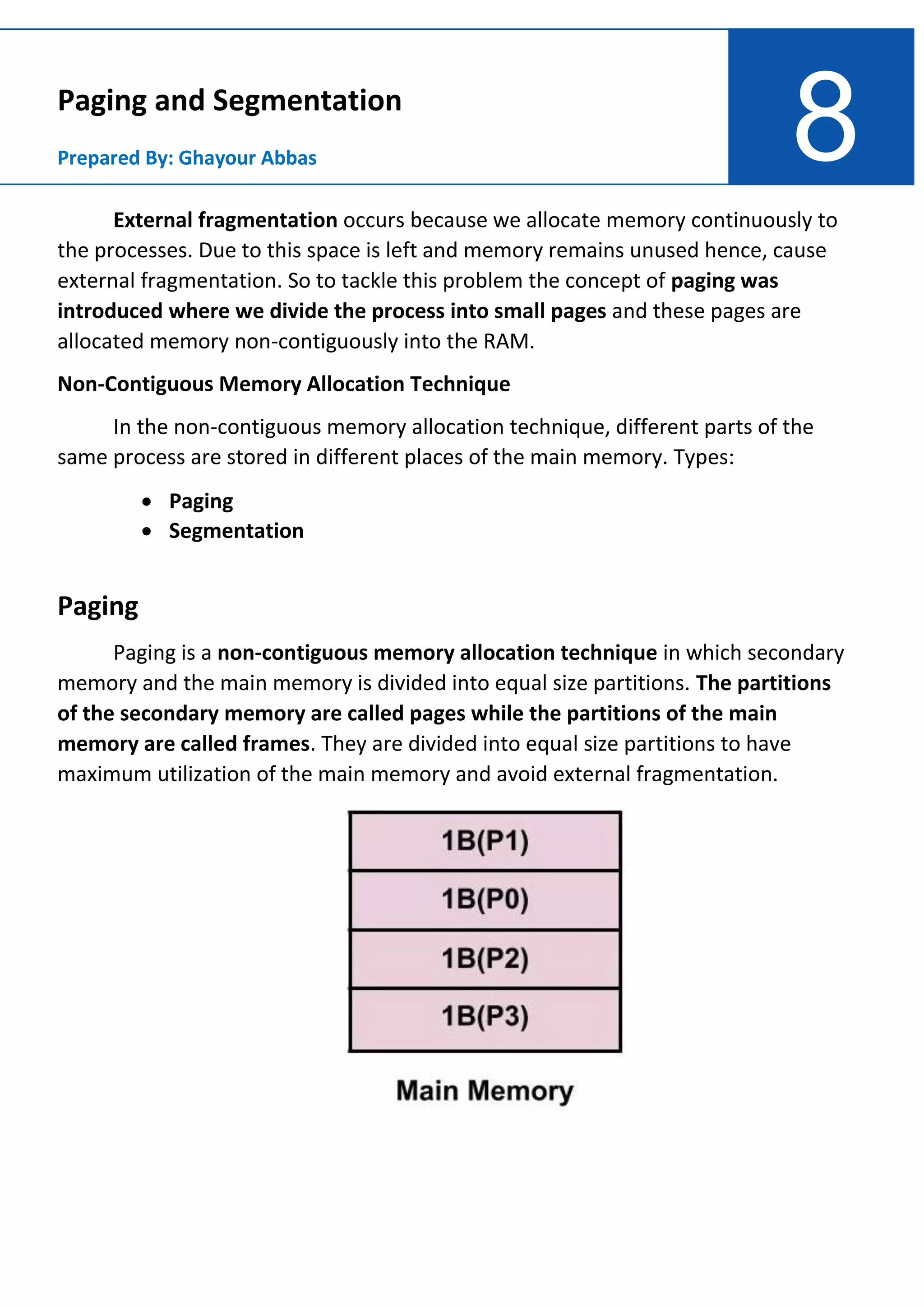
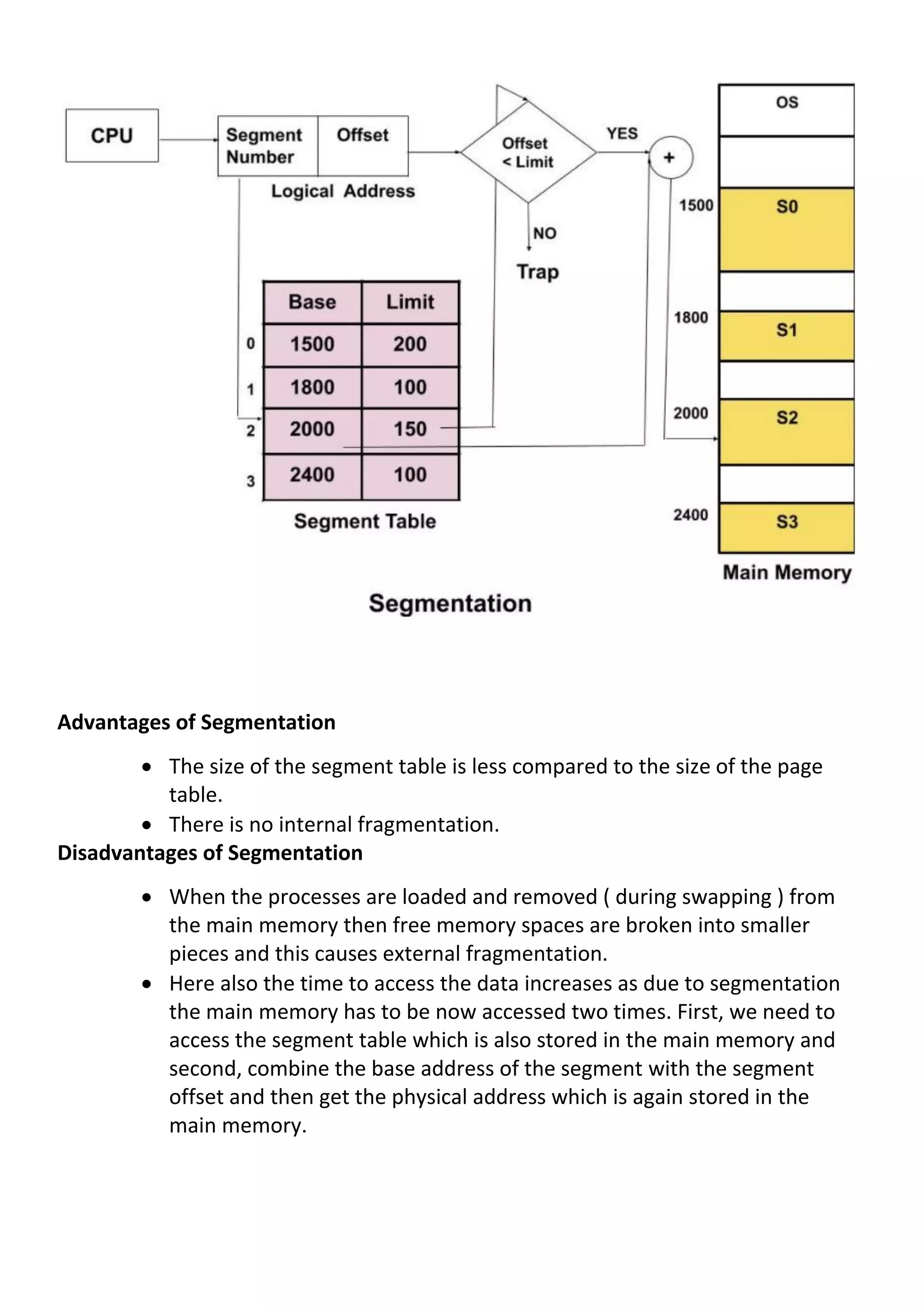
Paging and segmentation are non-contiguous memory allocation techniques that divide processes into smaller pages or segments. Paging divides memory into equal-sized pages and frames, using a page table to map logical page numbers to physical frame numbers. Segmentation divides processes into variable-sized segments, using a segment table to map logical segment numbers to physical base addresses. Both techniques reduce external fragmentation compared to contiguous allocation, but increase access time and require page/segment tables stored in memory.