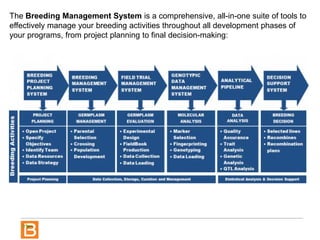
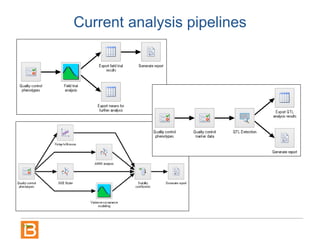
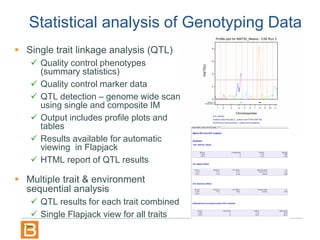
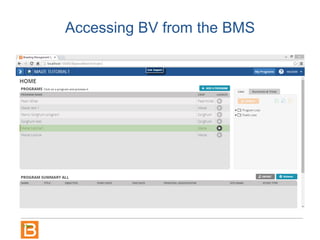
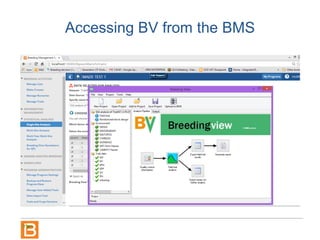
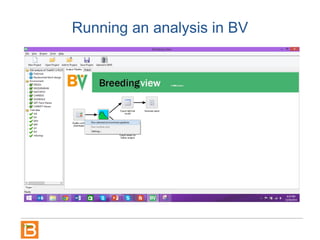
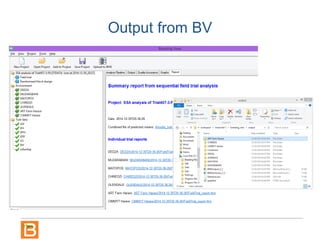
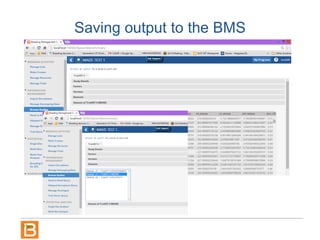
The document discusses the Breeding View, a statistical analysis tool integrated into the Breeding Management System (BMS) developed by the CGIAR Generation Challenge Programme. It provides a user-friendly interface for conducting phenotypic and genotypic data analyses, addressing the complexities of existing software by offering standard analyses suited for breeders' routine needs. Ongoing updates will enhance functionality, include new field designs, and allow user contributions of R scripts.