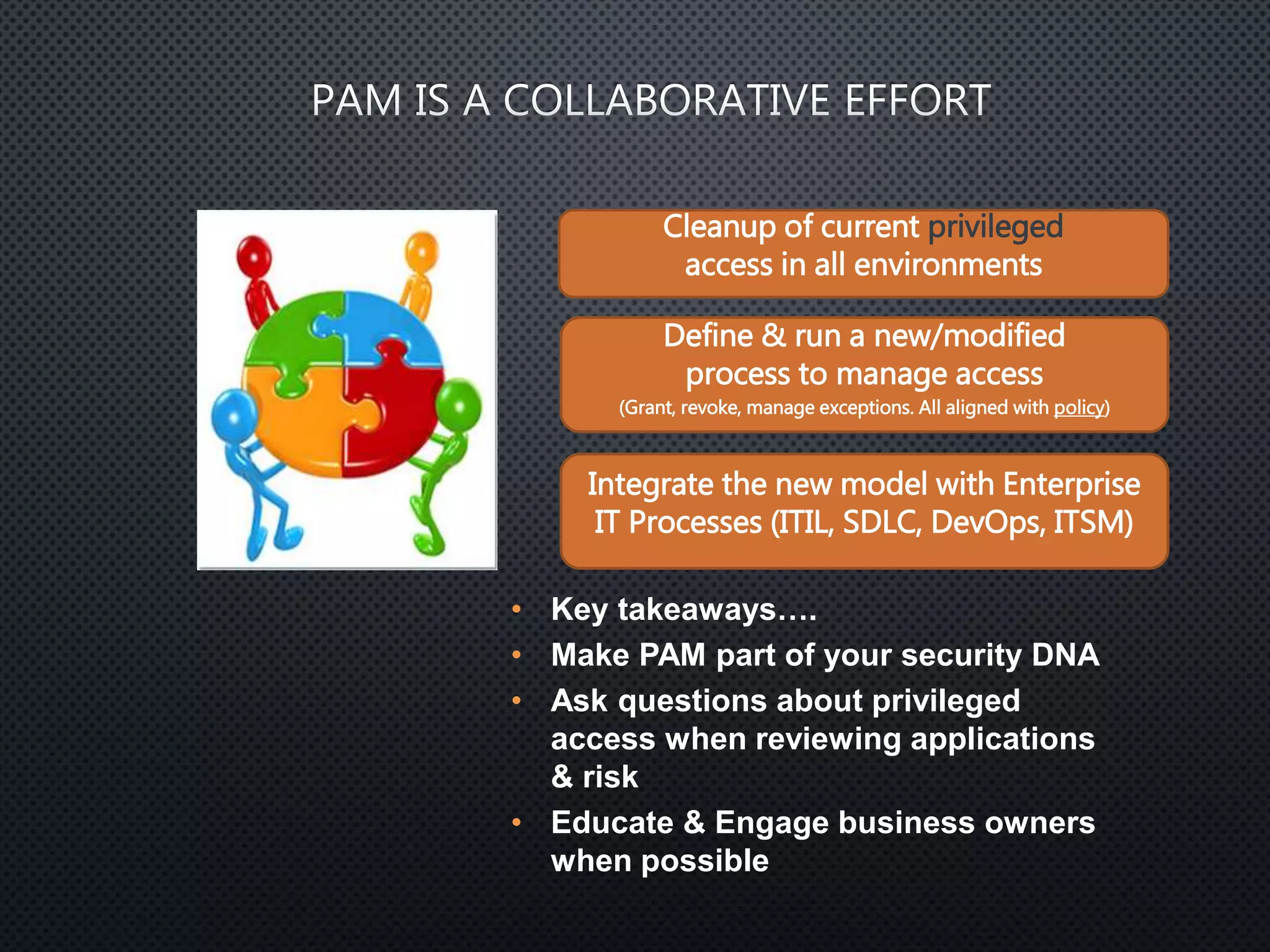
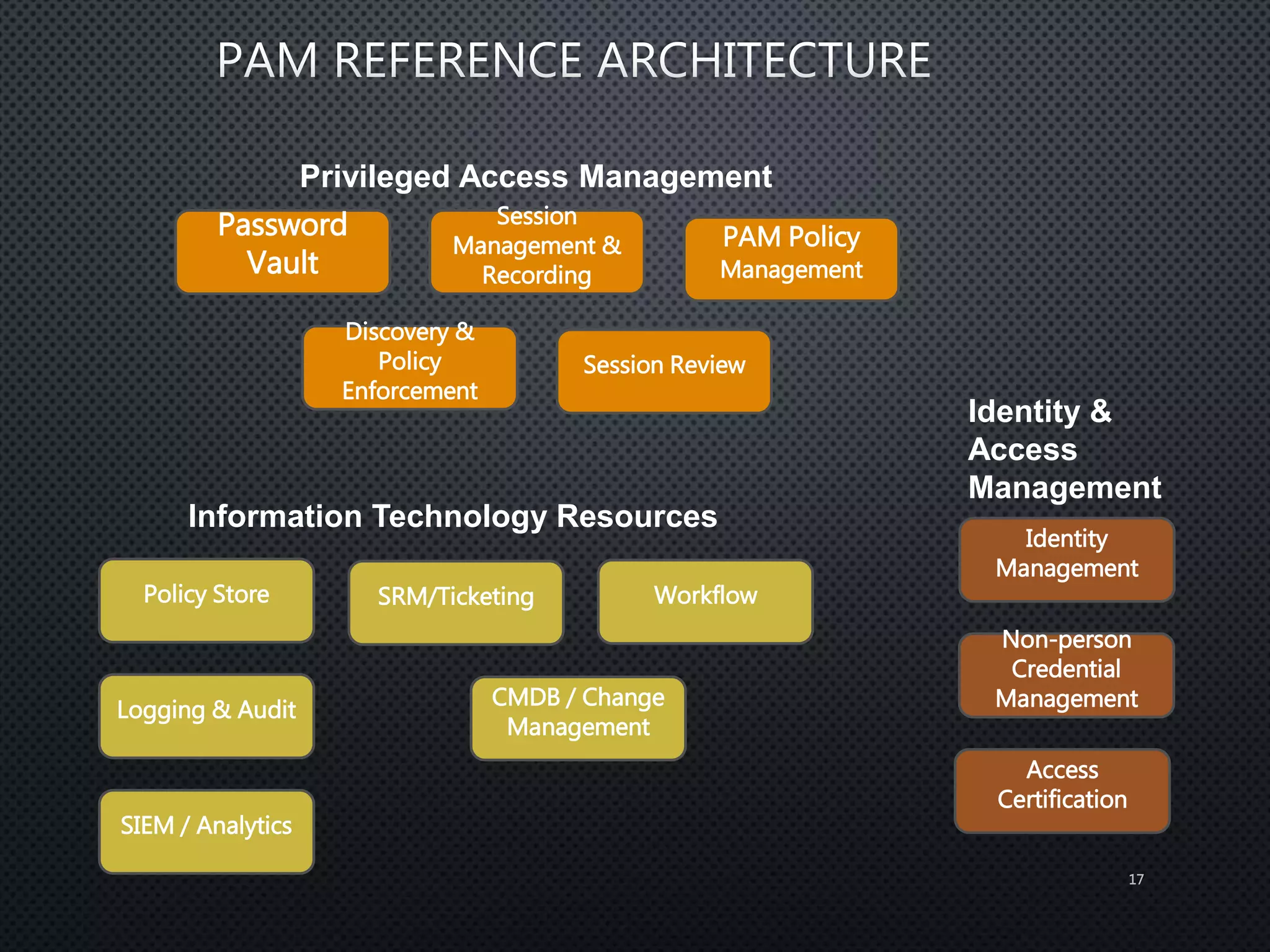
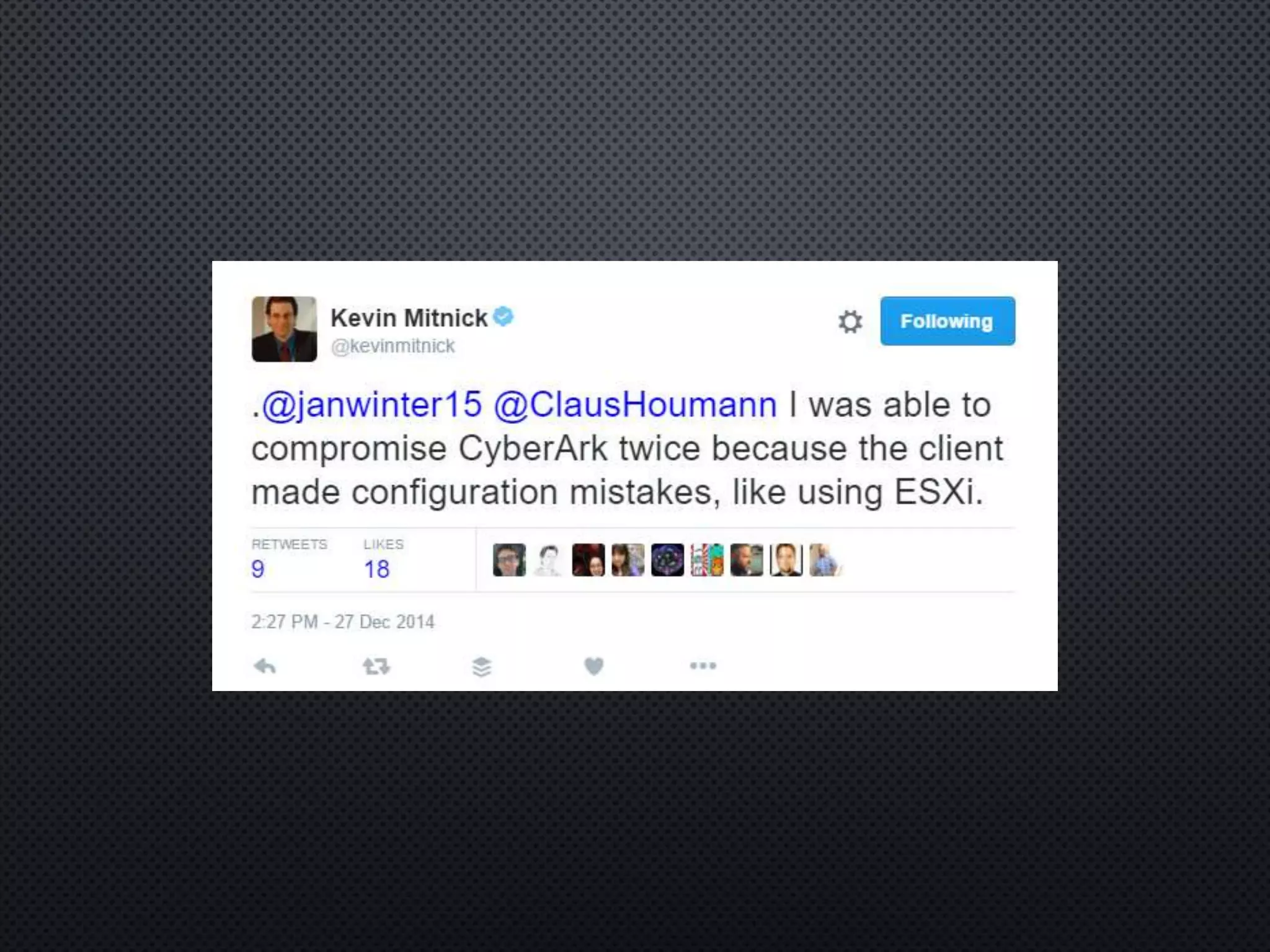
Privileged access refers to system permissions that allow overriding of controls and accessing sensitive information. Privileged accounts have special permissions that can significantly impact an organization's systems and databases. Proper management of privileged access is needed, including monitoring passwords, logging activity, and ensuring access is traceable to individual users. This is the goal of Privileged Access Management (PAM).