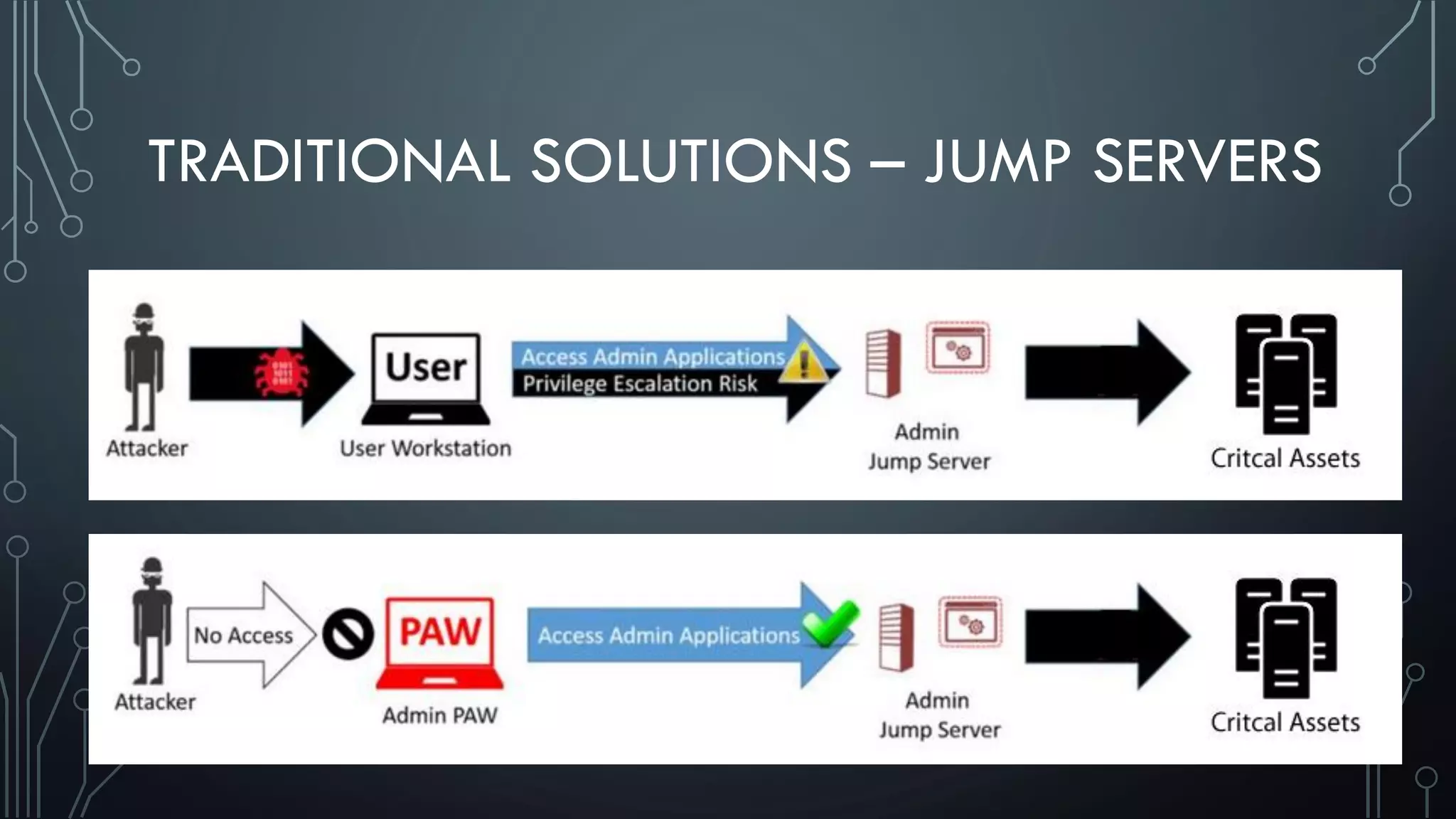
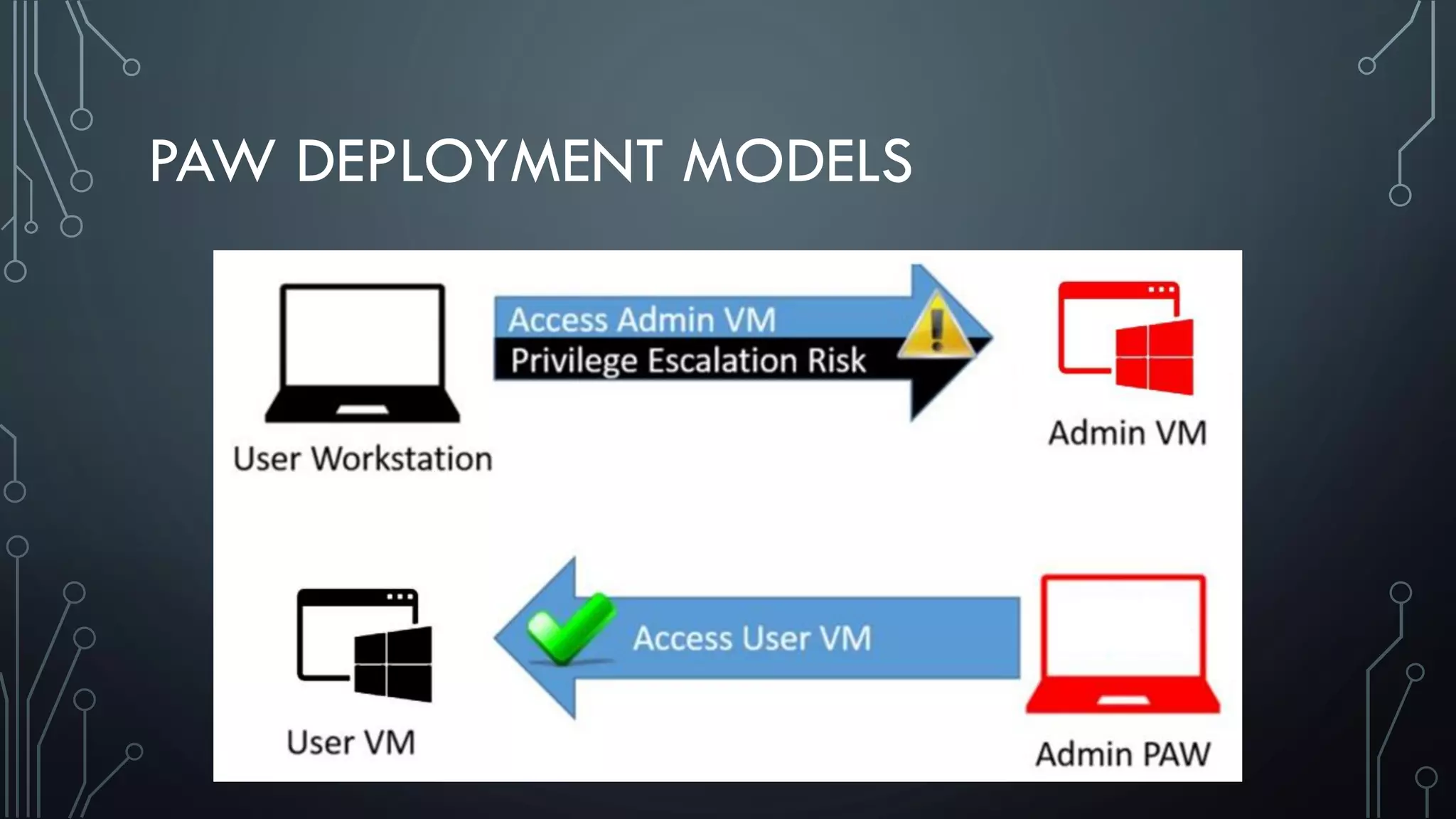
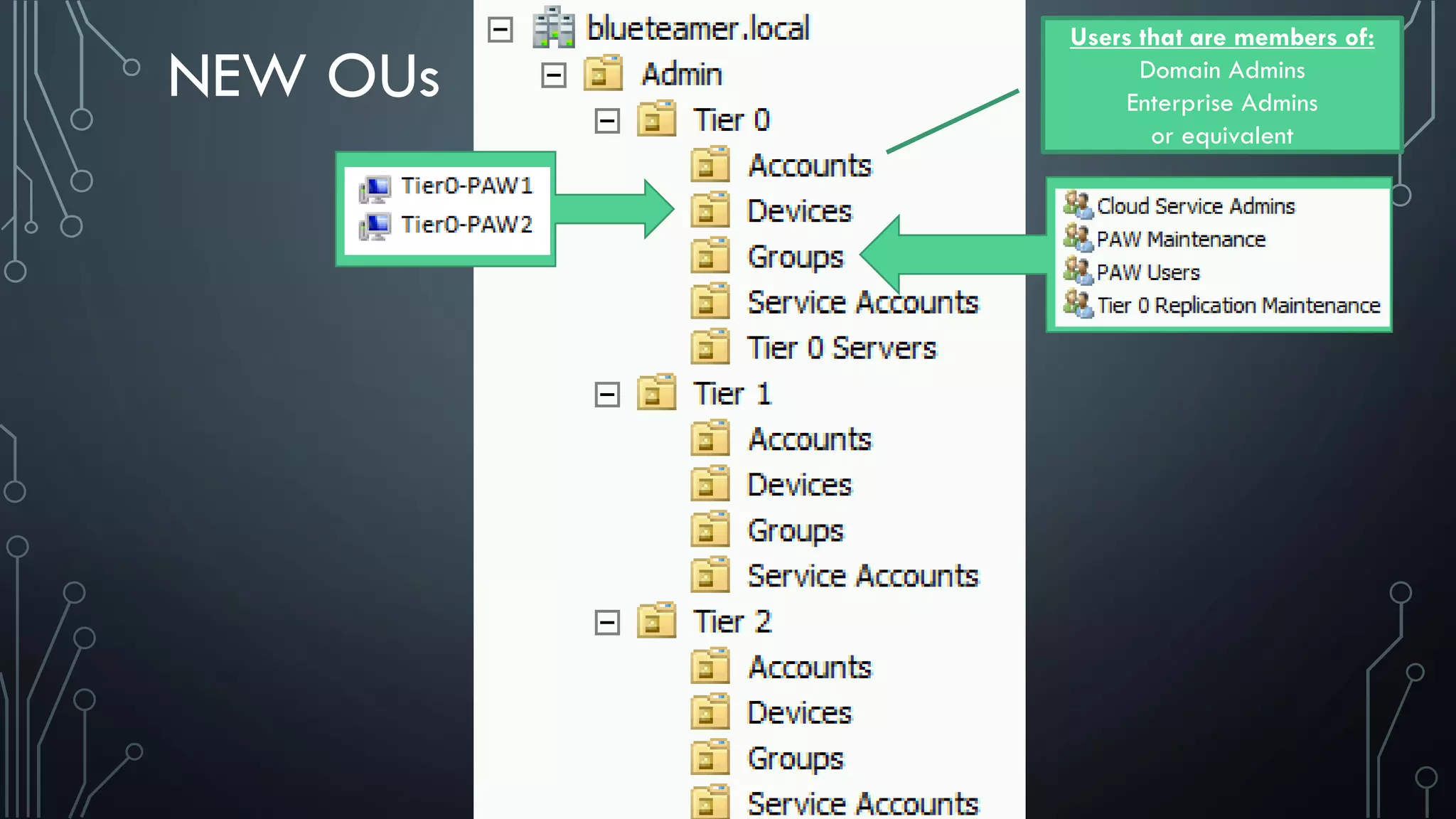
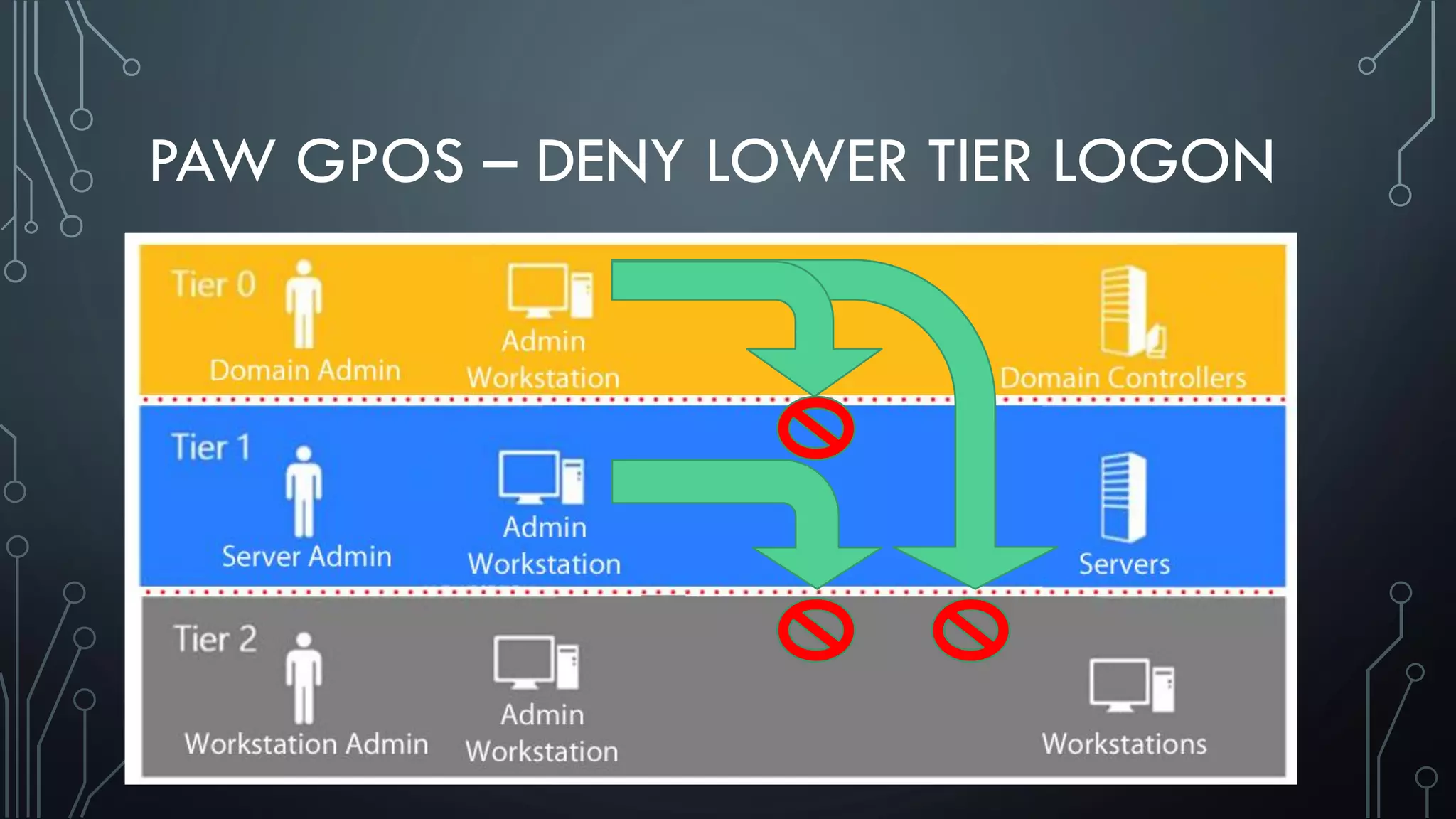
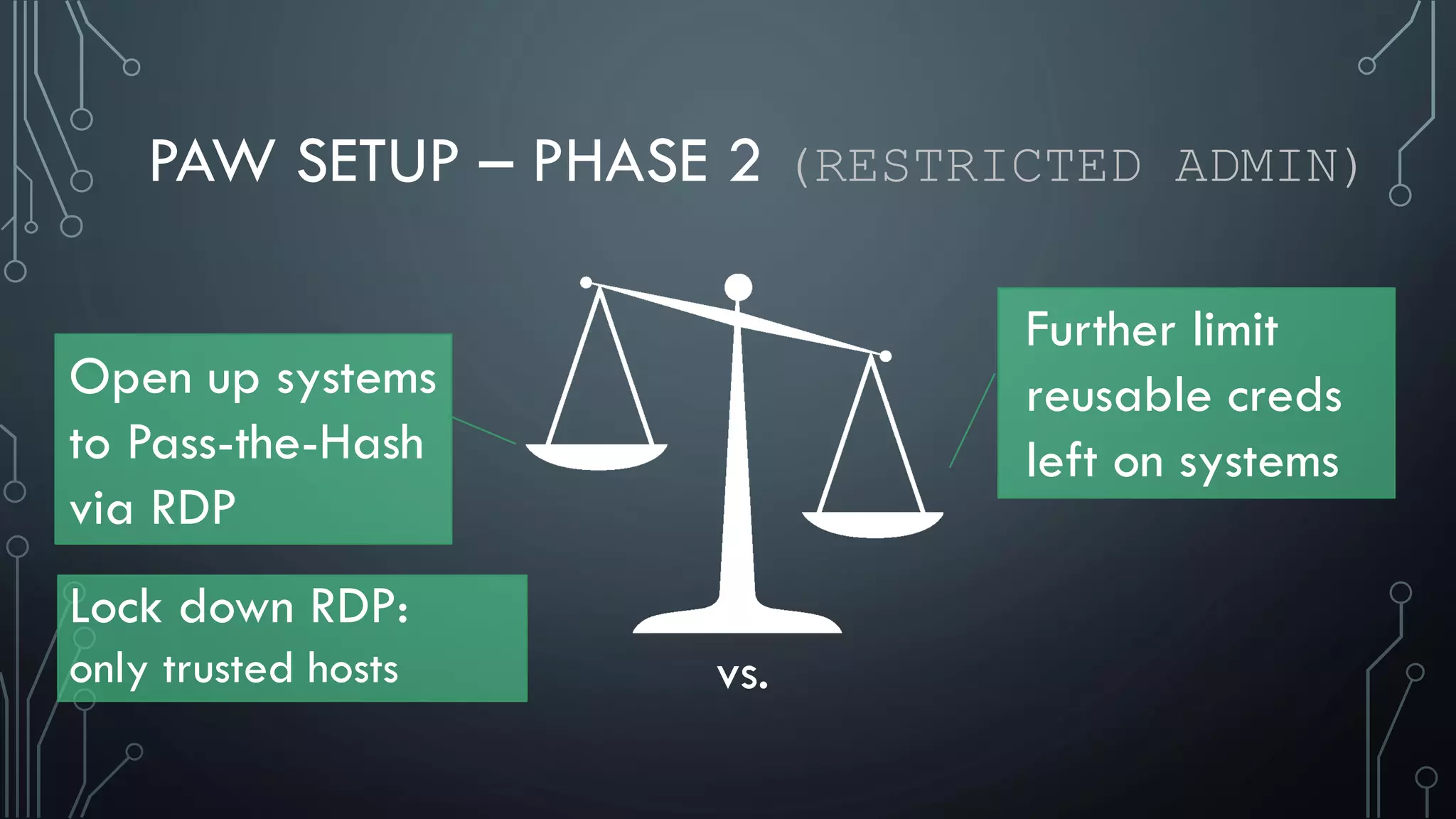
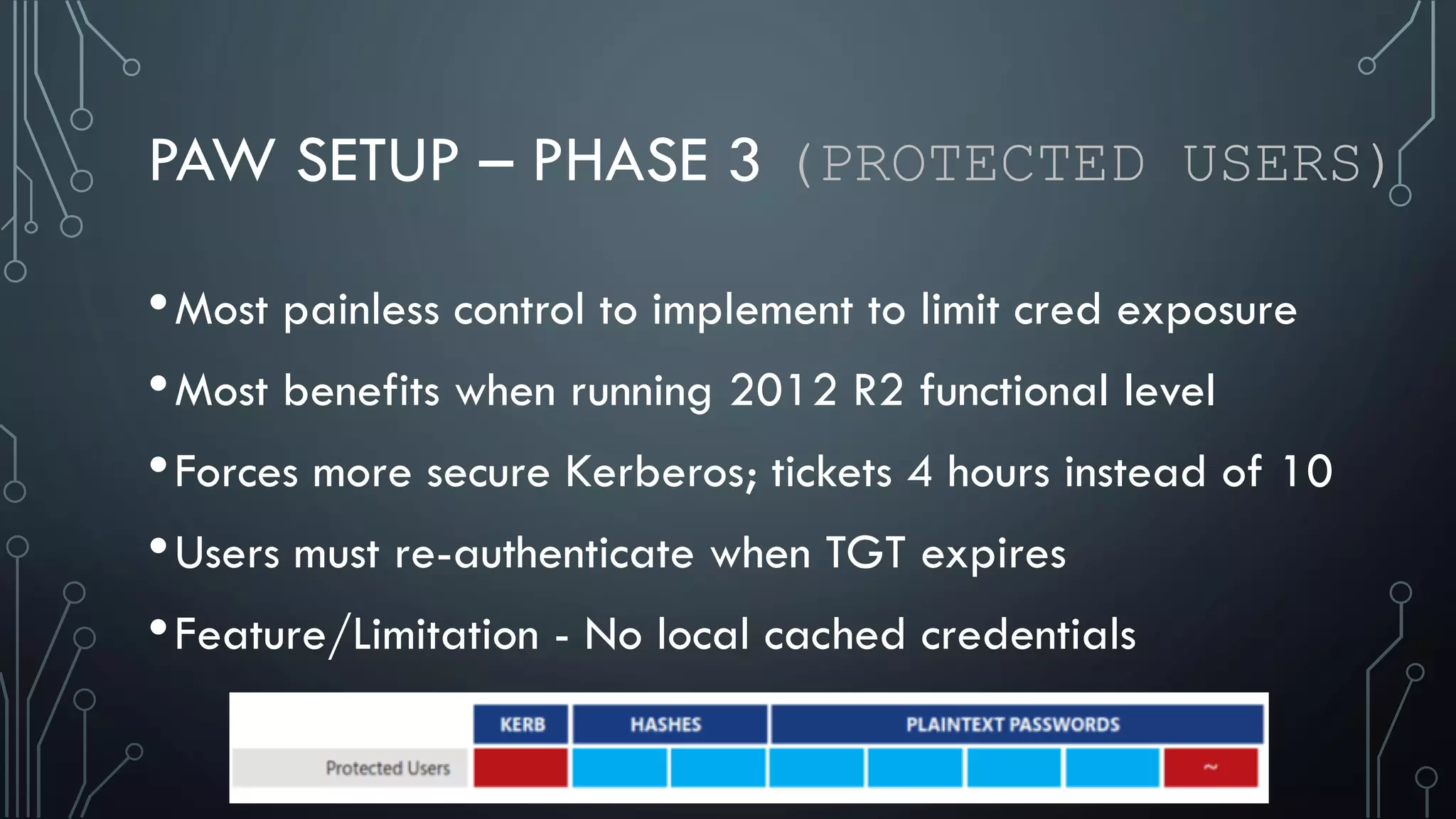
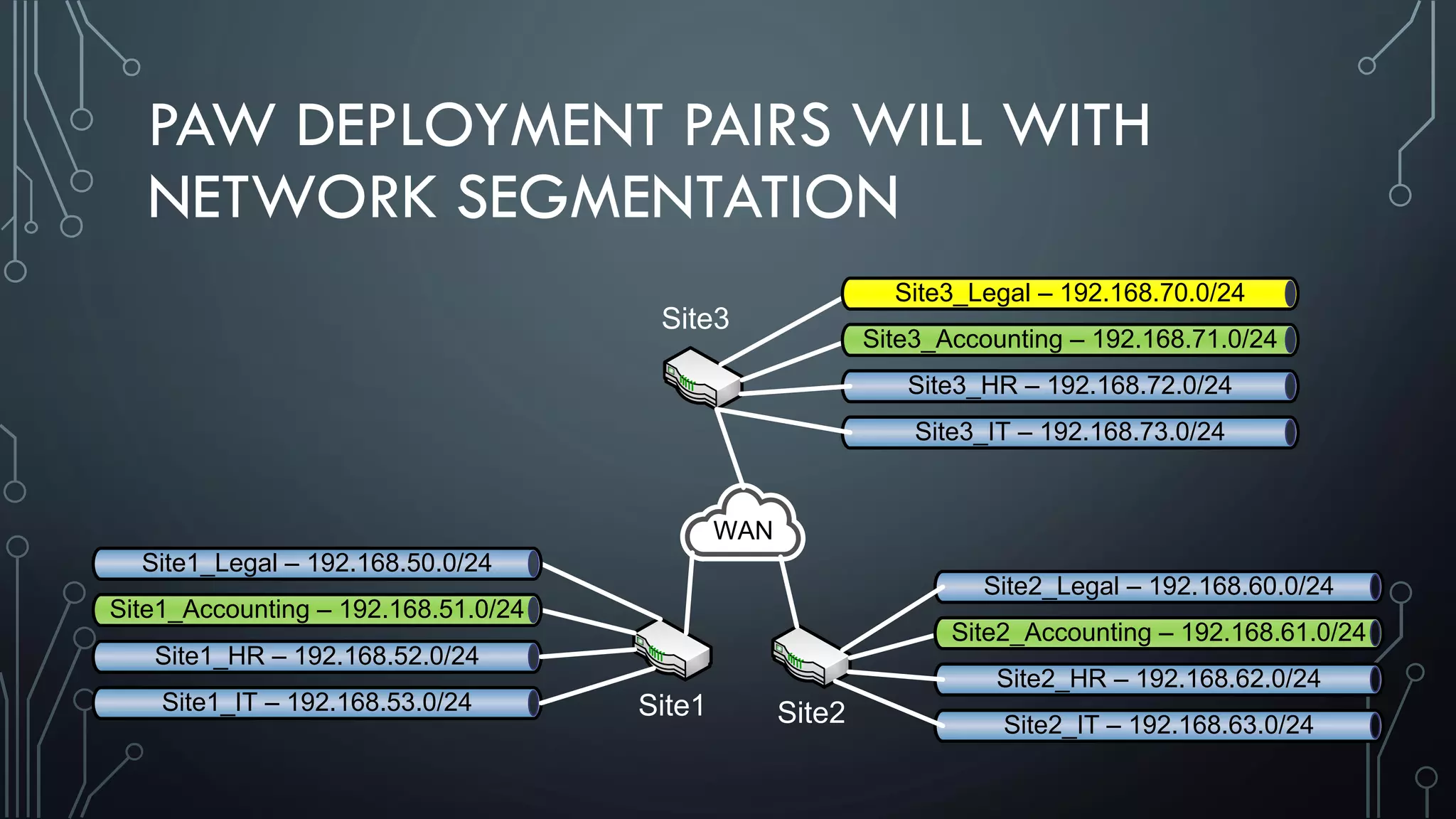
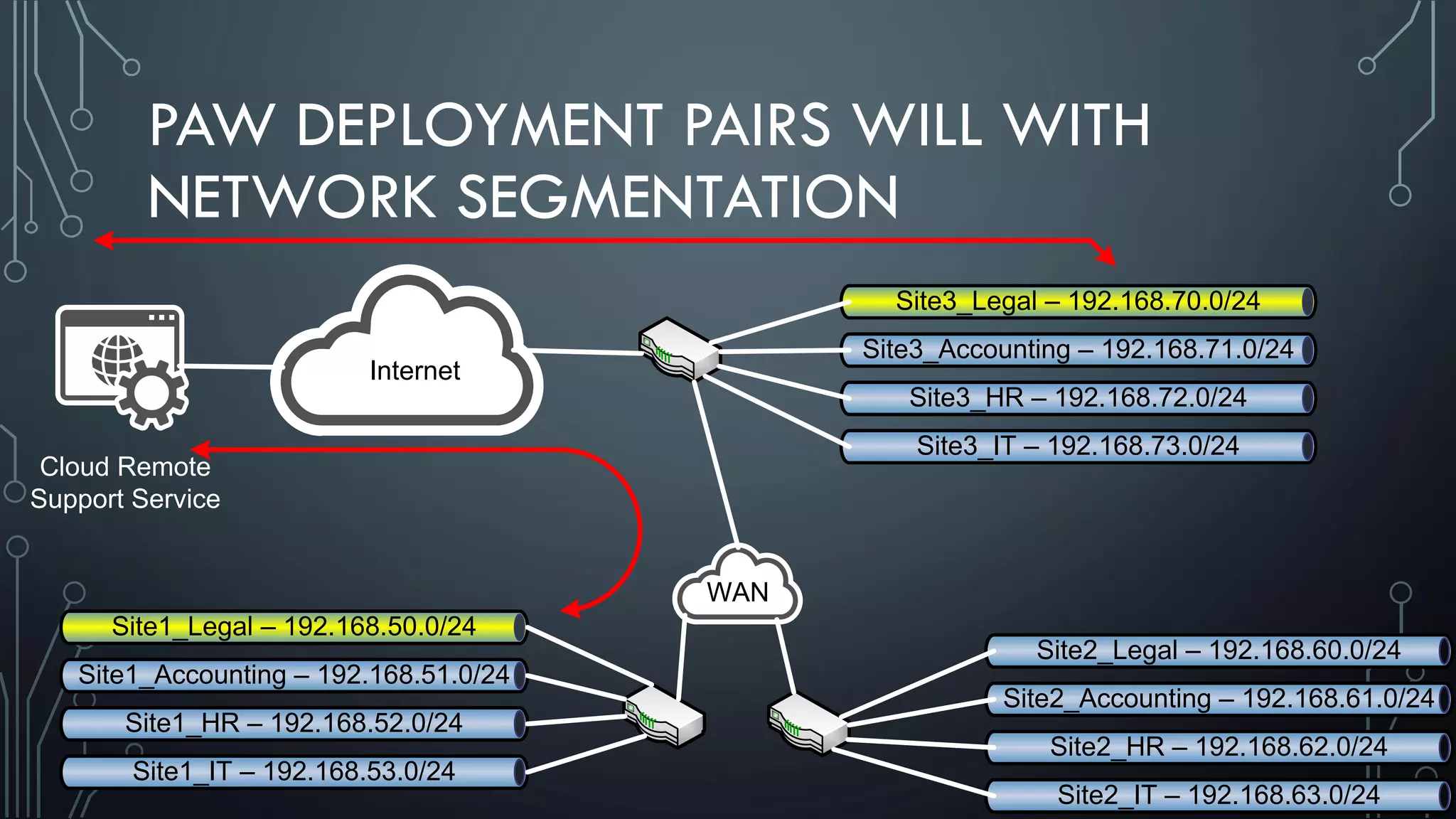
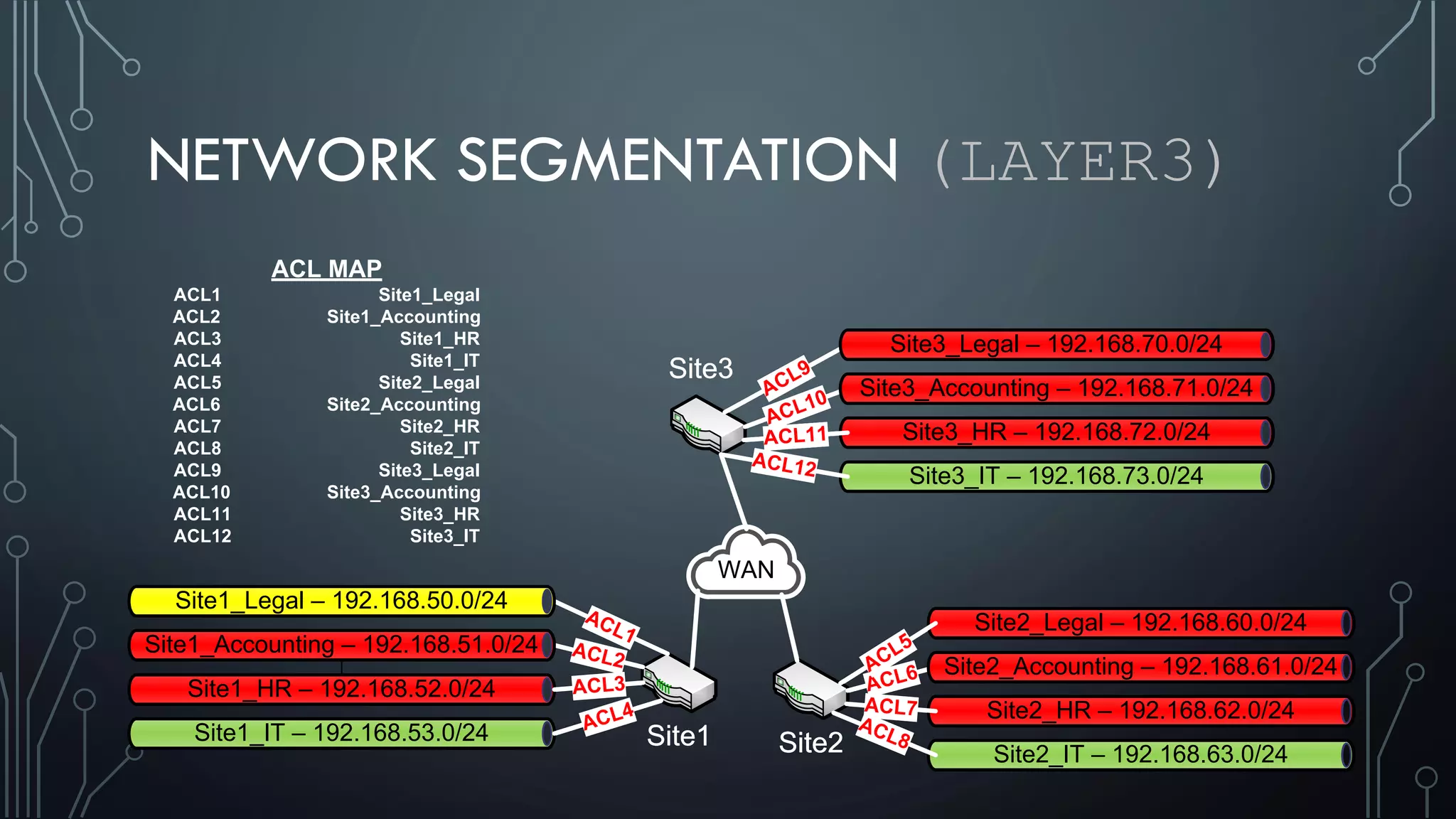
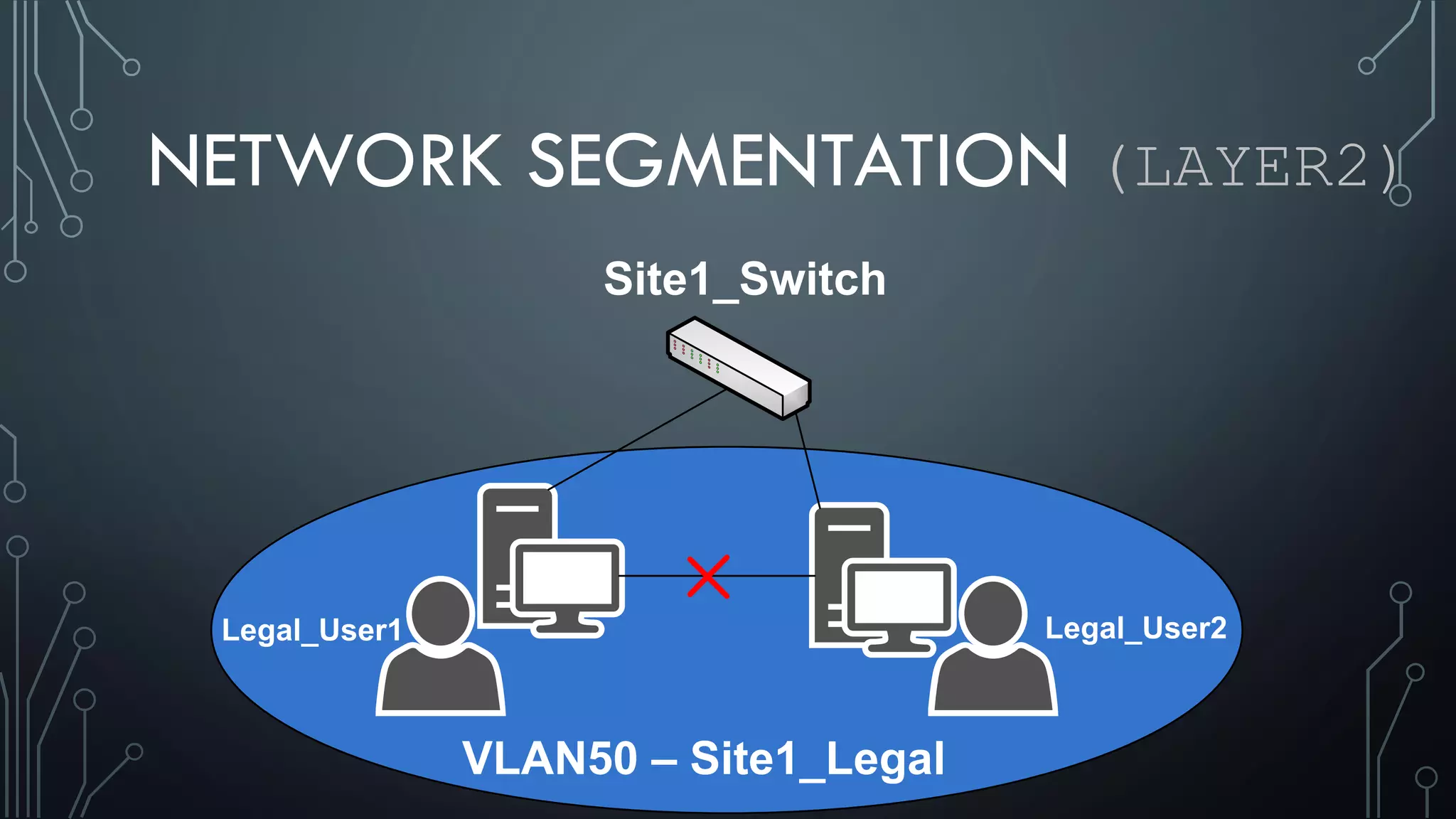
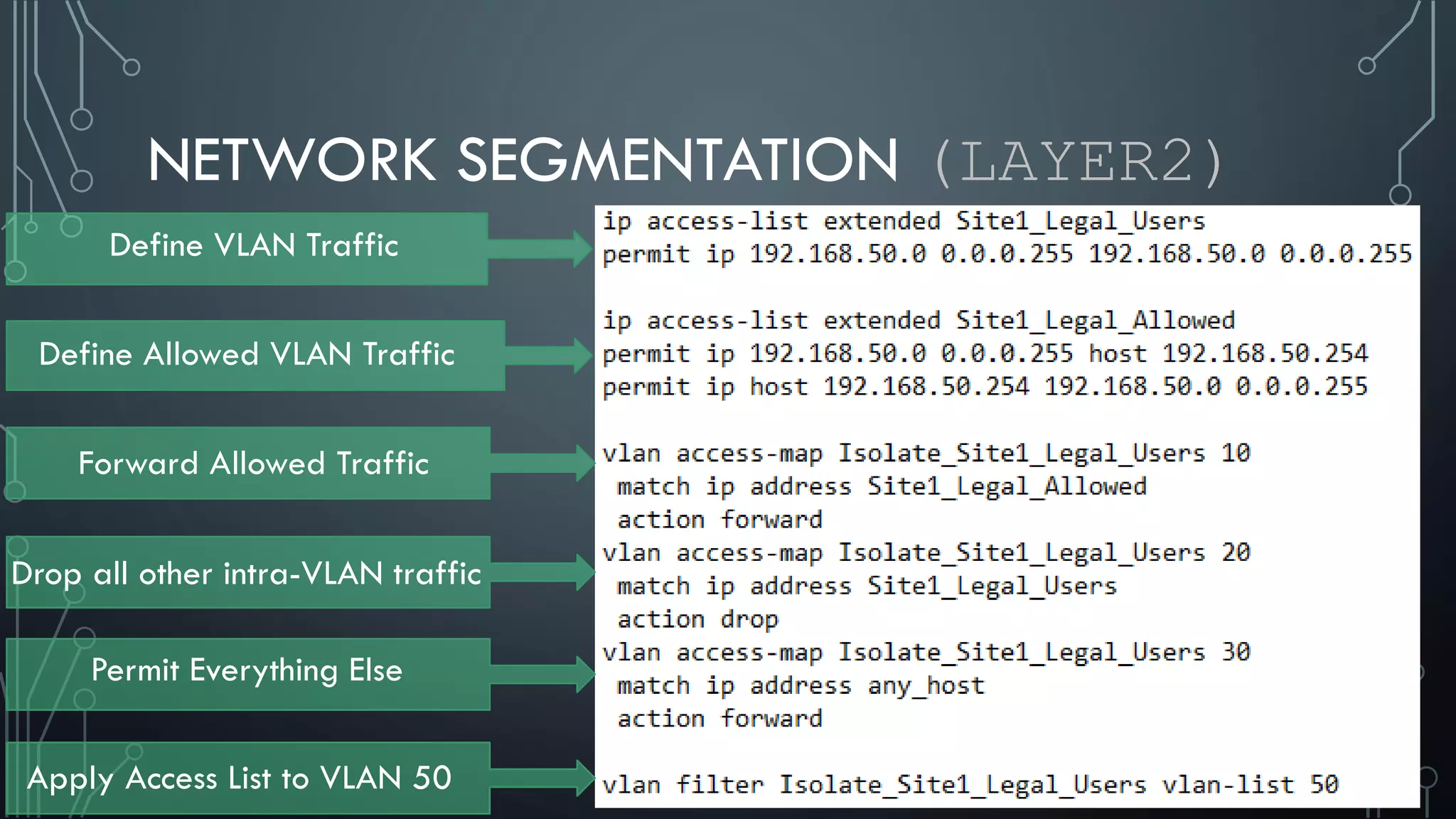
This document discusses deploying Privileged Access Workstations (PAWs) to limit credential theft and lateral movement in an attack. It describes common attack scenarios where attackers leverage stolen credentials to escalate privileges and access sensitive systems. PAWs aim to address this by restricting which accounts can be used to log on to different systems using techniques like logon restrictions, network segmentation, and credential hardening. The document provides guidance on implementing a phased PAW deployment starting with administrative systems and extending to other privileged accounts.






![• WINDOWS LOGON TYPES
•Interactive [2]
•Network [3] – No Reusable Credentials
• Net use
• SQL Windows
Authentication
• Powershell Remoting
• Remote Registry
• Other MMC Snap-ins
• WMI / WMIC
• Batch [4]
• Service [5]
• Unlock [7]
• Network Cleartext [8]
• New Credentials [9]
• Remote Interactive [10]
• Cached Interactive [11]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/derbycontalk2016final2-160924155455/75/Deploying-Privileged-Access-Workstations-PAWs-7-2048.jpg)