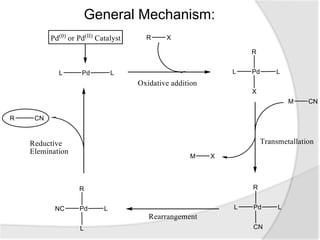
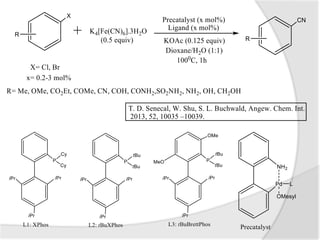
The document discusses palladium-catalyzed cyanation reactions. Specifically, it describes how palladium catalysts can be used to attach cyanide groups to various substrates under milder conditions compared to traditional metal complexes. It then provides examples of palladium-catalyzed cyanation of aromatic amines and methyl arenes. Finally, it summarizes a palladium-catalyzed cyanoalkenylation reaction of N-substituted indoles using K4[Fe(CN)6] as the cyanide source.



![ First Pd-catalyzed cyanation method was
reported by Takagi et al. 40 years ago.
Ushkov and Grushin uses reducing agents or
exploit low solubility of NaCN, KCN and
Zn(CN)2 in organic solvents to prevent
poisoning of cyanide group.
Beller and Weissman discovered K4[Fe(CN)6],
a nontoxic food additive, as cyanide source for
Pd-catalyzed coupling reactions.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/catalysis-140531124141-phpapp01/85/Palladium-Catalysed-Cyanation-4-320.jpg)

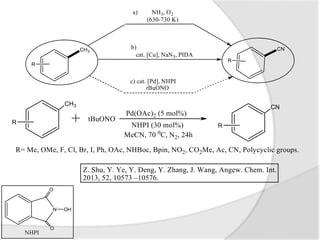
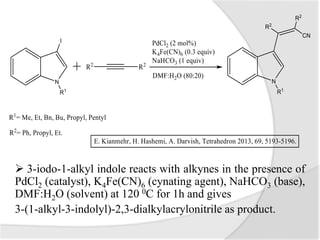
![Palladium-Catalyzed
Cyanoalkenylation of Indoles
Indoles are heterocyclic compounds consisting
on benzene ring fused to a five member
nitrogen containing ring.
Palladium catalyzed
cynaoalkenylation of N-substituted
indoles in the presence of
K4[Fe(CN)6] as cyanating agent.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/catalysis-140531124141-phpapp01/85/Palladium-Catalysed-Cyanation-8-320.jpg)